Mountain Magnolia
| Mountain Magnolia | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
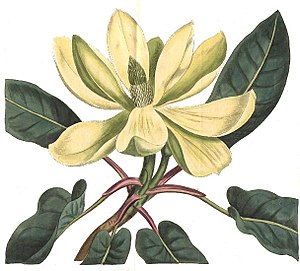
Mountain magnolia ( Magnolia fraseri ), illustration from Curtis's botanical magazine |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Magnolia fraseri | ||||||||||||
| Walter |
The Magnolia fraseri ( Magnolia fraseri ) is a plant from the genus of Magnolia ( Magnolia ) within the family of Magnoliaceae (Magnoliaceae). It thrives in the damp forests of the southern Appalachian Mountains , hence the common English name "mountain magnolia".
description
Vegetative characteristics
The mountain magnolia grows as a deciduous, medium-sized tree and reaches heights of up to 20 meters, in exceptional cases up to 30 meters. The smooth bark is gray or gray-brown.
The leaves are heaped at the ends of the branches. The petiole measures 5 to 10 centimeters. The simple leaf blade is rhombic to spatulate with a length of 15 to 30 centimeters and a width of 8 to 18 centimeters with a slightly pointed upper end and the base of the blade is heart-shaped or eyelet. The top of the leaf is green and smooth and the underside of the leaf is light green and bluish. Stipules are present.
Generative characteristics
The flowers stand individually at the ends of the branches. Depending on the altitude, they open from April to June from two hairless bracts that resemble bud scales. The fragrant flowers reach a diameter of 10 to 30 centimeters. The three outer bracts are greenish and bent back, the inner six open more slowly. The inner cream-white bracts are spatulate to oval with a width of up to 5 centimeters, and conspicuously narrow in the lower third. In the center of the flower there are 100 to 200 white stamens and 50 to 90 pistils .
The cone-like, hairless fruit stand ( collecting bellows ) is oval with a length of 5 to 13 centimeters and a diameter of 3 to 5 centimeters. It turns pink-red, brown or dark purple when ripe. The individual follicles are long beaked, they each contain one or two about 1 centimeter large, lenticular seeds. These are surrounded by a bright red seed coat ( arillus ).
Occurrence
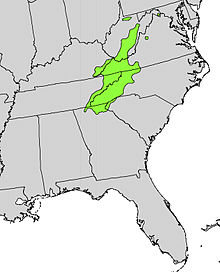
The mountain magnolia occurs only in the eastern NUS states from West Virginia via Virginia and Tennessee to Georgia and Texas .
They are located in the mountains in the southern Appalachians at altitudes of 300 and 1500 meters. The climate is temperate and humid with annual rainfall of 1000 to 2000 mm. The occurrences usually consist of a few individuals and are isolated. The locations are moist valleys and slopes with soils rich in humus and nutrients , the pH value is in the slightly acidic range. Seedlings can also be found in more exposed locations.
The mountain magnolia is associated with the sugar maple ( Acer saccharum ), the American beech ( Fagus grandifolia ), Aesculus flava , the American linden ( Tilia americana ), various hickory species ( Carya ) and oak species such as American white oak ( Quercus alba ), scarlet oak ( Quercus coccinea ), Quercus prinus and red oak ( Quercus rubra ).
use
The mountain magnolia is occasionally used as an ornamental plant. It was introduced to England in 1786 by both John Fraser and William Bartram , and to France in 1789 by André Michaux . It is seldom available in stores, no varieties have been selected. Crossings with other magnolia species are possible, but not commercially available.
The wood is occasionally marketed in the trade together with the tulip tree , but it has little value as firewood or in paper production.
Systematics
Magnolia fraseri was first published in 1788 by Thomas Walter in Flora Caroliniana , page 159. Walter honored his friend and colleague John Fraser with the specific epithet fraseri .
The species Magnolia fraseri belongs to the section Auriculata in the subgenus Magnolia within the genus Magnolia . The closest relative is Magnolia pyramidata , which can be distinguished by its smaller size and different leaf shape. It colonizes a geographically isolated area on the Gulf of Mexico. Sometimes Magnolia pyramidata is also listed as the variety Magnolia fraseri var. Pyramidata (Bartram) Pampanini . Other magnolias that grow in southeastern North America and are related to Magnolia fraseri are the large-leaved magnolia and the umbrella magnolia .
swell
literature
- DJ Callaway: The World of Magnolias. Timber Press 1994, ISBN 0-88192-236-6 , pp. 81 f.
- L. Delia-Bianca: Fraser Magnolia. In: RM Burns, BH Honkala (Ed.): Silvics of North America. Volume 2. Hardwoods. Agriculture Handbook. Volume 654. US Department of Agriculture Forest Service, Washington DC 1990, ISBN 0-16-027145-2 .
- Frederick Gustav Meyer : Magnoliaceae. : In: Flora of North America Editorial Committee (Ed.): Flora of North America North of Mexico , Volume 3 - Magnoliidae and Hamamelidae , Oxford University Press, New York a. a. 1997, ISBN 0-19-511246-6 . Magnolia fraseri - online with the same text as the printed work .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Rafaël Govaerts (ed.): Magnolia fraseri. In: World Checklist of Selected Plant Families (WCSP) - The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew . Retrieved January 16, 2020.
- ^ EL Little: Atlas of United States Trees. (PDF; 698 kB) US Department of Agriculture, accessed August 10, 2009 .
- ^ Classification of Magnoliaceae. Magnolia Society International, 2012, accessed December 22, 2015 . after: Figlar & Nooteboom: Notes on Magnoliaceae IV 2004.