Bis (trimethylsilyl) acetylene
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Bis (trimethylsilyl) acetylene | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 18 Si 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 170.40 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.752 g cm −3 (25 ° C ) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
21-24 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
136-137 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.427 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Bis (trimethylsilyl) acetylene (BTMSA) is an organosilicon compound with a CC triple bond , which is present as a colorless liquid at room temperature and can be dissolved in all commercial organic solvents . It is used, among other things, as a nucleophile in acylations and alkylations , as a reagent in cycloaddition reactions and as a ligand in organometallic chemistry .
Manufacturing
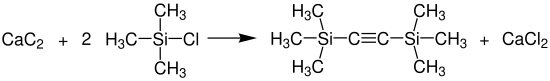
Bis (trimethylsilyl) acetylene was previously synthesized by reacting an acetylene Grignard compound with chlorotrimethylsilane with a yield of about 30%. Today BTMSA can be produced in a lithium chloride - potassium chloride melt at 400 ° C from technical calcium carbide and chlorotrimethylsilane.
With a yield of 77% based on the converted chlorotrimethylsilane, BTMSA is obtained, which can be separated easily and in pure form from the by-product hexamethyldisiloxane and remaining unreacted chlorotrimethylsilane. This procedure thus enables a solvent-free preparation with better yield and more easily accessible starting materials than the synthesis starting from the acetylene-Grignard compound.
Applications
Bis (trimethylsilyl) acetylene is used as a nucleophile in Friedel-Crafts acylations and alkylations and as a precursor of lithium (trimethylsilyl) acetylidene. In addition, it is used as a starting reagent benzenes in the synthesis of functionalized 1,2-bis (trimethylsilyl), which in turn as a starting material for the synthesis of Lewis acid - catalysts and certain bulbs are used. In cobalt-catalyzed reactions, BTMSA is used to provide chemoselectivity and functionality (in the form of the trimethylsilyl group ), which enables complex molecules to be represented.
Another important application is its use in the Rosenthal reagent to stabilize titanocene and zirconocene fragments. The use of BTMSA as a ligand of otherwise unstable metallocene compounds allows the synthesis of sophisticated organic structures, e.g. B. macrocycles and heterometallacycles, selectively and with high yields.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h data sheet bis (trimethylsilyl) acetylene from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on October 10, 2018 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Michael L. Curtin, Cheng Wang: Bis (trimethylsilyl) acetylene . In: Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis . John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, Chichester, UK 2008, ISBN 0-471-93623-5 , doi : 10.1002 / 047084289x.rb209.pub2 .
- ↑ a b A. Ohff, S. Pulst, C. Lefeber, N. Peulecke, P. Arndt: Unusual Reactions of Titanocene- and Zirconocene-Generating Complexes . In: Synlett . tape 1996 , no. 2 , February 1996, p. 111-118 , doi : 10.1055 / s-1996-5338 .
- ↑ a b Jürgen Stenzel, Wolfgang Sundermeyer: Chemical reactions in salt melts, XIV. On the representation of bis (trimethylsilyl) carbodiimide and bis-trimethylsilyl-acetylene . In: Chemical Reports . tape 100 , no. October 10 , 1967, p. 3368-3370 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.19671001027 .
- ↑ Christian Reus, Nai-Wei Liu, Michael Bolte, Hans-Wolfram Lerner, Matthias Wagner: Synthesis of Bromo-, Boryl-, and Stannyl-Functionalized 1,2-Bis (trimethylsilyl) benzenes via Diels – Alder or C – H Activation Reactions . In: The Journal of Organic Chemistry . tape 77 , no. 7 , March 28, 2012, p. 3518-3523 , doi : 10.1021 / jo3002936 .
- ↑ John R. Fritch, K. Peter C. Vollhardt, Michael R. Thompson, Victor W. Day: Apparent Concurrent Acetylene-Vinylidenecarbene Rearrangements, Silyl-Acetylide Metathesis, and Alkyne Cleavage in the Interaction of Bis (trimethylsilyl) acetylene with (η 5 -C 5 H 5 ) Co (CO) 2 . Crystal and Molecular Structure of a Novel Biscarbyne Complex: [μ 3 η 1 -CSi (CH 3 ) 3 ] [μ 3 η 1 -C 3 Si (CH 3 ) 3 ] [(η 5 -C 5 H 5 ) Co] 3 . In: Journal of the American Chemical Society . tape 101 , no. May 10 , 1979, pp. 2768-2770 , doi : 10.1021 / ja00504a065 .
- ↑ U. Rosenthal: Reactions of group 4 metallocene complexes of bis (trimethylsilyl) acetylene with nitriles and isonitriles . In: Angewandte Chemie . 23 August 2018, doi : 10.1002 / anie.201805157 .
- ^ Jonathan R. Nitschke, Stefan Zürcher, T. Don Tilley: New Zirconocene-Coupling Route to Large, Functionalized Macrocycles . In: Journal of the American Chemical Society . tape 122 , no. 42 , October 2000, p. 10345-10352 , doi : 10.1021 / ja0020310 .