Bromocriptine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
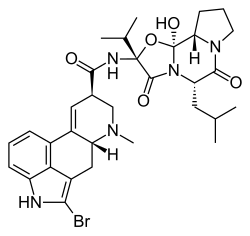
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Bromocriptine | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
2-bromoergocryptine ( WHO ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 32 H 40 BrN 5 O 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to slightly colored, fine, crystalline powder, very light-sensitive (bromocriptine mesilate) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 654.61 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
215–218 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water, slightly soluble in methanol , soluble in ethanol , slightly soluble in dichloromethane (bromocriptine mesilate) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Bromocriptine ( 2-bromergocryptine ) is a drug that is used in the therapy of Parkinson's disease , amenorrhea , acromegaly and to inhibit prolactin secretion .
Bromocriptine acts as a dopamine D 2 agonist - it post- synaptically stimulates dopamine D 2 receptors in the central nervous system . Corresponding neurons in peripheral organ systems (especially the cardiovascular system and gastrointestinal tract ) can also be influenced by bromocriptine. Chemically, bromocriptine is a derivative of ergocryptine , an alkaloid from ergot . It is subject to medical prescription in its applications .
application
Bromocriptine is used for the following indications:
- to inhibit prolactin production - and secretion
- Puerperal mastitis or other medical reasons for weaning
- increased prolactin levels e.g. B. Prolactinoma
- Failure to ovulate due to prolactin overproduction
- in early L-dopa combination therapy for Parkinson's disease
- in acromegaly to inhibit growth hormone release
- for the elimination of akinesia and Parkinson's symptoms in neuroleptic malignant syndromes
Indications in research
It is currently being investigated whether bromocriptine can be used in pregnant women who suffer from the rare disease PPCM (postpartum cardiomyopathy). The etiology of the disease is unknown. The symptoms are: acute heart failure late in pregnancy up to a few months after birth. Despite optimal medical therapy, there is a high mortality rate among pregnant women. The disease is accompanied by inflammation and subsequent apoptosis (controlled cell death) of the heart muscle cells (cardiomyocytes). According to the authors, it may have something to do with a breakdown product of prolactin in the heart, which reduces the density of the capillary network in the heart and promotes apoptosis. In healthy hearts, prolactin is not broken down.
Bromocriptine is able to inhibit prolactin in the organism and thus possibly interferes with the pathomechanism of PPCM. Bromocriptine showed promising effects in corresponding mouse models and a small-scale study on six patients. Four months after birth, all six treated patients were still alive - in the control group of six PPCM patients who were not given bromocriptine, three out of six died of acute heart failure within four months.
A current clinical study confirms the effectiveness of bromocriptine in PPCM: In more than half of the 63 patients, a complete recovery of the heart function was achieved during the therapy.
Side effects
The adverse drug reaction profile is similar to that of L-Dopa. It can be nausea , vomiting , as well as low blood pressure (orthostatic hypotension come). Especially in high doses, it can lead to restlessness, hallucinations and even psychoses . Dyskinesias are rare.
Trade names
Kirim (D), Parlodel (CH), Pravidel (D)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b European Pharmacopoeia Commission (ed.): EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOE 5TH EDITION . tape 5.0-5.8 , 2006.
- ↑ a b entry on bromocriptine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on September 30, 2014.
- ↑ Data sheet 2-Bromo-α-ergocryptine methanesulfonate salt from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 27, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Hilfiker-Kleiner, Kaminski, Podewski: "A Cathepsin D-cleaved 16kDa Form of Prolactin Mediates Postpartum Cardiomyopathy", in: Cell , 2007 February 9, 128 (3), pp. 589-600; doi : 10.1016 / j.cell.2006.12.036 ; PMID 17289576 .
- ↑ Denise Hilfiker-Kleiner, Arash Haghikia, Dominik Berliner, Jens Vogel-Claussen, Johannes Schwab: Bromocriptine for the treatment of peripartum cardiomyopathy: a multicentre randomized study . In: European Heart Journal . tape 38 , no. 35 , September 14, 2017, p. 2671–2679 , doi : 10.1093 / eurheartj / ehx355 ( oup.com [accessed October 24, 2017]).