Chlorin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
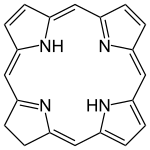
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Chlorin | |||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 20 H 16 N 4 | |||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 312.37 g · mol -1 | |||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Chlorine ( 7,8-dihydroporphyrin ) is a heterocyclic , aromatic chemical compound , which is composed of three pyrrole rings and one pyrroline ring. It is a macrocycle that is structurally closely related to porphine , the basic compound of porphyrins . Chlorin forms the basic structure of chlorins , a group of substances that occur as macrocyclic ligands in biological systems.
Occurrence
Derivatives of chlorine occur naturally in complex form with magnesium cations in certain chlorophylls (chlorophyll a , b and d ).
presentation
Chlorin can be made from the reaction between 2- ( N , N -dimethylamino) methylpyrrole and ethylmagnesium bromide .
properties
Physical properties
Chlorine is a colored compound whose maximum absorption in benzene is 388 nm ( Soret band ). Another intense absorption band occurs at 637.5 nm. The absorption maxima shift through complexation. The Soret band of the magnesium complex is at 402 nm, that of the copper complex at 396 nm.
Chemical properties
Chlorin has two acidic protons that are bound to nitrogen atoms. In deprotonated form it is a very good complexing agent and is able to form thermodynamically stable, but substitution-labile complexes with divalent cations .
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ A b U. Eisner, RP Linstead: Chlorophyll and related substances. Part I. The synthesis of chlorine. In J. Chem. Soc. 1955, pp. 3742-3749; doi: 10.1039 / JR9550003742 .
- ^ W. Kaim , B. Schwederski: Bioinorganische Chemie, 4th edition, pp. 26-27, Teubner 2005; ISBN 3-519-33505-0 .