Clonazepam
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
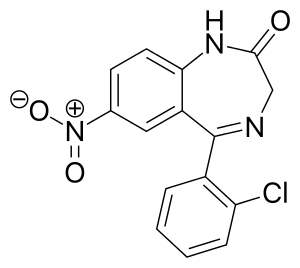
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Clonazepam | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 15 H 10 ClN 3 O 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
anti-convulsive effect |
||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 315.71 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
236.5-238.5 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
1.57; 10.50 |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Clonazepam ( trade name : Rivotril, manufacturer: Roche ) is an anticonvulsant from the benzodiazepine group of drugs used to treat cerebral seizures . Clonazepam is used for all forms of epilepsy, including that of childhood.
Pharmacokinetics
Clonazepam is rapidly absorbed after administration through the gastrointestinal tract. The maximum concentration in the blood is reached after two to three hours. Excretion is largely unchanged via the kidneys , and sometimes also via the stool. A small part is chemically converted and only then excreted. The plasma half-life is approximately 30–40 hours. The proportion that is bound to the protein molecules in the blood ( plasma protein binding ) is 83–87%, the bioavailability is 71–76%. It works by increasing the inhibition of GABAergic nerve cells and binds to the GABA A receptor .
application areas
In Germany, clonazepam is primarily approved as an anti-epileptic. Because of its anti-spasmodic effects, clonazepam is also used in children to treat epilepsy . Clonazepam is also recommended as a drug of first choice for the treatment of REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) or "Schenck syndrome". Taken at bedtime will reduce muscle activity during REM sleep . In this context, even with long-term use, there is hardly any development of tolerance or loss of effectiveness (despite existing addiction potential), which is important in the often chronic course of the disease.
Clonazepam plays a role as an alternative drug in restless legs syndrome and as the second line drug in treatment-resistant Tourette's syndrome . Since long-term treatment, as with all active substances in the benzodiazepine group, can lead to a rapid loss of effectiveness, in Germany it is mainly used in acute treatment, mostly intravenously or intramuscularly. But it is also available in drop form and as a tablet. In addition to its antispasmodic effect, clonazepam, like all benzodiazepines, has an anxiolytic and sleep-inducing effect. Clonazepam can therefore also be used in somnambulism (night walking). In addition, it is used in many countries as the first choice for panic attacks as an anxiolytic . It is also supposed to make states of derealization / depersonalization more bearable. In Germany, however, there is no official approval for these psychiatric indications, so that a corresponding use of the agent can only be considered by a specialist in individual cases.
Further areas of application are the medicinal support of inpatient alcohol withdrawal and the rare congenital hypereplexia .
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Animal studies have shown undesirable effects on the fetus . Therefore, the drug should only be used during pregnancy when it is absolutely necessary. However, clonazepam should not be suddenly stopped without consulting a doctor. Clonazepam should not be used during breastfeeding because it passes into breast milk . If there is a compelling indication, breastfeeding should be carried out.
Side effects
Corresponding to the suppression of cramps, clonazepam has a general depressant effect on the central nervous system , so that tiredness, drowsiness, fatigue, reduced muscle tension, muscle weakness, dizziness, drowsiness, balance disorders and prolonged reaction times can occur. With long-term therapy, these side effects are usually reduced by a habituation effect. They can be partially avoided by gradually starting treatment. Other more common side effects on the central nervous system are concentration disorders, restlessness, confusion and memory disorders, which can also be associated with inappropriate behavior. The paradoxical reactions observed were excitability, irritability, aggressive behavior, nervousness, hostility, anxiety, insomnia, nightmares, and vivid dreams. Allergic symptoms such as hives, itching, skin rashes, swelling of the face and oral mucosa as well as the larynx occur rarely. Temporary hair loss, pigment changes, nausea and upper abdominal discomfort, headache, chest pain, drop in blood platelets, disorder of sexual appetite , impotence and urinary incontinence are also rare . A premature onset of genital development has been reported in isolated cases in children. Also in individual cases, clonazepam can depress the respiratory center and lead to a reduced respiratory drive . Infants and young children can also experience increased salivation and increased production of mucus in the airways, which makes breathing difficult.
Dependency potential
Like all benzodiazepines, clonazepam can lead to physical and psychological dependency with associated withdrawal symptoms .
Trade names
Rivotril (D, CH), Antelepsin (D), and generics sold under the substance name
See also
Web links
- Clonazepam . In: Erowid . (English)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d data sheet clonazepam from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on December 19, 2012 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on clonazepam. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 29, 2019.
- ↑ Information from the manufacturer: Instructions for use clonazepam . Retrieved March 5, 2015
- ↑ FDA Prescription Clonazepam (PDF; 113 kB).
- ↑ S3 guideline for non-restful sleep / sleep disorders of the German Society for Sleep Research and Sleep Medicine (DGSM). In: AWMF online (as of 2009)
- ↑ Jiménez-Jiménez, García-Ruiz PJ .: Pharmacological options for the treatment of Tourette's disorder. Drugs. 2001; 61 (15): 2207-20.
- ↑ See Boghen, D., L. Lamothe, R. Elie, R. Godbout, J. Montplaisir: The treatment of the restless legs syndrome with clonazepam: A prospective controlled study. In: Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences 13 (1986), 245-247. PMID 3527387 .
- ↑ Clomethiazole vs. Clonazepam
- ^ Specialist information of the Swiss Medicines Compendium: Rivotril®, as of August 2005.
- ↑ Clonazepam in the "Yellow List" (accessed June 26, 2018).
- ↑ Documed: Clonazepam . In: Swiss Medicines Compendium (accessed on Aug. 4, 2013)