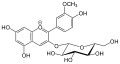
Cyanidine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Cyanidine | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 15 H 11 O 6 + | ||||||||||||
| Brief description |
violet solid (chloride) |
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 287.24 g mol −1
322.70 g mol −1 (chloride) |
||||||||||||
| Physical state |
solid (chloride) |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
> 300 ° C (chloride, decomposition) |
||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Cyanidin is a group of the anthocyanidins counting dye . Cyanidin chloride is practically insoluble in water and is suitable as an indicator , since the red flavylium cation is deprotonated at a pH of 6–6.5 to a red-violet product with a quinoid structure. Up to pH 8, this color changes to royal blue through further deprotonation . At an even higher pH, extracts of black elder or red cabbage also show green color.
Occurrence
Cyanidin is found in glycoside form as anthocyanin in many plants, including red cabbage , red roses , hibiscus , blueberry , raspberry , plum , elderberry , blackberry , blood orange, and rhubarb . In the form of an iron / magnesium / calcium chelate complex , cyanidine causes the blue color of the cornflower ( Centaurea cyanus ).
Methyl ethers of cyanidine ( peonidine and rosinidine ) also occur naturally as glycosides.
Cyanidin as an indicator
The structure of cyanidine changes depending on the pH of the environment. Since each structure has a different color, a solution containing cyanidin can be used to determine the pH value over almost the entire pH scale. The 3- O- glycosides and 3,5- O -diglycosides of cyanidine behave in the same way.
literature
- Norbert Welsch and Claus Chr. Liebmann: colors, nature technology. In: Art. 2nd edition 2006, Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, ISBN 3-8274-1563-2 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c data sheet Cyanidin chloride, ≥95% (HPLC) from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on February 12, 2019 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Entry on anthocyanins. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 26, 2014.
- ↑ a b c Sujata V. Bhat, BA Nagasampagi, Meenakshi Sivakumar: Chemistry of Natural Products . Springer Science & Business Media, 2005, ISBN 978-3-540-40669-3 , p. 602 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Axxora.com: Cyanidin chloride ( Memento of March 11, 2007 in the Internet Archive ), accessed on September 11, 2013.
- ^ Albert Gossauer: Structure and reactivity of biomolecules , Verlag Helvetica Chimica Acta, Zurich, 2006, p. 422, ISBN 978-3-906390-29-1 .
- ↑ Peter Keusch, University of Regensburg: Anthocyanins as pH indicators and complexing agents ( Memento from July 9, 2009 in the Internet Archive ).