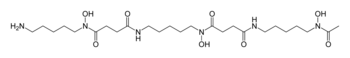
Deferoxamine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Deferoxamine | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 25 H 48 N 6 O 8 | ||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | |||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 560.68 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
140 ° C |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Deferoxamine is a drug that is used as an antidote for iron poisoning due to its high affinity for trivalent iron ions and its chelating property . It is marketed by Novartis in Germany, Austria, Switzerland and the rest of the EU as deferoxamine mesilate under the name Desferal .
Pharmacological properties
Deferoxamine is a high molecular weight compound with three hydroxamic acid groups and has a high affinity for iron (III) ions. It binds the iron released during hemoglobin breakdown and causes its renal excretion. Iron deficiency symptoms do not occur with short-term use.
Clinical information
Application areas (indications)
Deferoxamine is used as a parenterally administered drug for iron overload, including hemochromatosis , sideroblastic anemia , secondary hemosiderosis after blood transfusions and acute iron poisoning.
The deferoxamine test is used to determine pathological iron deposits. At the same time, a pathological deferoxamine test (desferal test) can be an indication of the presence of aluminum-induced osteopathy (low turnover osteopathy).
Other Information
Deferoxamine occurs naturally as a reddish color in Actinobacterium Streptomyces pilosus .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on deferoxamine in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ Deferoxamine mesylate salt data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 9, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Red List online, as of September 2009.
- ↑ AM comp. d. Switzerland, as of September 2009.
- ↑ AGES-PharmMed, as of September 2009.
literature
- Pschyrembel , 256th edition.
- Aktories / Förstermann / Hofmann / Starke: General and special pharmacology and toxicology. 9th edition, Urban & Fischer, Munich / Jena 2005. ISBN 3-437-44490-5 .
- Herold, Internal Medicine 2010, p. 619.