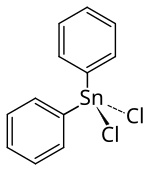
Diphenyltin dichloride
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Diphenyltin dichloride | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 10 Cl 2 Sn | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 343.82 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
42 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
333-337 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Diphenyltin dichloride is a chemical compound from the group of organotin compounds .
history
The first preparation of diphenyltin dichloride was reported by B. Aronheim as early as 1878. For this purpose, tin tetrachloride was reacted with diphenylmercury for 12 hours at the boiling point in ligroin :
Extraction and presentation
Diphenyltin dichloride can be produced industrially by the gradual splitting off of phenyl groups from tetraphenyltin with chlorine :
Diphenyltin dichloride can also be produced by comproportioning tetraphenyltin with tin tetrachloride ( Kocheshkov rearrangement ):
properties
Physical Properties
Diphenyltin dichloride dissolves easily in ether , alcohol and ligroin, but only slightly in water with partial decomposition. In the 13 C nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum (NMR) diphenyltin dichloride shows the following signals:
| Sn – C 1 - | -C 2 | -C 3 | -C 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ppm | 137.1 | 135.2 | 129.8 | 131.7 |
| J ( 13 C– 119 Sn) | 785 | 64.7 | 86.3 | 17.5 |
In the 119 Sn NMR it gives a signal at −26.4 ppm. In the crystal, the tin-carbon distance is 2.112 (5) and the tin-chlorine distance is 2.345 (2) Å . In benzene it has a dipole moment of 4.21 Debye .
Chemical properties
In moist air or in water, diphenyltin dichloride hydrolyzes to diphenyltin hydroxychloride, from which diphenyltin dichloride is re-formed in the presence of hydrochloric acid:
While diphenyltin oxide is formed in the presence of ammonia or sodium hydroxide solution , the action of concentrated acids such as hydrochloric acid splits off benzene or corresponding substitution products:
use
By reacting diphenyltin dichloride with diethylaluminum hydride in diethyl ether , diphenyltin dihydride can be obtained:
safety instructions
Diphenyltin dichloride has a flash point of 113 ° C.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h data sheet Diphenyltin dichloride from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on September 22, 2018 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d e B. Aronheim: Synthesis of tin phenyl compounds . In: Justus Liebig's Annals of Chemistry . tape 194 , no. 2-3 , 1878, pp. 145-175 , doi : 10.1002 / jlac.18781940202 .
- ^ Phenyltin compounds [MAK Value Documentation in German language, 2010] . In: The MAK Collection for Occupational Health and Safety . January 31, 2012, doi : 10.1002 / 3527600418.mb240668verd0048 .
- ↑ a b GJM van der Kerk, JGA Luijten, JG Noltes: New results in organotin research . In: Angewandte Chemie . tape 70 , no. 10 , May 21, 1958, pp. 298-306 , doi : 10.1002 / anie.19580701004 .
- ↑ Alwyn George Davies: chemistry organotin . tape 1 . Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2004, ISBN 3-527-31023-1 ( page 167 in the Google book search).
- ↑ a b Cathrin Zeppek, Johann Pichler, Ana Torvisco, Michaela Flock, Frank Uhlig: Aryltin chlorides and hydrides: Preparation, detailed NMR studies and DFT calculations . In: Journal of Organometallic Chemistry . tape 740 , September 2013, p. 41-49 , doi : 10.1016 / j.jorganchem.2013.03.012 .
- ↑ Jörg Lorberth, Heinrich Nöth: Dipole moments of some organotin chlorides . In: Chemical Reports . tape 98 , no. 3 , March 1965, p. 969 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.19650980342 .
- ^ Wilhelm P. Neumann, Horst Niermann: Organozinnverbindungen, II. Representation of organotin mono-, di- and tri-hydrides . In: Justus Liebig's Annals of Chemistry . tape 653 , no. 1 , May 24, 1962, p. 164 , doi : 10.1002 / jlac.19626530119 .








![{\ displaystyle \ mathrm {Cl_ {2} Sn (C_ {6} H_ {5}) _ {2} \ + \ 2 \ Et_ {2} AlH \ {\ xrightarrow [{Et_ {2} O}] {\ }} H_ {2} Sn (C_ {6} H_ {5}) _ {2} \ \ + \ 2Et_ {2} AlCl \ \ \ Et = Ethyl}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/b2bbf7df5d135d2e2a7da3536303089a2c909406)