Dutasteride
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
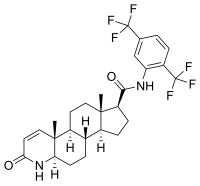
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Dutasteride | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 27 H 30 F 6 N 2 O 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class |
Urological drugs - prostate drugs |
||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
non-selective 5 α reductase - inhibitor |
||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 528.53 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
242-250 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Dutasteride is an organic chemical compound belonging to the class of steroids . Because of its effectiveness as a 5 α -reductase inhibitor, which lowers the rate of conversion of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and thereby lowers the DHT concentration, it is used as a medicinal substance for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). The trade name of the globally available finished drug from the manufacturer GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) is Avodart ® .
application areas
Dutasteride is used to treat the symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Dutasteride is also used to reduce the risk of acute urinary retention and before prostate operations in the presence of BPH symptoms.
Prostate cancer
Dutasteride reduces the risk of progression in patients with low-grade prostate cancer who follow a wait-and-see strategy . In the randomized, double-blind, multicenter REDEEM study, 302 men with low-grade prostate cancer were randomized. After three years, 38% of the men treated with dutasteride had tumor progression, compared with 48% in the placebo group. No tumor-related death or metastasis was observed in either group . This treatment is not discussed in either the DKG's S3 guideline on prostate cancer or the EAU's guidelines on prostate cancer . There is no approval for this indication.
pharmacology
Dutasteride inhibits the 5α-reductase isoenzymes of type 1, 2 and 3, which are responsible for the breakdown of the hormone testosterone to dihydrotestosterone. It thus lowers the concentration of circulating dihydrotestosterone. Most of this transformation occurs in the prostate, liver, and skin. In the cells of these three organs, DHT binds to the nucleus. Especially in the prostate cells, DHT increases the cell division rate of the prostate tissue and ensures that it enlarges. Dutasteride is currently only approved for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). The similar finasteride is also used to treat androgenetic alopecia with a fifth of the BPH drug dose.
Side effects
Side effects occur more frequently and more intensely with dutasteride than with finasteride. The reason for this is the stronger inhibition of DHT in the blood plasma:
- Erectile dysfunction : 6.0%
- Decreased libido : 3.7%
- Ejaculation disorder: 1.8%
- Gynecomastia : 1.3%
The side effects can persist for up to about six months after discontinuation of therapy. The reason for this is the long plasma half-life of dutasteride of around five weeks. Persistent damage after drug discontinuation has also been reported, similar to the related finasteride , see post-finasteride syndrome .
Use against hair loss
A doctor's prescription of dutasteride for androgenetic alopecia is a so-called off-label use . The technical term off-label-use describes the use of a medicinal substance outside of the approved indication. Dutasteride is currently not approved for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia, unlike the pharmacologically and chemically closely related active ingredient finasteride , whose indications are BPH and androgenetic alopecia. 0.5 mg of dutasteride are able to lower the concentration of DHT in the scalp more than ten times the amount of finasteride. In June 2010, a phase III study for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia was published, which is required for approval for an indication.
Contraindications
Medicines containing the drug dutasteride must not be taken by women, children and adolescents, nor by people with severe liver dysfunction and hypersensitivity to other 5α-reductase inhibitors.
Abuse in Sports
Dutasteride is used to prevent the typical steroid side effects of strongly androgenic steroids. These include hair loss , increased body hair growth, and acne . Dutasteride works with every androgenic steroid with the exception of drostanolone .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e FDA label for Avodart ® (dutasteride) - as of September 2010 (PDF; 315 kB) on the website of the Food and Drug Administration FDA .
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Neil E Fleshner, M Scott Lucia, Blair Egerdie, Lorne Aaron, Gregg Eure: Dutasteride in localized prostate cancer management: the REDEEM randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial . In: Lancet (London, England) . tape 379 , no. 9821 , March 24, 2012, p. 1103-1111 , doi : 10.1016 / S0140-6736 (11) 61619-X , PMID 22277570 .
- ↑ Leading professional society German Society for Urology e. V. (DGU): Interdisciplinary guideline of quality S3 for early detection, diagnosis and therapy of the different stages of prostate cancer. Version 5.0. Oncology guideline program of the Working Group of the Scientific Medical Societies in Germany (AWMF), German Cancer Society (DKG) and German Cancer Aid (DKH), 2018, archived from the original on April 11, 2019 ; accessed on April 11, 2019 .
- ↑ Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. European Association of Urology (EAU), 2019, accessed April 11, 2019 .
- ↑ AM Traish, J. Hassani, AT Guay, M. Zitzmann, ML Hansen: Adverse side effects of 5α-reductase inhibitors therapy: persistent diminished libido and erectile dysfunction and depression in a subset of patients. In: The Journal of Sexual Medicine , 8/2011 pp. 872-884. doi: 10.1111 / j.1743-6109.2010.02157.x ; PMID 21176115 .
- ↑ Hee Chul Eun et al .: Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of dutasteride 0.5 mg once daily in male patients with male pattern hair loss: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III study. In: Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology , Volume 63, 2010, pp. 252-258. doi: 10.1016 / j.jaad.2009.09.018 .
- ^ The Black Book - Anabolic Steroids , 2007, ISBN 978-3-00-020944-4 , p. 114.