Tax reform
A major or fundamental change in the tax system or an individual tax law in a country is called a tax reform . A tax reform proposal describes a concrete model or concept for changing tax law as part of a tax reform.
Justifications for tax reforms
Recurring reasons for reforms are:
- Elimination of too high or too low taxation (e.g. non-taxation , national double taxation ) of certain parts of the income or taxpayers in the sense of increasing tax equity . This also includes the discussion about the dismantling of unjustified tax breaks as well as the demands for the adjustment of tax tariffs or tax rates to those of other countries.
- Simplification of tax law and increased transparency.
- Especially in the area of corporate taxation, increasing the attractiveness of the location for investments. The increased mobility of companies and high earners, combined with intensified global tax competition , however, considerably reduces the scope for government action here.
- Prevention of creeping tax increases (so-called cold progression ) through the interaction of creeping inflation and a progressive tax rate .
- Changes to tax law based on the requirements of case law, e.g. as a reaction to judgments by the European Court of Justice , the Federal Fiscal Court or the Federal Constitutional Court .
Tax reforms in Germany
Tax reforms as far-reaching changes to detailed regulations in Germany's tax legislation and with a major impact on tax revenues relate in particular to the Income Tax Act , the Corporation Tax Act and the Sales Tax Act .
Implemented tax reforms
Tax cuts on capital income and cuts in the top tax rate have occurred several times since the 1970s:
- Abolition of double taxation through the introduction of the credit system on January 1, 1977
- Abolition of the payroll tax on January 1, 1980
- Introduction of a continuously linear-progressive tariff and reduction of the top tax rate from 56% to 53% on January 1, 1990
- Abolition of the stock exchange tax on January 1, 1991
- Company tax abolished on January 1, 1992
- Abolition of trade capital tax on January 1, 1998
- Suspension of wealth tax on January 1, 1997
- Introduction of a special top income tax rate of 47% instead of 53% on business income on January 1, 1999
- Reduction of the corporate tax rate from 45% to 40% on January 1, 1999
- Introduction of the half-income method and lowering of the corporate income tax rate to 25% on January 1, 2001. The trade tax can now be offset against income tax.
- Reduction of the top income tax rate to 45% on January 1, 2004; Introduction of an inheritance tax allowance of 225,000 euros and conversion of the calculation basis from the market value to the tax balance sheet approach
- Lowering of the top income tax rate to 42% on January 1, 2005.
- Increase in the top income tax rate to 45% on January 1, 2007 (only for the part exceeding 250,000 euros as a tiered tariff )
- Introduction of retention taxation as part of the corporate tax reform 2008
- Introduction of the final withholding tax for capital income from 2009
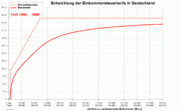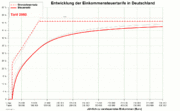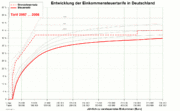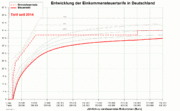
These reductions in income tax rates were also accompanied by repeated increases in VAT rates, as the chart above shows.
Examples of tax reform proposals
- In 1994, a commission headed by tax scientist Peter Bareis from the University of Hohenheim presented a model in which 85 tax breaks were abolished. The then Federal Minister of Finance Theo Waigel rejected the concept.
- In 1996, the CDU member of the Bundestag and economics spokesman for the parliamentary group, Gunnar Uldall, put the abolition of exceptional circumstances and a three-tier income tax rate of 8%, 18% and 28% with a basic allowance of DM 12,000 up for discussion.
- The Ulm model is a possible income tax model for realizing an unconditional basic income . It was developed in 1996 at the University of Ulm under the main direction of Helmut Pelzer at the Center for General Scientific Further Education and represents a revenue-neutral basic security for all citizens. Tax liability and basic income are offset against each other. If the tax liability is higher, the amount is to be paid as tax, otherwise the amount is paid out as a state subsidy to income, which is also known as negative income tax .
- In January 2001, the research group on the Federal Tax Code , headed by Paul Kirchhof from Heidelberg University, presented its proposal for a tax reform entitled “ Income Tax Code ”. The model provides only one type of income and one flat tax .
- In its 2003 annual report, the Advisory Council on the Assessment of Overall Economic Development proposed the introduction of a dual income tax . In April 2006 he specified these proposals. After that, a split into capital and earned income is to be made. The former is to be taxed at 25%, the rest is subject to the well-known linear-progressive income tax rate. With the so-called final withholding tax , this was partially realized from January 1, 2009, so that now labor income over approx. 47,500 euros is taxed higher than interest income.
- In 2003, the CDU politician Friedrich Merz presented his concept for the abolition of exemptions and the introduction of a tiered tariff in income tax under the catchphrase “beer mat tax”. According to the DIW's calculations, Friedrich Merz's tax concept would lead to permanent tax revenue shortfalls of around € 26-27 billion per year.
- Also in 2003, under the leadership of the then Prime Minister Roland Koch and Peer Steinbrück, the “Koch-Steinbrück List” for the abolition of tax subsidies was drawn up.
- In February 2005, a working group led by the Cologne legal scholar Joachim Lang presented the “Cologne draft of an income tax law”, which is intended to purify the current income tax law and bring it back to its systematic roots. Individual tax breaks, especially for employees, are to be deleted, and basic case law that has further developed the law is to be included in the legal text. Lang is currently head of the “Tax Code” commission under the umbrella of the Market Economy Foundation , which wants to develop a comprehensive reform concept.
- In 2005, the entrepreneur Götz Werner proposed the “unconditional basic income and consumption tax” model. It aims to abolish all types of tax - with the exception of sales tax (consumption tax). This should be increased to around 50% to compensate. An unconditional basic income is to be financed from the tax revenue.
Tax reform proposals in Switzerland
The FDP has presented a tax concept under the name Easy Swiss Tax (FDP of the Canton of Zurich ) or beer mat tax return (FDP of the Canton of Schaffhausen ) propagated.
The Easy Swiss Tax is intended to greatly simplify the tax return by eliminating many options for deductions. This is intended to plug tax loopholes. With the concept, the FDP also wants to lower income tax on balance. A flat tax is also being discussed.
At the cantonal level, parliamentary initiatives, popular initiatives and petitions in favor of Easy Swiss Tax were launched in the cantons of Aargau, Basel-Land, Schaffhausen, Schwyz, St. Gallen, Thurgau, Zurich and Zug.
At the federal level, the subject was dealt with in the National Council on the basis of two parliamentary proposals: The interpellation Is the simplification of the tax system a priority? by FDP National Councilor Markus Hutter (submitted on June 21, 2007, completed on October 1, 2007, examination of specific measures by the FDF pending) and the motion for individual taxation and simplification of the tax system. EasySwissTax by FDP National Councilor Charles Favre (submitted on March 14, 2007, rejected on October 1, 2007).
Tax reform proposals in other countries
In the United States, a proposal has been under discussion since 1999 that all federal taxes, in particular income tax and social security contributions, should be replaced by a sales tax. The supporters of this reform proposal promise a simplification of tax law and economic stimulation.
- Main article: FairTax Act
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Table 1: Revenue effects of the reform proposals for income tax compared to the legal status 2005 In: DIW weekly report 16/2004 ( PDF )
- ↑ Hessian State Chancellery: Subsidies Reduction ( Memento of the original from July 15, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ EasySwissTax website ( memento of the original from February 27, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Beer mat tax return website ( Memento of the original from December 28, 2009 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Archived copy ( Memento of the original from March 22, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ http://www.parlament.ch/D/ sucht/Seiten/geschaefte.aspx?gesch_id= 20073439
- ↑ http://www.parlament.ch/d/suche/seiten/geschaefte.aspx?gesch_id=20073046