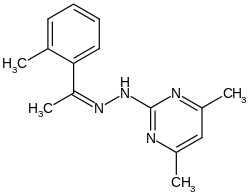
Ferimzon
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Ferimzon | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 15 H 18 N 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 254.33 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
172-177 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Ferimzone is a chemical compound from the group of pyrimidines and hydrazones .
Extraction and presentation
Ferimzone can be obtained from 2-methylacetophenone .
properties
Ferimzone is a colorless solid that is sparingly soluble in water.
use
Ferimzon is used as a fungicide against fungal diseases in rice cultivation ( rice blight , Helminthosporium oryzae , Cercospora oryzae , Curvularia , Epicoccum , Alternaria ). It was registered by Takeda in 1991 . The name Ferimzone only refers to the ( Z ) isomer of the compound, as this is more stable. The mixture of both isomers is called meferimzone (CAS number: 77359-18-3).
Ferimzone inhibits spore germination, but so far the effect could not be assigned to any known mode of action.
Admission
No crop protection product with this active ingredient is currently approved in any EU country or in Switzerland.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i data sheet Ferimzone, analytical standard at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on December 20, 2014 ( PDF ).
- ^ Farm Chemicals International: Crop Protection Database | Farm Chemicals International , accessed December 20, 2014.
- ↑ Ulrich Schirmer, Peter Jeschke, Matthias Witschel: Modern Crop Protection Compounds: Herbicides . John Wiley & Sons, 2012, ISBN 978-3-527-32965-6 , pp. 661 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Kazuho Matsuura, Yasuo Ishida, Takashi Kuragano, Kazuo Konishi: Development of a New Fungicide, Ferimzone . In: Journal of Pesticide Science . tape 19 , no. 4 , 1994, pp. 325–327 , doi : 10.1584 / jpestics.19.4_325 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on Ferimzon. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed December 20, 2014.
- ↑ Tetsuro Okuno, Iwao Furusawa, Kazuho Matsuura, Jiko Shishiyama: Mode of Action of Ferimzone (TF-164), a Novel Systemic Fungicide for Rice Diseases . In: Japanese Journal of Phytopathology . tape 55 , no. 3 , 1989, pp. 281-289 , doi : 10.3186 / jjphytopath.55.281 ( PDF ).
- ^ Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: EU pesticide database ; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on February 14, 2016.

