Flusilazole
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
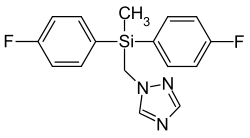
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Flusilazole | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Bis (4-fluorophenyl) (methyl) (1 H -1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl) silane |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 16 H 15 F 2 N 3 Si | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless to brown solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 315.39 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.31 g cm −3 (bulk density) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
52-53 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
393 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
3.9 10 −8 Pa (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
2.5 (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Flusilazole is a chemical compound from the group of organosilicon compounds and triazoles .
Extraction and presentation
Flusilazole can be obtained by reacting chloromethyldichloromethylsilane with p -fluorolithiobenzene and the sodium salt of 1,2,4-triazole .
properties
Flusilazole is a colorless to brown solid that is insoluble in water.
use
Flusilazole is used as an active ingredient in crop protection products. It is used as a fungicide against asphyxia , Deuteromycetes and mushrooms . It influences the ergosterol biosynthesis by inhibiting the demethylation of steroids. It was brought onto the market in 1985 and has been approved in the FRG since 1988.
Admission
In the European Union, flusilazole was approved for use as a fungicide on cereals (except rice), maize, rapeseed and sugar beet since January 1, 2007. There were concerns about the toxicity of flusilazole, particularly its possible endocrine effects . The approval ended on April 12, 2013. In Switzerland, too, no pesticides containing this active ingredient are approved any more.
safety instructions
Flusilazole is suspected of causing cancer in humans. It causes bladder and testicular tumors in rats and liver tumors in mice.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on Flusilazole in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB) of the University of Hertfordshire , accessed on August 1, 2013.
- ↑ a b c data sheet Flusilazole, PESTANAL at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 19, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c Terence Robert Roberts, David Herd Hutson: Metabolic Pathways of Agrochemicals: Part 2: Insecticides and Fungicides . Royal Society of Chemistry, 1999, ISBN 0-85404-499-X , pp. 1050 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on flusilazole in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 23, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on bis (4-fluorophenyl) (methyl) (1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl) silane in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 1, 2016. Distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 698 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Horst Börner: Plant diseases and plant protection . Springer DE, 2009, ISBN 3-540-49067-1 , pp. 528 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Peter Brandt: Reports on Plant Protection Products 2009: Active Ingredients in Plant Protection Products ... Springer DE, 2010, ISBN 3-0348-0028-2 , p. 17 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Directive 2006/133 / EC of the Commission dated December 11, 2006 amending Council Directive 91/414 / EEC to include the active substance flusilazole (PDF)
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Flusilazole in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on December 7, 2019.
- ↑ Hans-Werner Vohr: Toxicology . John Wiley & Sons, 2012, ISBN 3-527-66003-8 , pp. ? ( limited preview in Google Book search).



