Great Sandy Strait
| Great Sandy Strait | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Great Sandy Strait from space (west is up) | ||
| Connects waters | Hervey Bay | |
| with water | Coral sea | |
| Separates land mass | Fraser Island | |
| of land mass | Australia (continent) | |
| Data | ||
| Geographical location | 25 ° 31 ′ S , 152 ° 57 ′ E | |
|
|
||
| length | 70 km | |
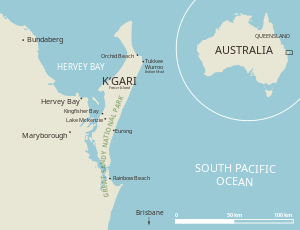
| Location of Fraser Island and Hervey Bay | ||
The Great Sandy Strait is a sea canal in the southeast of the Australian state of Queensland . It separates the large sandy island of Fraser Island , which is listed as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO , in the east from the mainland in the west. The large body of water, which is subject to a strong tidal range , is mostly a protected area for water birds and waders . It is listed as a significant protected area by UNESCO according to the Ramsar Convention .
location
The Great Sandy Strait covers an area of almost 932 km² and extends over a length of about 70 kilometers. It begins in the south at Inskip Point north of Rainbow Beach and extends to Hervey Bay near Hervey Bay . To the east, the sea channel, also known as the estuary in Australia , is bounded by Fraser Island. In the north and south the sea channel opens into the coral sea . The strait that opens in the north is 10.5 kilometers wide, followed by Hervey Bay.
The Mary River , which carries large masses of sand, flows into the sea channel at River Heads . There are several islands in the Great Sandy Strait, including Big Woody Island and Little Woody Island, Walsh, Pookar and Turkey Island.
The Woody Islands have lighthouses and associated buildings that were built from 1866 to 1870 and were entered on the Australian National List of Historic Monuments in 2011 as Woody Island Lighthouses .
Half a dozen settlements are scattered on the west bank, most of them very small. Tin Can Bay is the largest place on the shores of the Great Sandy Strait. Rainbow Beach is at the southern end, Hervey Bey at the north and the town of Maryborough in the hinterland around 15 kilometers away .
geology
The deposited sand is a product of erosion from the Great Dividing Range , which stretches along the entire east coast of Australia. The sand was transported to the sea by the river systems of northern New South Wales and from there northwards by the prevailing southeast trade winds and ocean currents along the coast.
Until 10,000 years ago, the Great Sandy Strait and Fraser Island were part of the mainland. The end of the Australian continental shelf ran about 25 kilometers from Woody Island. There the Mary River was diverted to the southeast and drained into what is now the Great Sandy Strait. This river and its tributaries dug deep valleys into the landscape of that time. After the last ice age, the sea level rose by up to 120 meters and the Mary River with its tributaries formed wide flat, sandy estuaries that were flooded by salt water. Living in this area Aborigines of Butchulla retreated to the mainland coast and Fraser Iceland.
economy
Fishing and tourism are economically important . However, the fish stocks in the Great Sandy Strait are overexploited.
Tourism is primarily concentrated on Fraser Island and Hervey Bay. Boating and fishing are of great economic importance for the region. Whale watching is operated from August to November. Every year there is a sailing regatta through the Great Sandy Strait, the Bay to Bay Yacht Race .
Ferries connect the mainland to Fraser Island from River Heads and Inskip Point.
environment
The landscape of the Great Sandy Strait is characterized by mangroves , sandbanks , mud flats, seagrass fields and strong tidal ranges. The tidal range reaches an average of 4.1 meters. According to a measurement from 1992, 28 km² consist of salt marshes and areas of clay , 155 km² are covered by mangroves and seaweed grows on a water surface of 123 km². The wetlands in the west reach a width of 5.5 to 13.5 kilometers.
After several floods, plans were made to dam the Mary River by building the Traveston Crossing Dam . As this would have had a significant impact on the water conditions in the Great Sandy Strait, the project was abandoned in 2009 due to resistance from the local population.
Conservation areas on or near Great Sandy Strait include Great Sandy National Park , Poona National Park, and Great Sandy Conservation Park .
Flora and fauna
The strait is an important habitat for fish, shellfish , dugongs and dolphins . Six species of seaweed grow in the large seagrass fields. Sea turtles such as green turtle , Echte- and loggerhead turtle and leatherback turtle walk on these streets. Humpback whales roam the calm waters of the Great Sandy Strait from August through November .
The wetlands in the Great Sandy Strait with a size of 806 km² have been designated by UNESCO as a Ramsar area of international importance since 1999 . This area offers protection to around 120,000 birds. These represent about one percent of the world population of common woodcock , Siberian curlew , great knot , gray-tailed sandpiper , Mongolian plover , Australian oyster fishermen , red throat sandpiper and red- headed plover . A small number of mangrove honey-eaters also live there . Various species of ducks , ibises , herons , as well as the brolga crane and black swan can be found in this area.
63 species of fish were counted in the wetlands, 104 at Tin Can Bay. 27 species of mussels also live there.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ Great Sandy Strait (including Great Sandy Strait, Tin Can Bay, and Tin Can Inlet) . In: Ramsar Sites Database , Wetlands International. Accessed September 1, 2016.
- ↑ Woody Island Lighthouses & Ancillary Building Site , at environment.ehp.qld.gov.au. Retrieved September 1, 2016
- ↑ A History of Aboriginals of Fraser Island , at fido.org.au. Retrieved September 1, 2016
- ↑ Fishing stocks drop in Great Sandy Strait , November 4, 2005, on abc.net.au. Retrieved September 1, 2016
- ↑ Information Sheet on Ramsar Wetlands (RIS) ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , on environment.gov.au. Retrieved September 1, 2016
- ↑ Tony Moore: Report to Garrett says dam species will die , November 26, 2008, on brisbanetimes.com.au. Retrieved September 1, 2016
- ^ Great Sandy Strait - Hervey Bay Area, Hervey Bay, QLD, Australia . In: Australian Heritage Database . Commonwealth of Australia. Retrieved September 1, 2016.