Hafnium nitride
| Crystal structure | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||
| __ Hf 3+ __ N 3− | |||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Hafnium nitride | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | HfN | ||||||||||||
| Brief description |
dark gray to brown solid |
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 192.50 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| density |
11.7 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
3305 ° C |
||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Hafnium nitride is an inorganic chemical compound of hafnium from the group of nitrides .
Extraction and presentation
Hafnium nitride can be prepared using the same methods as titanium nitride .
- This is how hafnium nitride is obtained during the synthesis from the elements at 1400 ° C to 1500 ° C.
- In the production of hafnium nitride from hafnium (IV) chloride by the growth process , a lower temperature (2000 to 2400 ° C) is required in the presence of hydrogen (H 2 + N 2 or ammonia ) than in pure nitrogen (2900 ° C). In the latter case, the deposition takes place significantly more slowly than in the presence of hydrogen.
- Under high pressure conditions, ammonolysis or reaction of hafnium nitride with nitrogen forms a hafnium nitride Hf 3 N 4 of the cubic Th 3 P 4 type with the space group I 4 3 d .
properties
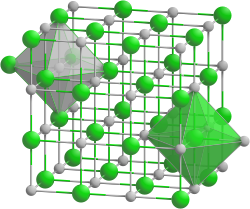
Hafnium nitride is a dark gray to yellow-brown odorless solid. It is electrically conductive and has a cubic crystal structure of the sodium chloride type with the space group Fm 3 m (no. 225) . Due to voids in the lattice structure, the real density of hafnium nitride is only 11.70 g · cm −3 instead of the 13.39 g · cm −3 determined on the basis of lattice structure analyzes with X-ray methods . It is a very hard and stable material and has a Vickers hardness of 46 GPa.
use
Hafnium nitride is used as a sputtering material to increase the stability of diodes, transistors and electronic circuits. It is also used as a coating material for cutting tools, as it is the most stable hard material with a high melting temperature.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Roger Blachnik (Ed.): Pocket book for chemists and physicists . Volume III: Elements, Inorganic Compounds and Materials, Minerals . founded by Jean d'Ans, Ellen Lax. 4th, revised and revised edition. Springer, Berlin 1998, ISBN 3-540-60035-3 , pp. 479 ( limited preview in Google Book search). .
- ↑ a b M. E. Straumanis, CA Faunce: The imperfect structure of hafnium nitride and the bonding problem. In: Journal of Inorganic and General Chemistry. 353, 1967, pp. 329-336, doi : 10.1002 / zaac.19673530514 .
- ↑ READE: Hafnium Nitride Powder (HfN) ( Memento of the original dated August 6, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ a b c Georg Brauer (ed.), With the collaboration of Marianne Baudler a . a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume II, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1978, ISBN 3-432-87813-3 , p. 1379.
- ↑ a b Dzivenko, Dmytro: High-pressure synthesis, structure and properties of cubic zirconium (IV) - and hafnium (IV) nitrides. Dissertation (2009), urn : nbn: de: tuda-tuprints-18742
- ↑ Werner Martienssen, Hans Warlimont: Springer Handbook of Condensed Matter and Materials Data. Springer, 2005, ISBN 9783540304371 , p. 468 ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ^ A b Dale L. Perry: Handbook of Inorganic Compounds, Second Edition. Taylor & Francis US, 2011, ISBN 1439814627 , p. 194 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ Derya Deniz: Texture evolution in metal nitride (aluminum nitride, titanium nitride, hafnium nitride) thin films prepared by off-normal incidence reactive magnetron sputtering. ProQuest, 2008, ISBN 9781109037821 , p. 6 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ Serope Kalpakjian, Steven R. Schmid, Ewald Werner: materials technology. Pearson Deutschland GmbH, 2011, ISBN 978386894006-0 , p. 634 ( limited preview in the Google book search)
- ↑ Hmt, Hmt, H. M T. Bangalore: Production Technology. Tata McGraw-Hill Education, 2001, ISBN 9780070964433 , p. 41 ( limited preview in Google book search).
