Hafnocene dichloride
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
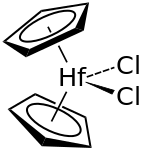
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Hafnocene dichloride | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 10 Cl 2 Hf | ||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless crystals |
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 379.59 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| density |
12.7 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
230-233 ° C |
||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in aromatic solvents and chloroform , slightly soluble in THF and diethyl ether , insoluble in n-hexane . Decomposes in water |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Hafnocene dichloride or, according to the IUPAC nomenclature, dichlorobis ( η 5 - cyclopentadienyl ) hafnium (IV) , is an organometallic compound from the metallocenes family . Like the analogous titanocene dichloride , hafnocene dichloride is also a 16-electron complex. The reactive colorless solid decomposes rapidly in water.
Extraction and presentation
The preparation of hafnocene dichloride by the reaction of hafnium tetrachloride with cyclopentadienyl sodium in a mixture of toluene and DME was reported in 1969 by Druce, Kingston, Lappert, Spalding and Srivastava.
properties
Physical Properties
In contrast to the metallocenes, the cyclopentadienyl rings are not in hafnocene dichloride coplanar arranged, but are in the molecule with the two chloride - ligand distorted tetrahedral around the central hafnium arranged.
use
Hafnocene dichloride is used in polymerization catalysts, which were described in 1980 by Hansjörg Sinn and Walter Kaminsky . These so-called Kaminsky catalysts , which consist of mixtures of metallocene dihalides (type 1) with methylaluminoxane (MAO), allow the polymerization of ethylene, propylene or olefin mixtures with very high productivity.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Takeo Taguchi, Yuji Hanzawa, Keisuke Suzuki, Yasuhito Koyama: Dichlorobis (cyclopentadienyl) hafnium . In: e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis . tape 28 , 1990, pp. 267-270 , doi : 10.1002 / 047084289X.rd089s.pub2 .
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet bis (cyclopentadienyl) hafnium (IV) dichloride from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on July 22, 2014 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Guidechem: Hafnium, dichlorobis (h5-2,4-cyclopentadien-1-yl) - (CAS No. 12116-66-4) , accessed on March 11, 2015.
- ↑ a b data sheet bis (cyclopentadienyl) hafnium dichloride (PDF) from Strem, accessed on March 11, 2015.
- ^ PM Druce, BM Kingston, MF Lappert, TR Spalding, RC Srivastava: Metallocene halides. Part I. Synthesis, spectra, and redistribution equilibria of di-n-cyclopentadienyldihalogeno-titanium (IV), - zirconium (IV), and -hafnium (IV). In: Journal of the Chemical Society A: Inorganic, Physical, Theoretical. 1969, p. 2106, doi : 10.1039 / J19690002106 .
- ↑ Wolfgang A. Herrmann: Synthetic Methods of Organometallic and Inorganic Chemistry, Volume 8, 1997. Georg Thieme Verlag, 2014, ISBN 978-3-131-79481-9 , p. 32 ( limited preview in the Google book search).
- ↑ Hansjörg Sinn, Walter Kaminsky, Hans-Jürgen Vollmer, Rüdiger Woldt: “Living Polymers” in Ziegler catalysts of extreme productivity . In: Angewandte Chemie . tape 92 , no. 5 , 1980, pp. 396-402 , doi : 10.1002 / anie.19800920517 .

![{\ mathrm {HfCl_ {4} + \ 2 \ Na (C_ {5} H_ {5}) \ {\ xrightarrow [{Toluene / DME}] {}} \ Hf (C_ {5} H_ {5}) _ {2} Cl_ {2} + \ 2 \ NaCl}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/96be098479647dce770570bd7ecf9561530b7edc)
