Hydrazinium chloride
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
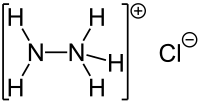
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Hydrazinium chloride | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | N 2 H 5 Cl | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 68.51 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.5 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
89 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
240 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Hydrazinium chloride is a chemical compound from the group of hydrazinium salts .
Extraction and presentation
Hydrazinium chloride is formed by neutralizing one mole of hydrazine with one mole of hydrochloric acid .
properties
Hydrazinium chloride is a crystalline colorless solid that is easily soluble in water. It decomposes when heated above 240 ° C, producing hydrogen chloride and nitrogen oxides . The compound has an orthorhombic crystal structure (a = 1.249 nm, b = 2.185 nm, c = 0.441 nm) with the space group Fdd 2 (space group no. 43) .
use
Hydrazinium chloride is used as a catalyst in the synthesis of titanium oxide polymers via catalytic sol-gel processes , in the production of amorphous titanium dioxide thin films with high refractive indices and high transparency, and in the production of other chemical compounds. It can also be used to precipitate elements such as gold, palladium, platinum, selenium and tellurium from hydrochloric ore solutions.
Related links
- Hydrazinium dichloride N 2 H 6 Cl 2
- Hydrazinium bromide N 2 H 5 Br
- Hydrazinium fluoride N 2 H 5 F
- Hydrazinium difluoride N 2 H 6 F 2
- Hydrazinium iodide N 2 H 5 I.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on hydrazinium chloride in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on November 15, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ^ A b c Dale L. Perry: Handbook of Inorganic Compounds, Second Edition . CRC Press, 2016, ISBN 978-1-4398-1462-8 , pp. 199 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Lexicon of Chemistry: Hydrazinium Chloride , Spectrum of Science, accessed on November 16, 2016
- ^ Niels Bjerrum, Ludwig Ebert: Short textbook of inorganic chemistry . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-91147-7 , pp. 153 ( books.google.de ).
- ↑ Sakurai K., Tomiie Y .: The crystal structure of hydrazinium chloride, N2H5Cl . In: Acta Crystallographica . tape 5 , no. 2 , March 2, 1952, doi : 10.1107 / S0365110X5200085X .
- ↑ Datasheet Hydrazine monohydrochloride, 97% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on November 15, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Peter Kurzweil, Paul Scheipers: Chemistry basics, structural knowledge, applications and experiments . Springer-Verlag, 2011, ISBN 978-3-8348-8280-6 , pp. 279 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Hans Peter Latscha, Gerald W. Linti, Helmut Klein: Analytical Chemistry Chemistry — Basic Knowledge III . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-18493-2 , pp. 95 ( limited preview in Google Book search).



