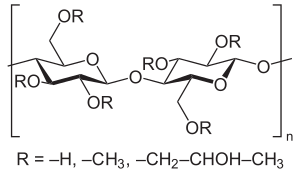
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose
| Structural formula | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||
| General | |||||||||
| Surname | Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose | ||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||
| CAS number |
|
||||||||
| Monomers / partial structures | Hydroxypropyl methyl glucose | ||||||||
| PubChem | 57503849 | ||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||
| DrugBank | DB11075 | ||||||||
| Brief description |
Powder or granules, white to yellowish white or grayish white, hygroscopic when dried |
||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||
| Drug class |
Artificial tears |
||||||||
| properties | |||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||
| solubility |
Practically insoluble in hot water, in acetone , in anhydrous ethanol and in toluene ; soluble in cold water to form a colloidal solution . |
||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose ( HPMC ) is a methyl cellulose substituted with propylene oxide . It comes onto the market in various degrees of polymerization and various degrees of substitution .
use
- Building materials industry: Additive for regulating flow properties
- Food industry: thickeners , viscosity control substances. They are approved in the EU as a food additive with the number E 464 , in the USA by 21CFR 172.874 (FDA).
- Tobacco products: HPMC is used as a binder and film former in the production of tobacco leaves and flakes and as an adhesive for cigarette paper.
- Cosmetics: Due to their thickening and stabilizing properties and their skin tolerance, HPMC is used in emulsions, toothpastes, shampoos , soaps, creams and lotions .
- Pharmacy: thickener , emulsion stabilizer , soluble film coatings . As early as 1962, HPMC was proposed in a US patent for use to delay the release of active ingredients from tablets.
- Medicine: in an aqueous solution for the symptomatic treatment of dry eyes ("artificial tears")
Special features: Aqueous HPMC gels tend to increase their viscosity very quickly when heated to a certain temperature. This temperature is often referred to as the gel point , but in this case it is not entirely correct. This solidification process is reversible, i.e. as soon as the temperature has dropped sufficiently, the gel becomes more fluid again. One makes this effect z. B. Benefit in food technology: HPMC is added to patties so that they are firm when fried (high temperature), but tender again when consumed (lower temperature).
Manufacturing
Cellulose is swollen in hot sodium hydroxide solution and reacted with propylene oxide and high methyl chloride pressure at 50 to 80 ° C ; the latter only reacts at a high temperature. Typical by-products of polycondensation and hydrolysis of propylene oxide are propylene glycol , di- and tripropylene glycol and, in addition to methanol, their methyl ethers (e.g. methoxypropanol , dipropylene glycol monomethyl ether , etc.). For isolation, all substances volatile up to 110 ° C. are first distilled off and then all glycols and salts are washed out with hot water, the solid is dried and ground to a powder. Production under GMP conditions is mandatory for the food and pharmaceutical sectors.
HPMC is determined by the average degree of substitution (DS) and the methyl vs. Characterized by hydroxypropyl. In connection with the general name "Hypromellose" this is symbolized by a four-digit number, whereby the first two correspond to the methoxy content, the last two to the hydroxypropoxy content.
The size of the macromolecule is usually characterized by its viscosity in a 2 percent aqueous solution; The HPMC types 4M (for approx. 4,000 mPas), 15M (for approx. 15,000 mPas) and 100M (for approx. 100,000 mPas) are commercially available.
Trade names
ARBOCEL, Benecel, Methocel, Metolose , Tylose , VIVAPHARM, Walocel, AnyAddy
Finished preparations as "artificial tears" (selection):
- Monopreparations : Berberil Dry Eye (D), Okuselect (A), Prosicca (A), Sicca-Stulln (D), Sic-Ophtal (D)
- Combination preparations: Lacrisic (D), Oculotect (D), Herba Vision (CH), Isopto- Tears (CH), Pilocarpine Puroptal (A), Tears Naturale (CH)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on E 464: Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose in the European database for food additives, accessed on August 6, 2020.
- ↑ Data Hypromellose at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on February 20, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b European Pharmacopoeia, 8th edition, 6th supplement, p. 7595. The properties mentioned above refer to the qualities described in the pharmacopoeia monograph with the CAS no. 9004-65-3 and substitution types 1828, 2208, 2906 and 2910, which denote the percentage ratio of methoxy and hydroxypropoxy groups.
- ↑ a b data sheet hydroxypropylmethylcellulose from AlfaAesar, accessed on January 2, 2012 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Entry on hydroxypropylmethylcellulose in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ a b c Hydroxy Propyl Methyl Cellulose - Applications ( Memento from May 4, 2010 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ hydroxypropyl methylcellulose 9004-65-3. In: inhaltsstoffe-kosmetik.de. Retrieved February 20, 2017 .
- ↑ Entry on (hydroxypropyl) methylcelluloses. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 22, 2013.
- ↑ Patent US3065143 : Sustained release tablet. Published November 20, 1962 , Inventors: George L. Christenson, Lamar B. Dale.
- ↑ General Properties of METHOCEL ™ premium cellulose ether. (PDF; 117 kB) (No longer available online.) In: colorcon.com. Archived from the original on April 18, 2016 ; accessed on February 20, 2017 (English). Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Tab. 2, USP substitution type: ( Memento of the original from March 4, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. z. B. 2910, 2906 and 2208.
- ↑ KC Sung, Phillip R. Nixon, John W. Skoug, T. Robert Ju, Ping Gao, EM Topp, MV Patel: Effect of formulation variables on drug and polymer release from HPMC-based matrix tablets . In: International Journal of Pharmaceutics . tape 142 , no. 1 , 1996, p. 53-60 , doi : 10.1016 / 0378-5173 (96) 04644-3 (K4M approx. 95 kDa , K15M approx. 120 kDa, K100M approx. 250 kDa).