Jutiapa Department
| Jutiapa | |
|---|---|
| Location of Jutiapa in Guatemala | |
| Data | |
| Capital | Jutiapa |
| population | 482.200 ( ber . 2016) |
| surface | 3,219 km² |
| Population density | 150 people / km² |
| Highest elevation | 2,104 m |
| ISO 3166-2 | GT-JU |
| Website | Inforpressca.com |
| Coat of arms of the Jutiapa department | |
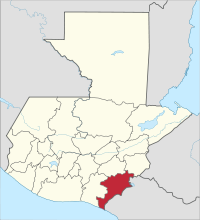
Jutiapa is a department of Guatemala and is located in the southeast of the country (Region IV) on the border with El Salvador . It covers over 3,200 square kilometers and has about 482,200 inhabitants. The capital of the department is the Jutiapa of the same name .
The Jutiapa department is bordered by the Jalapa and Chiquimula departments to the north, El Salvador to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the southwest and the Santa Rosa department to the west .
National nature
Jutiapa is mainly located in the central highlands. Especially in the northwest, the Sierra Madre reaches heights of 2,000 meters again. To the south, the mountain range slopes down to the Pacific coast. The highland area is criss-crossed by deep valleys and rivers. Due to the different altitudes, there is a multitude of different climatic regions. In the highlands the climate is temperate, in the Pacific it is tropical hot.
population
The population speaks mainly Spanish, the few indigenous people also speak Xinka . Jutiapa is divided into seventeen Municipios ( large municipalities or districts ):
| Jutiapa | El Progreso |
| Santa Catarina Mita | Agua Blanca |
| Asunción Mita | Yupiltepeque |
| Atescatempa | Jerez |
| El Adelanto | Zapotitlán |
| Comapa | Jalpatagua |
| Conguaco | Moyuta |
| Pasaco | San José Acatempa |
| Quesada |
As a state administrative district , the department is headed by a governor sent by the central government . The Municipios are independent regional authorities with elected mayors and representatives of the people and are subdivided into Aldeas (rural communities) and Caseríos, Parajes or Fincas ( hamlets and farms ).
economy
Agriculture generated due to the different altitudes a wide range of products, including coffee , potatoes , corn , beans , bananas , plantains , coconuts , cocoa , cassava , tobacco and sugar cane . Also of importance is the horse - and cattle breeding and milk - and cheese production . Tourism only plays a subordinate role. However, the department benefits from through traffic on the three transport axes to El Salvador . Jutiapa has an airfield for general aviation .
Attractions
There are eight volcanoes and a few lakes in Jutiapa, including Lago de Güija on the border with El Salvador. In the southern lowlands are the Mayan ruins of La Nueva and a few poorly developed beaches.
history
In the colonial times, the area of today's department belonged to the Corregimiento de Chiquimula . Jutiapa was elevated to a department on May 8, 1852, but later lost some parts to its neighbors Santa Rosa , Jalapa and Chiquimula . The name Jutiapa comes from a Mayan term that means "cradle of the sun".
Web links
- Overview of the department (Spanish)
Coordinates: 14 ° 17 ′ N , 89 ° 54 ′ W