Diphenyl carbonate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
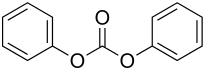
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Diphenyl carbonate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Diphenyl carbonate |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 13 H 10 O 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white odorless scales |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 214.22 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.272 g cm −3 (14 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
76-79 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
301 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
0.014 Pa (at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water (12 mg / l at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Diphenyl carbonate (also known as diphenyl carbonate is) an organic - chemical compound . At room temperature it is a white, almost odorless solid.
Manufacturing
Diphenyl carbonate is obtained industrially by transesterification of dimethyl carbonate with phenol . However, numerous other methods are known with which diphenyl carbonate can be produced, such as the direct oxidative carbonylation of phenol with carbon dioxide or the transesterification of dialkyl oxalates with phenol.
use
Diphenyl carbonate is mainly used in the production of polycarbonates . A transesterification with bisphenol A takes place . This reaction is of particular interest because it avoids the use of the highly toxic phosgene .
Web links
- Entry to diphenyl carbonate . In: P. J. Linstrom, W. G. Mallard (Eds.): NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69 . National Institute of Standards and Technology , Gaithersburg MD
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on diphenyl carbonate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 9, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ OECD : Screening Information Dataset (SIDS) Initial Assessment Report (SIAR) for Diphenyl carbonate , accessed on November 3, 2014.
- ↑ Registration dossier on Diphenyl carbonate (section Vapor pressure ) at the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on June 6, 2017.
- ^ Yong Tae Kim, Eun Duck Park: Transesterification between dimethyl carbonate and phenol in the presence of (NH 4 ) 8 Mo 10 O 34 as a catalyst precursor . Applied Catalysis A: General, 361, 26-31, 2009. doi : 10.1016 / j.apcata.2009.03.029 .
- ↑ Zu-hua Fu, Yoshio Ono: Two-step synthesis of diphenyl carbonate from dimethyl carbonate and phenol using MoO 3 / SiO 2 catalysts . Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 118, 293-299, 1997, DOI: 10.1016 / S1381-1169 (96) 00409-8 .

