Carbonic acid dimethyl ester
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
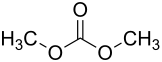
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Carbonic acid dimethyl ester | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 6 O 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with a pleasant odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 90.08 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.07 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
0.5-4.7 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
90 ° C (1016 hPa) |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
53 h Pa (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
139 g l −1 (20 ° C) in water |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.3687 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Dimethyl carbonate or dimethyl carbonate is an organic chemical compound that can be seen as the dimethyl ester of carbonic acid .
Presentation and extraction
Dimethyl carbonate can be obtained in a two-phase reaction by reacting methanol with phosgene or methyl chloroformate in concentrated sodium hydroxide solution . A more modern synthesis is the direct oxidative carbonylation of methanol using carbon monoxide and oxygen in the presence of copper catalysts.
properties
Dimethyl carbonate is a highly flammable, colorless liquid . The compound boils at 90 ° C. under normal pressure. The vapor pressure function results according to Antoine according to log 10 (P) = A− (B / (T + C)) (P in kPa, T in K) with A = 11.7067, B = 2158.837 and C = −153.531 in the temperature range from 310 K to 364 K. The critical point is reached at a temperature T c = 284 ° C and a pressure P c = 48 bar with a critical density of 3.97 mol·l −1 . It has a flash point of 14 ° C and an ignition temperature of 458 ° C. It forms explosive mixtures with air between 4.22 and 12.87% by volume.
use
In a mixture with ethylene carbonate , the compound is used in non-aqueous electrolyte solutions for lithium batteries . In organic synthesis, dimethyl carbonate is used as a methylation reagent . In addition, it is increasingly replacing the very toxic phosgene in the manufacture of polycarbonate plastics. The use as a fuel component is discussed.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on dimethyl carbonate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f g Data sheet: Dimethyl carbonate (PDF) from Merck , accessed on January 19, 2011.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-196.
- ↑ Entry on Dimethyl carbonate in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ H.-J. Buysch, H. Krimm, H. Böhm: EP21211 (Bayer 1979).
- ^ L. Cassar: Chim. Ind. Milan. Volume 72, 1990, p. 18.
- ↑ U. Romano, F Rivetti: European Patent 365 083 A1 (Enichem Synth. 1988).
- ↑ a b Yan Xing, Dongbei Shao, Wenjun Fang, Yongsheng Guo, Tuisen Lin: Vapor pressures and flash points for binary mixtures of tricyclo [5.2.1.0 2.6 ] decane and dimethyl carbonate. In: Fluid Phase Equilibria. Volume 284, 2009, pp. 14-18. doi: 10.1016 / j.fluid.2009.06.002 .
- ↑ WV Steele, RD Chirico, SE Knipmeyer, A. Nguyen: Vapor Pressure, Heat Capacity, and Density along the Saturation Line, Measurements for Dimethyl Isophthalate, Dimethyl Carbonate, 1,3,5-Triethylbenzene, Pentafluorophenol, 4-tert-Butylcatechol , α-methylstyrene, and N, N'-bis (2-hydroxyethyl) ethylenediamine. In: J. Chem. Eng. Data. Volume 42, 1997, pp. 1008-1020. doi: 10.1021 / je970102d .
- ^ MS Ding, K. Xu, TR Jow: J. Electrochem. Soc. Volume 147, 2000, p. 1688.
- ^ Ernest Foy, Joseph B. Farrell, Clement L. Higginbotham: Synthesis of linear aliphatic polycarbonate macroglycols using dimethyl carbonate. In: Journal of Applied Polymer Science. Volume 111, 2009, pp. 217-227, doi: 10.1002 / app.28887 .
