Cross-domed church
The cross-domed church has been a typical form of Byzantine church construction since around the 9th century and is maintained in the entire area of the Orthodox churches to this day. The so-called New Church ( Nea Moni ) in the Imperial Palace of Constantinople, consecrated in 881, is one of the first known large cross-domed churches .
Orthodox cross-domed churches
The naos of a cross-domed church is a square room with four set columns or pillars, which carry four barrel vaults arranged in the shape of a Greek cross and a dome above in the middle . The technical prerequisite for the cross-domed church is the pendent dome . The pendentives, spherical triangles, allow the round dome to be supported by a square made up of four arches. An early and at the same time the most monumental example of the pendent dome is the Hagia Sophia in Constantinople ( Istanbul ), itself not a cross-domed church.
While most churches in the narrower Byzantine-Greek area and also the places of worship of the Apostolic Armenian and Georgian churches have only one dome, churches in the Slavic countries of Southeast and Eastern Europe often have five domes. The secondary domes usually rise above the corner rooms of the building.
The St. Basil's Cathedral in Moscow even has nine domes, with the major side dome are the transepts and the smaller ones on the corners. Inside, the hall under the main dome and the adjoining chancel are surrounded by side rooms.
Cross-domed church without anteroom in Cattolica di Stilo in Calabria, which was still characterized by Byzantine influence in the Middle Ages
Agia Sofia in Thessaloniki with a strong distinction between outdoor and indoor areas
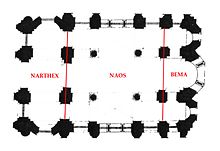
A three-part chancel with one or three apses adjoins the naos, i.e. the space under the (main) dome, to the east, separated by a templon or an iconostasis . The demarcation can be between the two eastern pillars of the square hall, making the community space shorter than it is wide, or at the beginning of the eastern cross arm.
In any case, the area behind the iconostasis is reserved for the priests. Viewed from the naos point of view, these parts lie next to each other. The middle one is the widest and is called Bema. This is where the altar stands and sometimes a bench for the priests. The area north of it is called the prothesis and is used for the preparation of the Lord's Supper. The southeast corner area is called Diakonion and is used to store liturgical books and vestments. On the west side there is mostly a narthex , occasionally with a gallery .
In many churches, the anteroom called the narthex adjoins the square room under the dome to the west . It comprises one yoke (i.e. three vault fields) or two yokes (i.e. six vault fields). Depending on how much the central area is shielded from it, flowing transitions to the basilica are possible, in the sense of an admittedly very short nave. The narthex also has liturgical functions, for example it is used for baptism. Galleries can be located above the narthex, but also in the side arms of the cross.
Larger cross-domed churches, especially in the architecture of Constantinople , often have side chapels and outer porticos . In monastery churches, first in the Megisti Lavra church, built around 1000 on Mount Athos , the naos is often extended by two lateral apses.
Dome hall of Agia Sofia of Thessaloniki
Anteroom of Agia Sofia of Thessaloniki
The Kapnikarea Church in Athens (11th century)
Etchmiadzin Cathedral . Churches with conical domes are typical in Armenia and Georgia
Catholic cross-domed churches
Outside of Orthodoxy , the architectural form of the cross-domed church was occasionally adopted, but without the strict functional division. The best-known example is St. Mark's Basilica in Venice with its five domes. In contrast to most orthodox buildings, the secondary domes also rise above the cross arms. In this context, the domed large churches of southwest France (e.g. the Romanesque cathedrals of Périgueux and Cahors as well as the abbey church of Souillac ) or the traditional building of the Sacré-Cœur de Montmartre should also be mentioned.
Side domes on the arms of the cross: St. Mark's Basilica in Venice
literature
- Dorothea Lange: Theories on the origin of the Byzantine cross-domed church . In: Architectura 16 (1986), pp. 93-113.