List of flag signs in motorsport
The list of flag symbols in motorsport describes the flag symbols required in motorsport . These are used for communication on racetracks between the race management, the sports officials and the participants.
The flag signs are used by the race management and the sports officials to warn the participants of dangerous situations or to intervene in the run. In addition, the flag signs from vehicles can be shown to the race control, for example to block or unblock the track, or in the lead vehicle. The flags are held still or waved, shown individually or doubled or supplemented by boards with further information or light signals.
The wrong term flag is often used in this context , although the flags are used for signaling .
The use of the flags is decided independently by the trained sports warden based on the acute situation. In Formula 1 , the flag signs are now instructed directly from the race management and simultaneously transmitted electronically to the driver's cockpit. Alternatively, reflective signs or, in Formula 1, so-called electronic flags are used at night races. "Light panels" are also being used more and more in motorsport, where the flag symbols are displayed via a light display. These can be served directly by the race management as well as by the marshals at their posts.
The route safety regulations are set by the respective national sports associations, i.e. the carriers of national sports sovereignty in motorsport. National sports sovereignty is exercised in Germany by the German Motor Sport Federation , in Austria by the AMF and in Switzerland by Auto Sport Switzerland and the Swiss Federation of Motorcyclists .
Although there are international regulations in automobile and motorcycle racing, the sports associations can define different regulations and determine their own flag symbols or other uses of the flags.
history
In 1899, in the early days of motorsport, flags were already being used by race management to communicate with drivers. The red flag and the yellow flag , which are still valid today, were used here.
In the first automobile magazine in the world, The Horseless Age , the invitation to tender for the Paris – Madrid trip was printed in the motor sport year 1903 and the flag symbols specified by the organizer were described there. The “yellow flag” marked a mandatory stop at the Paris-Madrid race in 1903, and the “blue flag” a dangerous point that was slower to pass.
In the 1906 Grand Prix season at the Vanderbilt Cup in Long Island, the race was flagged with a black and white checkered flag.
Circuit racing
The flags in Germany, Austria and Switzerland correspond to the guidelines of the FIA and the FIM. In Germany, the DMSB flag symbols are defined in Appendix H of the International Sports Act (automobile) or the general provisions for street sports (motorcycle).
The colors of the flags are determined according to the Pantone color scale:
The flags are at least 60 cm × 80 cm, the red flag and the checkered flag at least 80 cm × 100 cm. In Formula 1, since the 2007 season, the flags have been directed and controlled directly by the race management and also displayed directly on the Formula 1 steering wheel of the participants. The DTM introduced a similar system in the 2012 season , this is called the Marshalling System here .
| flag | Location | use | meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
 National flag |
race management only | reduce |
If the race is started with the national flag , the start takes place when the starter lowers the flag. Alternatively, the race can be started with a traffic light countdown, which is mandatory in Formula 1. (Colloquially, this flag is called the start flag .) |
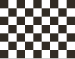 |
race management only | panned | The practice, qualifying or race ends with the checkered flag , the flag is shown to the leader and all following participants. No overtaking applies in the run-out lap. |
 |
race management only | Held still with start number |
A driver is warned that his car has a technical problem and that he will have to pull into the pits on the next lap. This flag is shown together with the respective start number. (Colloquially this flag is called a fried egg ) |
 |
race management only |
Held still with start number |
A participant will be cautioned for unsportsmanlike conduct. This flag is shown together with the respective start number. (Colloquially, this flag is called the Rüpelflagge .) |
 |
race management only |
Held still with start number |
The participant is excluded from the race and has to go to the pits immediately. This flag is shown together with the respective start number. |
 |
entire route |
panned |
Interruption or termination of the training or the race. After completing 75% of the total distance or duration, the race is deemed to have ended and will not be restarted. The flag is shown first at the start and finish and only when instructed by the race management. The speed must be reduced and overtaking is prohibited. The pit is approached during training; stopped at the Red Flag Line in the race . |
 SC VSC |
entire route |
swiveled with SC / VSC shield or FCY shield if necessary |
No passing! Attention danger! Two flags waved: Great danger, the route may be partially or completely blocked or there are safety officers on the route. Be ready to stop! In some racing series, the double yellow flag also includes a speed limit, e.g. B. 120 km / h in the 24-hour race on the Nürburgring . If the Safety Car (partly virtual since 2016) is on the track, this is indicated next to the yellow flag by showing a white sign or a digital display with black SC or VSC for Virtual Safety Car. In the case of the VSC, the drivers have to adhere to specific sector times independently. Full Course Yellow (FCY): There is a speed limit on the entire route. Is shown on the instructions of the race management, usually after a countdown, and the driver is displayed in the cockpit. A speed limiter is activated in the racing cars automatically and at the same time. At certain racing events, these can also be shown over a certain section of the route - so-called slow zones . A speed limit applies in these areas and is lifted at the end of the slow zone with the green flag. |
 |
entire route |
panned motorcycle: held still |
End of danger and no overtaking. Free ride! During the start procedure: Behind the starting grid, a sports steward shows the starter with the green flag that the entire field is ready and the start can take place. |
 |
entire route |
panned | Signals to a driver who is being lapped that a faster vehicle is approaching that must be allowed to pass. |
 |
entire route |
panned | Attention, there is a significantly slower vehicle on the route. |
 |
entire route |
kept still |
The route is slippery (oil, sand or rain). This flag is shown for at least 4 rounds. (Colloquially, this flag is called the oil flag .) |
 |
entire route |
kept still | Only in automobile races: 60 km / h speed limit, no overtaking! The use can be announced by the tender and can replace the use of a safety car. The flag is shown on the instructions of the race management, usually at the same time as the yellow flag. |
 |
entire route |
kept still | For motorcycle races only: Ambulance service or a doctor are on the route. The flag is shown together with the yellow flag . |
After the stewards' decision, the black flag indicates to the driver that he has to drive to the pits or to a certain place.
Examples
Formula 1 starting lights
A race can be started by lowering the national flag, alternatively the race can be started by a traffic light countdown. In Formula 1, the traffic light start is mandatory.
| Light sign | meaning |
|---|---|
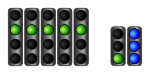 |
Practice is open, the pit lane is open. A blue light signal warns exiting participants of approaching vehicles on the route. |
 |
The training is canceled, the pit lane is closed. |
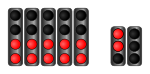 |
The training is over, the pit lane is closed. |
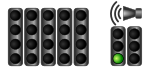 |
Starting grid: 30 minutes until the start of the introductory lap, the pit lane is open. A beep will sound 17 minutes before the introductory lap. |
 |
Countdown introduction round:
|
 |
Behind the starting grid, a sports attendant shows the starter with the green flag that the entire field is ready and the start countdown can begin.
Start countdown:
|
 |
Race abort: Red lights and flashing yellow lights signal the participants that the race has been aborted. |
Flag signals at night
In 2008, with the first night race of Formula 1 at the Singapore Grand Prix, “electronic flags” were introduced. Since these light panels have the same meanings as the conventional flag signals, the displays are also called digital flags ; the English brand name Digiflag is also often used. The digital flag symbols have been used in all Formula 1 races since 2011.
The light signals replace the waved red, yellow, green, blue and white flags. They must blink at a frequency of 3 to 4 Hertz and go on and off without delay. The luminosity must be designed so that the colors can be clearly seen even in sunlight from 250 meters at an angle of 70 degrees. The back plate must be matt black and the colors displayed must be sufficiently clear. The electronic flags are implemented with light-emitting diodes due to the requirements for brightness, clear color and switching speed .
Certain light signals can be activated by the sports attendant, some are controlled directly from the race management. The current light signal is also passed on to the following marshals.
If necessary, additional electronic flag symbols, such as the yellow flag with red stripes, can be defined in the event advertisement .
At other events, reflective boards are used; these must be highly reflective.

| Light sign | reflective board |
meaning |
|---|---|---|
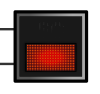 |
 |
Interruption or termination of the training or the race. After completing 75% of the total distance or duration, the race is considered to be over and will not be restarted. The flag is only shown at the start and finish and only when instructed by the race management. The speed must be reduced and overtaking is prohibited. The pit is approached during training; stopped at the Red Flag Line in the race . (The light signal can only be activated by the race management; the board is shown on the instructions of the race management.) |
 |
 |
No passing! Great danger, the route may be completely or partially blocked. Be ready to stop! |
 |
 |
Safety car phase, no overtaking applies. |
 |
 |
Formula 1 only, from 2015: Virtual Safety Car phase , the previously set speed limit and overtaking ban apply in the section of the route. No Safety Car is used at VSC. |
 |
 |
End of danger and no overtaking. Free ride! |
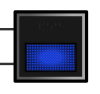 |
 |
Signals to a driver who is being lapped that a faster vehicle is approaching that must be allowed to pass. A faster vehicle starts to overtake. It is to be let past immediately. If the blue flags are ignored three times, a drive-through penalty is due. (Can only be activated by the race management.) |
 |
 |
Attention, there is a significantly slower vehicle on the route. |
 |
 |
Attention, changed road surface, risk of slipping. (will be announced in the event announcement if required) |
Karting
In kart racing, the following flag can be used in addition to the flag symbols for circuit races:
| flag | Location | use | meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
race management only | Held still with start number |
The race is over for lapped participants. The use must be announced in the tender. |
In karting, the waving of the black flag stands for the disqualification of the participant. It is shown in connection with the start number.
Rallying
In rally sport according to the DMSB route safety regulations of 2019, only the yellow and green flags are used on the route, and the red flag is also used at the main radio post. The leader of the special stage (WP leader) only uses the red and green flags .
Hill climb
In the event of imminent danger, a hill climb will not be aborted, only those participants who are on the route will be stopped with the red flag .
The other flags have the same meaning as in circuit racing, with no use of the different black flags.
Rail sports
In track sports, the motorcycle participants are shown the last lap with a yellow flag with black stripes .
| flag | Location | use | meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
race management only | kept still | In the last round, the participants are shown the yellow flag with a 5 cm wide black diagonal stripe . |
National characteristics
Isle of Man
With the Isle of Man TT , additional flags are used for weather signaling due to the typical weather of the British Isles .
| flag | Location | use | meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
entire route |
kept still | Damp or wet areas in this section of the route reduce the road grip. |
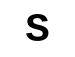 |
entire route |
kept still | In this section of the route there is a risk of blinding sun. This flag can also be labeled with the word "SUN". The "S" stands for the English word "Sun", and means "sun". |
 |
entire route |
kept still | In this section of the route, visibility is restricted (e.g. due to fog). The "V" stands for the English word "Visibility" and means "visibility". |
United States

Nationally defined flag symbols are used in the US series NASCAR and IndyCar .
As a special feature, no changes may be made to the cars after showing the red flag; In contrast, the rules of the Red Flag Line apply in the FIA area .
literature
- Deutscher Motor Sport Bund (Ed.): Handbuch 2012. Automobilsport / Kartsport . Deutsche Motor Sport Wirtschaftsdienst, Frankfurt am Main 2012.
- Deutscher Motor Sport Bund (Ed.): Handbuch 2012. Motorradsport . Deutsche Motor Sport Wirtschaftsdienst, Frankfurt am Main 2012.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ Anthony Harding: The Guinness Book of Car. Facts & Feats . 3. Edition. Jarrold and Sons, Norwich 1980, ISBN 0-85112-207-8 , pp. 51 .
- ^ Rules of the Paris – Madrid Race . In: The Horselass Age (today: Automotive Industries) . No. 11 , 1903, pp. 349-351 .
- ↑ Appendix H to the international sports law , PDF file [555.9 KB], DMSB homepage, accessed on December 5, 2012.
- ↑ Motorcycle Sports Handbook 2012 - General Regulations for Street Sports , PDF file, Part II, page 3, accessed on December 5, 2012.
- ↑ DTM sporting regulations 2012, flag signs / signaling , PDF file, page 47, DMSB homepage, accessed on May 8, 2012.
- ↑ Flag signals ignored: flood of penalties in Suzuka , motorsport-total.com of October 22, 2011, accessed on January 30, 2012.
- ↑ VLN: New double yellow regulation - 120 instead of 60 km / h. Retrieved July 9, 2019 .
- ↑ Appendix H of the International Sports Act ( Memento of June 27, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF file)
- ↑ Recommended light signals for standing starts in circuit events , PDF file, FIA homepage, accessed on January 17, 2012.
- ^ Night race in Singapore with glowing flags , Focus Online from September 23, 2008, accessed on November 3, 2011.
- ↑ Digi-Flags in Singapore , auto-motor-sport.de of April 17, 2008, accessed on November 3, 2011.
- ↑ 2015 F1 Sporting Regulations of January 8, 2015, FIA homepage, accessed on January 25, 2015.
- ↑ Flag signs and signals in karting - racing 2011 (PDF file)
- ↑ ̈ Austrian Automobile Hill Climbing Championship 2011 - event data sheet , PDF file, accessed on February 2, 2012.
- ↑ DMSB_Reglement_fuer_Bergrennen_2011 , PDF file, DMSB homepage, accessed February 2, 2012.
- ↑ FIM standards for race tracks in rail sports (PDF; 3.1 MB), page 19, DMSB homepage, accessed on February 13, 2012.
- ↑ 2012 International Isle of Man Tourist Trophy Races - Regulations ( Memento June 15, 2012 in the Internet Archive ), cdn.iomtt.com, page 17, accessed on February 13, 2012.
- ↑ Flags of NASCAR , NASCAR Homepage, accessed November 3, 2011.