m -xylylenediamine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
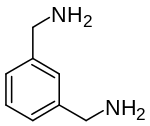
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | m -xylylenediamine | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 12 N 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless to yellowish liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 136.20 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.052 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
14.1 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
247 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
4 Pa (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
miscible with water |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.5718 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
Switzerland: 0.1 mg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
m -Xylylenediamine is a chemical compound that is used in the manufacture of plastics.
Manufacturing
m -Xylylenediamine can be produced by reducing m -benzenedicarbonitrile with hydrogen in the presence of ammonia using a cobalt catalyst.
properties
The spectroscopic data of m -xylylenediamine are given in the literature.
use
Similar to the phenylenediamines , m -xylylenediamine is also used as a crosslinker for epoxides and for the production of polyurethanes. The thermoset made from bisphenol A diglycidyl ether cross-linked with m- xylylenediamine has such advantageous properties that it is used as a material in construction and automotive engineering.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on m-phenylenebis (methylamine) in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 23, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ CDC: NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards - m-Xylene-alpha, alpha'-diamine , accessed April 14, 2015.
- ↑ R. Brömme: About some amido derivatives of m-xylene . In: Reports of the German Chemical Society . 21, No. 2, 1888, pp. 2700-2706. doi : 10.1002 / cber.18880210292 .
- ↑ Galperin et al. J. Appl. Chem. USSR (Engl. Transl.), 1971, 44, pp. 403, 396, 397.
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 1477-55-0 or M-xylylenediamine ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ a b Patent US4482741A : Preparation of xylylenediamine. Published November 13, 1984 , Inventor: Paul R. Kurek.
- ↑ Xinzhi Chen, Zhou Shaodong, Chao Qian: hydrogen transfer reduction of nitriles in DBU based ionic liquids . In: Arkivoc . 2012, No. 8, 128-136, pp. 128-136. doi : 10.3998 / ark.5550190.0013.812 .
- ↑ Albert Jeyakumar, Han Goossens, Bart Noordover, Manoranjan Prusty, Matthias Scheibitz, Cor Koning: Polyamide-6,6-based blocky copolyamides obtained by solid-state modification . In: Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry . 51, No. 23, December 1, 2013, pp. 5118-5129. doi : 10.1002 / pola.26944 .
- ^ Ha Q. Pham, Maurice J. Marks: Epoxy Resins . In: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry . September. doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.a09_547.pub2 .
- ↑ Patent US3379683 : Polyurethanes prepared from m-xylylenediamine.
- ↑ F. Fragaa, C. Castro-Dı́aza, E. Rodrı́guez-Núñeza, JM Martı́nez-Ageitos: Physical aging for an epoxy network diglycidyl ether of bisphenol A / m-xylylenediamine . In: polymer . 44, No. 19, September 2003, pp. 5779-5784. doi : 10.1016 / S0032-3861 (03) 00624-4 .

