N -hydroxysulfosuccinimide sodium salt
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| Structural formula of the sodium salt without stereochemistry | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide sodium salt | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 4 H 4 NNaO 6 S | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white solid or light yellow powder |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 217.13 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
250 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water and organic solvents, such as. B. N , N -dimethylformamide |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
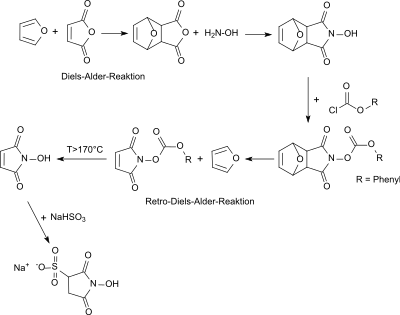
N -hydroxysulfosuccinimide sodium salt (sulfo-NHS) is the additionproductof N -hydroxymaleimide and sodium hydrogen sulfite NaHSO 3 formedby hydrolysis in aqueous solution from sodium disulfite Na 2 S 2 O 5 .
Like N -hydroxysuccinimide , 1-hydroxybenzotriazole or 1-hydroxy-7-azabenzotriazole , sulfo-NHS is suitable for the formation of so-called amine-reactive active esters with carboxylic acids or protected amino acids for the modification, immobilization and cross-linking of peptides and proteins .
Manufacturing
The original synthesis of sulfo-NHS from the N -hydroxymaleimide, which is only accessible in several steps, is very time-consuming (> 50 days) and only gives modest yields (25–28% based on the starting material maleic anhydride ). Even after laborious purification by repeated recrystallization, an amorphous target product contaminated with 3 to 5% sulfosuccinimide sodium salt is obtained.
The direct synthesis from N -hydroxymaleimide and sodium disulfite also evidently only gives a contaminated and very hygroscopic N -hydroxysulfosuccinimide sodium salt.
A more direct access to sulfo-NHS enables the reaction of sulfosuccinic acid via the sodium salt of sulfosuccinic anhydride with hydroxylamine to form the sodium salt of sulfosuccinic acid monohydroxamic acid, which cyclizes with acetic anhydride to form N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide sodium salt.
Instead of using the sodium salt of sulfosuccinic anhydride, sulfo-NHS can also be produced by reacting sulfosuccinic acid diesters with hydroxylamine. The synthesis route starting from sulfosuccinic acid leads to sulfosuccinimide-Na-free sulfo-NHS as a racemic mixture .
properties
N- hydroxysulfosuccinimide sodium salt is usually obtained in the synthesis as an amorphous, pale yellow, hygroscopic solid. After recrystallization from 20% acetic acid , it is obtained as a white, crystalline substance. Sulfo-NHS is present in water and in polar organic solvents such as e.g. B. DMF soluble.
Applications
How N -hydroxysuccinimide with carboxylic acids with elimination of water by carbodiimides , such as. B. 1-ethyl-3- (3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide (EDC) can be converted to the NHS active ester, then N- hydroxysulfosuccinimide sodium salt reacts to form the analogous sulfo-NHS ester. Aktivester form with primary amino groups (for. Example, of lysine side chains in proteins), in high yields carboxamides and have, particularly in biochemistry for the synthesis of peptides and chemical cross-linking of proteins useful.
The activation of carboxylic acids before the reaction with N- hydroxysuccinimide sodium salt can also be carried out by reaction with triphosgene . Sulfo-NHS active esters are obtained quickly under mild conditions and in high yields.
The sulfo-NHS active esters, which are quite stable in anhydrous form at 4 ° C., can be isolated and the amidation can thus be carried out in two separate reaction steps.
The activation reaction of EDC and N- hydroxysulfosuccinimide sodium salt is preferred at a weakly acidic pH (pH 4.5-7.2), while the amidation proceeds best at a physiological pH of 7-8.
While activation with NHS leads to less water-soluble active esters, sulfo-NHS active esters are more water-soluble and much more polar due to the very hydrophilic sulfonic acid group , which means that they no longer penetrate biomembrane. As a result, primary amino groups on proteins on the outer surface of membranes can be selectively modified under physiological conditions.
With dual functional output compounds, e.g. B. α, ω- dicarboxylic acids , arise so-called homo-bifunctional sulfo-NHS-ester as the cross-linking spacer ( English spacer ) in which the number of methylene groups determined the length of the spacer between the carboxyl end groups.
So-called heterobifunctional crosslinkers can be obtained from doubly functional starting compounds with different types of end groups, which in addition to the amine-reactive sulfo-NHS group at one end of the molecule have a sulfhydryl-reactive maleimide group at the other end of the molecule.
With such coupling reagents, sequential linking reactions with different functional groups can be carried out.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c data sheet N-Hydroxysulfosuccinimide sodium salt at Acros, accessed on November 24, 2018.
- ↑ a b Data sheet N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide sodium salt from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 17, 2015 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Uptima, NHS / sulfo-NHS
- ↑ CW Lim, HT Le, JH Han, D.-H. Kim, JG Jang, TW Kim: New water-soluble alkynylating agent for cell surface protein: sulfosuccininimidyl-4-pentynoate (Supporting Information) . In: Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. tape 34 , no. 6 , 2013, p. 1895-1898 ( kcsnet.or.kr ).
- ^ A b Thermo Scientific, Crosslinking Technical Handbook .
- ↑ a b J.V. Staros: N-Hydroxysuccinimide active esters: Bis (N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide) esters of two dicarboxylic acids are hydrophilic, membrane-impermeant protein cross-linkers . In: Biochemistry . tape 21 , no. 17 , 1982, pp. 3950-3955 , doi : 10.1021 / bi00260a008 .
- ↑ PA Huber, Development of photoactivatable fluorescent reagents for marking hydrophilic intracellular phases , dissertation ETH-Zurich, 1986, p. 33, PDF
- ↑ Patent US5892057 : Preparation of sulfo-N-hydroxysuccinimide salts. Filed September 18, 1997 , published April 6, 1999 , Applicant: Pierce Chemical Co., Inventor: MC Wilkes, ML Bremmer.
- ↑ Patent US5872261 : Preparation of sulfo-N-hydroxysuccinimide salts with intermediate formation of diester. Filed September 18, 1997 , published February 16, 1999 , Applicant: Pierce Chemical Co., Inventor: ML Bremmer, MC Wilkes.
- ↑ M. Kim, K.-J. Han: Convenient synthesis of N-hydroxysuccinimide esters from carboxylic acids using triphosgene . In: Synth. Commun. tape 39 , no. 24 , 2009, p. 4467-4472 , doi : 10.1080 / 00397910902906628 .
- ↑ Thermo Scientific, Instructions: NHS and Sulfo-NHS ( Memento of the original from May 28, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ JV Staros, RW Wright, DM Swindle: Enhancement by N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide of water-soluble carbodiimide-mediated coupling reactions . In: Anal. Biochem. tape 156 , no. 1 , 1986, pp. 220-222 , doi : 10.1016 / 0003-2697 (86) 90176-4 .
- ↑ Z. Grabarek, J. Gergely: Zero-length crosslinking procedure with the use of active ester . In: Anal. Biochem. tape 185 , 1990, pp. 131-135 , doi : 10.1016 / 0003-2697 (90) 90267-D .