Sodium picosulfate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
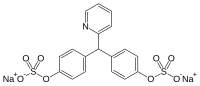
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Sodium picosulfate | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 18 H 13 NNa 2 O 8 S 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
White to almost white, crystalline powder |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 481.41 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
272–275 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
slightly soluble in water, poorly soluble in ethanol 96% |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Sodium picosulphate is a medicinal substance and belongs to the class of laxatives . It can be used for a short time in the case of constipation and diseases that require easier bowel movements .
The desired effect occurs approximately 6 to 12 hours after oral administration.
Mechanism of action
The mechanism of action of sodium picosulfate is the same as that of bisacodyl . It differs from the latter in that sodium picosulfate does not pass through the enterohepatic cycle . Therefore, the action of sodium picosulfate occurs more quickly.
In the large intestine , sodium picosulfate, similar to bisacodyl, is converted by intestinal bacteria into free diphenols, which are the actually active substance.
Side effects
The long-published electrolyte shifts in the serum could not be observed even after decades of use; habituation occurs only very rarely, even after years of use. The motor effect can lead to cramp-like abdominal pain.
The use of suppositories containing sodium picosulfate can cause pain and bleeding in the rectum area .
Trade names
Agaffin laxative gel, coated tablets and drops (A); Agiolax Pico laxative lozenges (D); Agiopic laxative lozenges (A); Darmol Pico tablets (D); Dulcolax NP drops (D); Dulcolax Picosulfate and Pearls (CH); Fructines (CH); Guttalax drops and pearl capsules (A); Laxasan (CH); Laxans Drops (D), Laxasan Drops (A); Laxoberal laxative pearls, tablets and drops (D); Laxoberon (CH); Regulax laxative cube picosulfate and picosulfate drops (D); Generics (D)
CitraFleet (with magnesium oxide ) (D); PICOPREP (with magnesium oxide) (D)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Data sheet SODIUM PICOSULFATE CRS (PDF) at EDQM , accessed on April 12, 2009.
- ↑ a b Entry on sodium picosulfate. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 10, 2014.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Technical information for Dulcolax ® Picosulfat Drops from BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM in the Swiss Medicines Compendium ® - October 16, 2008.
- ↑ awmf.org: S2k guidelines for chronic constipation: definition, pathophysiology, diagnostics and therapy ( memento of the original dated August 22, 2017 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF; 588 kB); Status: February 2013.