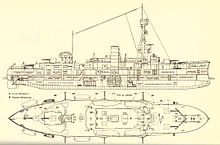
Niels Juel (ship, 1923)
|
|
|
|---|---|
 The NIELS JUEL |
|
| Overview | |
| Type | School cruiser |
| Shipyard | |
| Order | 1913 |
| Keel laying | 1914 |
| Launch | July 3, 1918 |
| Commissioning | May 23, 1923 |
| Whereabouts | August 29, 1943 ran aground after a German air raid, sunk on May 3, 1945, wrecked under water in 1952/53 |
| Technical specifications | |
| displacement |
3400 t |
| length |
89.95 m over everything |
| width |
16.3 m |
| Draft |
5.2 m |
| crew |
329 men |
| drive |
4 Yarrow boilers , |
| speed |
16 kn |
| Range |
5800 nm at 10 kn |
| Armament |
10 × 150 mm Krupp guns, |
| Fuel supply |
240 tons of oil, 250 tons of coal |
| Armor side armor deck |
|
The cadet training ship (Danish: Artilleriskib) Niels Juel was planned as a coastal armored ship for the Danish Navy . It was completed as a school cruiser after a very long construction period. The ship was named after the Danish admiral Niels Juel (1629–1697). The Niels Juel became known through a battle in the Isefjord with German aircraft on August 29, 1943, which prevented the ship from escaping from the German sphere of influence to Sweden.
In 1944 and 1945 the ship was called Nordland in service with the German Navy .
Building history
Ordered before the First World War , the Niels Juel was to be an improved version of the last-built coastal armored ship Peder Skram . However, the originally planned main armament with two 24 cm twin turrets no longer seemed up-to-date when the order was placed. The Danish Navy therefore ordered two 30.5 cm Krupp cannons in single turrets. As middle artillery, eight 10.5 cm guns were to be placed in casemates on top of each other.
Already laid down in 1914, the First World War delayed the completion of the ship because the planned weapons were not delivered by Krupp during the war. Niels Juel was therefore only launched in 1918 and put into service on May 23, 1923. After a frigate that was in service from 1856 to 1879, she was the second ship in the Danish Navy to bear the name of the Norwegian-Danish admiral, whose most significant victory was the sea battle in Køgebucht (1677) , which eliminated the Swedish fleet . The construction of the Niels Juel was significantly changed, as no heavy cannons were installed. The result was a kind of slow cruiser with ten 15 cm cannons in single line-up. Six cannons were set up to the side of the superstructure, the two stern guns stood at the rear on the midship line, and two guns stood side by side on the foredeck. Due to the long construction time, the construction was already out of date when it was commissioned, but appeared suitable as a yacht and training ship.
Use in the Danish Navy
The Niels Juel served, among other things, as a fleet flagship , training ship and escort ship on sea voyages of the Danish king. When she entered service, the Danish Navy still had four coastal armored ships: the Peder Skram , the Olfert Fischer (in service until 1936), Herluf Trolle (in service until 1932) and in reserve the Skjold (sold in 1929).
In 1923 the Niels Juel made her first trip abroad to the Faroe Islands , to Bergen , Leith and Gothenburg . A trip to South America followed from October 22, 1923 to March 1, 1924. Then she was used at the artillery school and in the maneuver squadrons. In 1925 the Niels Juel was the flagship of a Danish fleet association that visited Helsinki , Tallinn and Riga . The association also included the cruisers Gejser and Hejmdal , the mine- layer Lossen , the submarines Bellona , Flora and Rota and the torpedo boats Hvalrossen , Delfinen and Sværdfisken . From June 3 to June 27, 1926, Niels Juel visited the Faroe Islands again with King Christian X. and Finland in 1928 and the Faroe Islands and Iceland in 1930 . In 1931, as a cadet training ship, she made a voyage into the Black Sea as the first Danish warship and visited Odessa .
During the occupation of Denmark on April 9, 1940, the ship was in Copenhagen . There was no fighting.
Until August 29, 1943, the ship was used to train crews in the Danish Navy. The fully manned since June 28, 1943, Niels Juel was ordered on the morning of August 29, 1943 off Holbæk to seek out Swedish waters. At the height of Hundested there was a fight with German aircraft. The ship's flak hit one of the attackers, but could not prevent the power supply and both fire control systems from being destroyed by the bombing. At the time the ship was built, it was not yet possible to imagine a massive aerial bombing and secure the hull against it. According to unconfirmed reports by observers ashore, another German plane was allegedly shot down. Due to the failure of the fire control systems, the Niels Juel was practically incapacitated; she was grounded by her own crew on the orders of her commander, Kommandørkaptajn Westermann. Guns and machines were made unusable and finally the flag was brought down. There had been one dead and four seriously injured on board.
Use as Nordland
After being put down in the Isefjord, the ship was salvaged on behalf of the German Navy , repaired and put into service as the training ship Nordland in September 1944 . The 15 cm cannons were delivered on land for use with coastal batteries. Three former 10.5 cm submarine cannons, four 3.7 cm anti-aircraft guns and two 2 cm quadruple anti-aircraft guns came on board as new armament. The Nordland served as a training ship in the Baltic Sea. On February 18, 1945, she ran with 500 refugees on board from Stolpmünde to Kiel , where she arrived safely two days later. On 3 May 1945 she was in the Eckernförde Bay by its German crew scuttled in position 54 ° 28 ' N , 9 ° 58' O to not having to hand them over to the victorious powers.
Two crews of the Niels Juel prevented the enemy from taking over the operational ship during the war - the Danes by sinking on August 29, 1943, the German crew by scuttling on May 3, 1945.
The wreck was dismantled underwater by divers in 1952/53 and the sections were sold as scrap. Only the keel and the ship's bottom remain at the sinking site to this day.
Renewed use of the name
From 1978 to 1982 the Danish Navy received three corvettes of the Niels Juel class (1320 ts), including the type ship Niels Juel (F 354). These corvettes were decommissioned in 2009.
The current Niels Juel (F 363) is an Iver Huitfeldt- class frigate (6600ts).
literature
- Hans H. Hildebrand / Albert Röhr / Hans-Otto Steinmetz: The German warships: Biographies - a mirror of naval history from 1815 to the present , Koehlers Verlagsgesellschaft, Herford,
- Jürgen Rohwer , Gerhard Hümmelchen : Chronicle of the naval war 1939-1945. Manfred Pawlak Verlag, Herrsching 1968, ISBN 3-88199-009-7 .
- Weyers Taschenbuch der Kriegsflotten 1941/42 , JF Lehmann Verlag, Munich (1941)
Web links
- The Niels Juel at navalhistory.dk (Danish)
Footnotes
- ^ Photo of Niels Juel arriving in Helsinki
- ↑ Photo of the Hejmdal arriving
- ^ Rohwer, p. 379.
- ↑ Hildebrandt, Vol. VII, p. 56.