Nura
|
Nura Нұра, Нура |
||
|
Nura in the middle |
||
| Data | ||
| location | Karagandy , Aqmola ( Kazakhstan ) | |
| River system | Nura | |
| source |
Kysyltas -Gebirge 49 ° 20 '24 " N , 74 ° 44' 4" O |
|
| Source height | approx. 900 m | |
| muzzle |
Tengissee coordinates: 50 ° 30 '55 " N , 69 ° 11' 54" O 50 ° 30 '55 " N , 69 ° 11' 54" O |
|
| Mouth height | 305 m | |
| Height difference | approx. 595 m | |
| Bottom slope | approx. 0.61 ‰ | |
| length | 978 km | |
| Catchment area | 60,800 km² | |
| Discharge at the Sergiopolskoye gauge (Ghabiden Mustafin) A Eo : 12,300 km² |
MQ Mq |
11.42 m³ / s 0.9 l / (s km²) |
| Discharge at Nur-Sultan (Romanovka) A Eo gauge: 54,938 km²
|
MQ Mq |
51.04 m³ / s 0.9 l / (s km²) |
| Discharge at the Tengissee gauge (Almas) A Eo : 78,080 km²
|
MQ Mq |
28.39 m³ / s 0.4 l / (s km²) |
| Left tributaries | Sherubai Nura | |
| Big cities | Temirtau , Nur-Sultan | |
| Medium-sized cities | Shakhtinsk | |
| Communities | Ghabid Mustafin | |
|
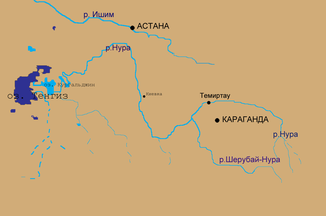
Course of the river Nura ( Нура ) to the Tengissee ( Тенгиз ) |
||
The Nura ( Kazakh Нұра ; Russian Нура ) is a river in Kazakhstan .
River course
It rises in the region Karaganda on the western edge of the Kysyltas -Gebirges and flows east to west through the Kazakh Uplands . A characteristic of the catchment area is the pronounced lack of precipitation. This explains why the majority of the annual runoff (90% and more) occurs in a flood-like manner in a short period of snowmelt. In summer, autumn and winter, on the other hand, the runoff is significantly reduced; in summer the upper reaches usually dry out completely. In years with high rainfall, the nura can carry up to 200 times more water than in dry years.
River length
On the southwestern outskirts of the Kazakh capital Nur-Sultan , the Nura reaches an average water flow of approx. 51 m³ / s, before water is channeled from the Nura into the Ischim / Jessil in Nur-Sultan via the Nura-Ishim Canal , to reduce its water flow increase and ensure the water supply of the capital. Shortly thereafter, the old Sarkyrama (Russian Саркырама) arm of the river, running northwest to the Jessil, branches off from the Nura, a little further west the river flows into an inland delta , which is also a bifurcation , in which about another third of the water over the to The north meandering Kosykosch (Russian: Козыкош) flows towards the Jessil, while the rest of the river continues to flow about 200 kilometers to the south-west without any major tributaries and after a total of 978 kilometers flows into the drainless Tengissee with a water flow of just over 28 m² / s .
Mercury pollution
In the second half of the twentieth century, 300 to 1000 tons of mercury were discharged from the “Carbide” chemical plant in Temirtau into the Nura, which was used as a catalyst in chemical production. In some sections of the river, the consumption of caught fish is therefore discouraged because of the likely exposure to mercury.
Since 2001 the river has been cleaned of mercury deposits on the initiative of the government of Kazakhstan; The project is co-financed by Kazakhstan and the World Bank . Between 2004 and 2006, among others, the Austrian company Posch & Partner was involved in river cleaning.
places
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Article Nura in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia (BSE) , 3rd edition 1969–1978 (Russian)
- ↑ Nura at the Sergiopolskoye gauge - hydrographic data from R-ArcticNET
- ↑ Nura At Sergiopolskoye. In: www.r-arcticnet.sr.unh.edu. Retrieved January 19, 2017 .
- ↑ The catchment areas and water network of Nura and Ischim. In: National Integrated Water Resource Management and Water Efficiency Plan for Kazakhstan. UNDP (United Nations Development Program), February 15, 2017, accessed February 15, 2017 (Russian).
- ↑ In Kazakhstan: Eliminating Mercury and Controlling Floods . In: World Bank . ( worldbank.org [accessed October 20, 2016]).
- ↑ Posch & Partner: River Nura renovation project. In: www.pap.co.at. Retrieved October 20, 2016 .