Cresols
| Cresols | |||||
| Surname | o -Cresol | m -Cresol | p -cresol | ||
| other names | 2-methylphenol 2-hydroxytoluene |
3-methylphenol 3-hydroxytoluene |
4-methylphenol 4-hydroxytoluene |
||
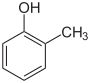
| Structural formula |
|

|
|
||
| CAS number | 95-48-7 | 108-39-4 | 106-44-5 | ||
| 1319-77-3 (mixture of isomers) | |||||
| PubChem | 335 | 342 | 2879 | ||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 8 O | ||||
| Molar mass | 108.14 g mol −1 | ||||
| Physical state | firmly | liquid | firmly | ||
| Brief description | colorless to yellowish crystals or liquid with a pungent, tarry odor |
||||
| Melting point | 31 ° C | 10.9 ° C | 34.8 ° C | ||
| boiling point | 191 ° C | 203 ° C | 202 ° C | ||
| pK s value | 10.28 | 10.09 | 10.26 | ||
| density | 1.05 g cm −3 | 1.03 g cm −3 | 1.03 g cm −3 | ||
| solubility | 25.0 g l −1 (25 ° C) | 23.5 g l −1 (20 ° C) | 20.0 g l −1 (20 ° C) | ||
|
GHS labeling |
|
||||
| H and P phrases | 301-311-314 | ||||
| no EUH phrases | |||||
| 201-280-301 + 310 + 330-303 + 361 + 353-304 + 340 + 310-305 + 351 + 338 | |||||
| MAK | Switzerland: 5 ml m −3 or 22 mg m −3 | ||||
In chemistry, the cresols (also hydroxytoluenes or methylphenols ) form a group of aromatic compounds that are derived from both phenol and toluene . The structure consists of a benzene ring with attached hydroxyl (-OH) and methyl groups (-CH 3 ) as substituents . Their different arrangement results in three constitutional isomers with the empirical formula C 7 H 8 O. They are primarily to be regarded as methyl-substituted phenols. The halogenated derivatives are also referred to as cresols.
Occurrence
Cresols and their derivatives (e.g. xylenols ) are widespread in nature. They are found as metabolites in various microorganisms as well as in the urine of mammals, in coal and beech tar .
presentation
Originally the non-derivatized cresols were isolated from coal and beech tar. A liquid, yellow-brown mixture of isomers, the so-called tricresol, is obtained . Single distillation leads to crude carbolic acid . The pure production of the three cresols takes place on the basis of carbolic oil by extraction with sodium hydroxide solution . Alternatively, the phenoraffin process is used, in which a sodium phenolate solution and diisopropyl ether are used for extraction .
Cresols can be synthesized by boiling the respective diazonium salt of the toluidines .
On an industrial scale, cresol is synthesized in a tube reactor , among other things by reacting chlorotoluene with sodium hydroxide solution at high temperatures (~ 250 ° C) and pressure (~ 300 bar).
properties
Cresols are very sensitive to light and air. At temperatures above 80 ° C, explosive mixtures form with air. They are sparingly soluble in water and burn with a lot of soot. Cresols have a tarry odor. M -cresol reacts with propene to form thymol .
pK s value
The methyl group has a (weak) + I effect on the aromatic, which increases the electron density in the ring. This u. a. the acidity of the phenolic OH is weakened. The pK s values will be somewhat higher than that of phenol (9.99).
Reactivity
In addition to the (weak) + I effect of the methyl group, however, the + M effect of the hydroxyl group is more decisive for chemical reactivity . Both effects significantly increase the electron density in the ring. The −I effect of the hydroxyl group has very little influence on the properties of the cresols. The cresols therefore enter into electrophilic aromatic substitutions with relative ease.
use
Cresols act as a bactericide , insecticide, and fungicide . They are therefore often part of disinfectants . m -Kresol is used as a fungicide in agriculture. 8 µl / g is sufficient to keep grain free from fungal attack for 60 days at a storage temperature of 30 ° C. As a pharmaceutical excipient , m- cresol is, for example, a component of insulin glargine . Typical concentrations are in the range from 1.5 to 3 mg per ml of solution for injection.
Cresols are also used to make synthetic and dyes, synthetic resins ( cresol resins ) and pharmaceuticals from them. In homeopathy , a raw cresol obtained from coal tar , known under the name of Cresolum crudum , is used for inflammation, skin diseases and paralysis.
toxicology
Cresol poisoning causes quite unspecific symptoms. Signs of chronic poisoning are headaches, coughing and nausea, loss of appetite as well as fatigue and insomnia. A dermal by absorption is very fast. Acute poisoning with kidney damage and disorders of the central nervous system such as cramps, unconsciousness and respiratory paralysis can result. Cresols are considered carcinogenic .
As with phenols in general, (whitish) chemical burns occur when taken orally, which are painless as phenols have an anesthetic effect. Symptoms of poisoning occur in humans from around 3 g, from around 10 g there is the possibility of a fatal shock.
In addition, phenols and especially cresols have a strong protein-degrading effect. Since they are highly corrosive, they cause acute skin damage on contact with the skin, destroy the protein in the skin cells and almost immediately overcome the protective mechanism of the skin, which is slightly acidic. If open mucous membranes (oral cavity, nose, anus) are contaminated , they get directly into the blood, where they are quickly distributed in the body and lead to multiple protein damage to the internal organs. Without immediate countermeasures, cresols can have life-threatening effects even in small quantities.
Risk assessment
In 2012, p -Kresol was included in the EU's ongoing action plan ( CoRAP ) in accordance with Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH) as part of substance evaluation . The effects of the substance on human health and the environment are re-evaluated and, if necessary, follow-up measures are initiated. The reasons for the uptake of p -cresol were concerns about consumer use , high (aggregated) tonnage and widespread use as well as the dangers arising from a possible assignment to the group of CMR substances and as a potential endocrine disruptor . The re-evaluation started in 2015 and was carried out by the United Kingdom . A final report was then published.
proof
Cresols can already be smelled in concentrations of a few micrograms per cubic meter of air.
literature
- Klemm, Elias: Direct synthesis of phenol and cresol. From catalyst to process , Shaker Verlag GmbH 2002, ISBN 3-8265-9896-2 .
- Author collective: Organikum , 22nd edition, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2004, ISBN 3-527-31148-3 .
Web links
- IR spectra of the cresols: o -cresol ; m -cresol ; p -cresol
- Phenols and cresols
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on cresol, isomers in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on May 8, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on o-cresol in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on September 2, 2012(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on m-cresol in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on September 2, 2012(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on p-cresol in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on September 2, 2012(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b CRC Handbook of Tables for Organic Compound Identification , Third Edition, 1984, ISBN 0-8493-0303-6 .
- ↑ Data sheet Cresol mixture of isomers from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 8, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values , accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ Werner Waldhäusl: Diabetes in Practice. Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-97435-9 , p. 406 ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ↑ Peter Hürter: Diabetes in Children and Adolescents. Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-662-06575-4 , p. 134 ( limited preview in the Google book search).
- ↑ European Chemicals Agency (ECHA): Substance Evaluation Conclusion and Evaluation Report .
- ↑ Community rolling action plan ( CoRAP ) of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA): p-cresol , accessed on May 20, 2019.


