Eastern Japan
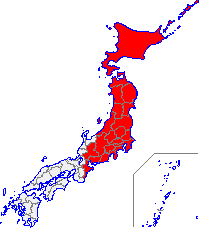
As East Japan ( jap. 東日本 , Higashi-Nihon or Higashi-Nippon ) is referred to in a rough, not legally defined regional division of Japan about the eastern half of the country. In contrast to Western Japan , it then includes the regions of Hokkaidō , Tōhoku and Kantō and, depending on the definition, other prefectures from the Chūbu region , mostly Shizuoka and the three prefectures in Kōshin'etsu , often Aichi and Gifu . In some contexts, Northern Japan (Hokkaidō and Tōhoku) is not counted as part of Eastern Japan, which then only consists of Kantō and parts of Chūbus in the narrower sense.
use
The term is used, among other things, in a number of names of regionally divided, formerly public companies such as B. the transport companies JR Higashi-Nihon and NEXCO Higashi-Nihon , the utility Higashi-Nihon Gas or the telecommunications company NTT Higashi-Nihon . For historical reasons, the frequency of the power grid in large parts of eastern Japan (for the energy suppliers Hokkaidō Denryoku , Tōhoku Denryoku and Tōkyō Denryoku ) is 50 Hz, in western Japan it is 60 Hz across the board.

Geologically a fault that separates Itoigawa-Shizuoka Line ( Engl. Shortly ISTL ) between the Amur and the Okhotsk microplate (is disputed their autonomy), East West Japan.
Linguistically, the dialects of Eastern Japan are grouped as Higashi-Nihon hōgen ( 東 日本 方言 ) or Tōbu hōgen ( 東部 方言 ), and further differentiated regionally. The dividing line between Eastern and Western Japanese dialects is also known as the Itoigawa- Hamana Lake Line.
In March 2011, eastern Japan was hit by a major earthquake .
Other names
Historical names for eastern Japan that have existed since ancient Japan - in different definitions, all without Ezo (Hokkaidō) - are Tōgoku or Azuma no kuni ( 東 国 , "eastern provinces" or just "east country"), Azuma ( 東 , "the east") ) and Bandō ( 坂 東 ). Bandō denoted all areas east of the Ashigara slope ( 足 柄坂 , Ashigara-saka ) on the pass of the same name on the important Tōkaidō highway , which formed the border between the provinces of Sagami and Suruga , the names Tōgoku and Azuma initially all areas east of the capital region .


