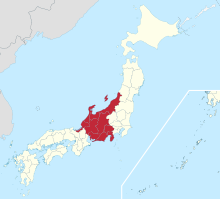
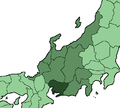
Chūbu
The region Chūbu ( Jap. 中部地方 , Chūbu-CHIHO ) comprises the central portion ( Chūbu ) of the island Honshu , the main island of Japan . The region connects the two culturally central regions of Kantō and Kansai .
The Chūbu region covers an area of 66,801.14 km² and is in turn divided into three geographical regions:
- Hokuriku in the north on the Sea of Japan , a rocky coastal landscape,
- Chūō-kōchi or Tōsan in the middle with the Japanese Alps , a mountain region, as well
- Tōkai in the south on the densely populated Pacific coast .
The names are based on the historical regions of the Gokishichidō system: Hokurikudō , Tōsandō and Tōkaidō .
Nagano and Niigata are also referred to as a separate region of Shin'etsu and, with the addition of Yamanashi, as Kōshin'etsu . Shin'etsu and Hokuriku are also combined to form Hokuriku-Shin'etsu .
The main city is Nagoya . The Fuji is located in Chūbu.
Prefectures
Coordinates: 35 ° 53 ′ 0 ″ N , 137 ° 57 ′ 0 ″ E