Gokishichidō
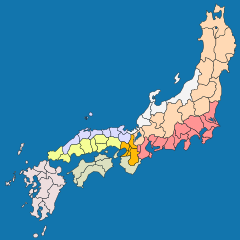
As Gokishichidō ( Japanese 五 畿 七 道 , "5 provinces of Kinai and 7 highways"), also: Kinai shichidō ( 畿内 七 道 ), the administrative units in ancient Japan were referred to.
After the Ritsuryō system towards the end of the 7th century , an administrative system with five inner provinces and seven outer regions was created in the Asuka period . The Chinese administration served as a model at the time of the Sui dynasty . The 60 or so provinces were grouped into these regions.
Inner provinces
The five inner provinces ( Kinai ) in the Capital Region ( Kinki ) were:
They included about the area of today's prefectures Nara and Osaka and the cities of Kyōto and Kobe and the area between the cities of Kyoto and Nara .
Outer regions
The seven outer regions were:
- Tōkaidō ( 東海 道 ): from Iga and Ise (today's Mie prefecture ) along the Pacific coast from Shima (with the Shima peninsula ) to Hitachi ( Ibaraki prefecture )
- Hokurikudō ( 北 陸 道 ): Coast on the Sea of Japan from Wakasa and Echizen ( Fukui Prefecture ) to Echigo and Sado ( Niigata Prefecture )
- Tōsandō ( 東山 道 ): the interior of the country between the above regions from Ōmi ( Shiga Prefecture ) to the northeastern end of the empire, which soon expanded to all of Tōhoku ,
- San'indō ( 山 陰道 ): Coast on the Sea of Japan westward from Tamba and Tango (northern part of Kyoto prefecture ) to Iwami and Oki ( Shimane prefecture )
- San'yōdō ( 山陽 道 ): entire inland sea coast of Honshū from Harima ( Hyōgo ) to Suō and Nagato ( Yamaguchi prefecture )
- Nankaidō ( 南海 道 ): Kii ( Kii peninsula ), Awaji ( Awaji-shima ) and the "Four Provinces" (= Shikoku )
- Saikaidō ( 西海 道 ): The "Nine Provinces" (= Kyūshū ) as well as Iki and Tsushima
The -dō ( 道 ; cf. Chinese Dao ) always designates an administrative district in this context , even if the outer regions were of course opened up by trunk roads ( -dō ).
The starting point of all streets was the respective capital of Japan : First Heijō-kyō ( Nara ), then Heian-kyō ( Kyōto ).
In the Edo period , the names of the administrative districts continued to be used, but the road system now started with the Gokaidō from Edo .