Oxadiargyl
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
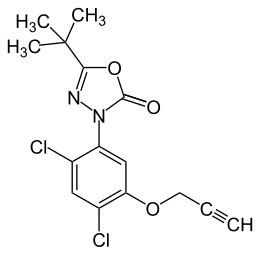
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Oxadiargyl | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 15 H 14 Cl 2 N 2 O 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to yellowish odorless solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 341.19 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.41 g cm −3 (bulk density) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
131 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
2.5 × 10 −6 Pa (25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Oxadiargyl is an active ingredient for crop protection and a chemical compound from the group of oxadiazoles . It is a propargylic analog of Oxadiazon .
Extraction and presentation
Oxadiargyl can be obtained by phosphorylation of N -aryl- N '-pivaloylhydrazine. The latter itself is obtained by reacting aryl hydrazine with pivaloyl chloride.
properties
Oxadiargyl is a white to yellowish solid. It decomposes when heated before it reaches the boiling point.
use
Oxadiargyl is used as an active ingredient in plant protection products. It serves as a herbicide and was first approved in South America in 1996. It is mainly used in rice and sunflowers and works by inhibiting protoporphyrinogen oxidase (PPO).
Admission
Oxadiargyl was added to the list of approved active ingredients by the European Union in 2003, but approval expired on March 31, 2014. In Germany, Austria and Switzerland no pesticide products with Oxadiargyl are permitted.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on Oxadiargyl in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB) of the University of Hertfordshire , accessed on July 31, 2013.
- ↑ a b c Entry on Oxadiargyl in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 23, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ EU: Review report for the active substance oxadiargyl (PDF; 266 kB).
- ↑ Entry on 3- [2,4-dichloro-5- (2-propynyloxy) phenyl] -5- (1,1-dimethylethyl) -1,3,4-oxadiazol-2 (3H) -one in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Oxadiargyl data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 21, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Peter Böger, Ko Wakabayashi: Peroxidizing Herbicides . Springer, 1999, ISBN 978-3-540-64550-4 , pp. 42 (English, limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ BAYER: oxadiargyl
- ↑ Commission Directive 2003/23 / EC of March 25, 2003 amending Council Directive 91/414 / EEC to include the active substances imazamox, oxasulfuron, ethoxysulfuron, foramsulfuron, oxadiargyl and cyazofamid
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Oxadiargyl in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on December 7, 2019.

