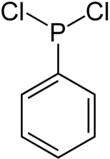
Dichloro (phenyl) phosphine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Dichloro (phenyl) phosphine | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 5 Cl 2 P | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with a pungent odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 178.99 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.32 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−51 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
225 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
Decomposes with water, miscible with benzene , chloroform and carbon disulphide |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.5962 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Dichlorophenylphosphine is a chemical compound from the group of phosphines . It has a phenyl residue and two chlorine atoms attached to the central phosphorus .
Manufacturing
The reaction between phosphorus trichloride and benzene in the presence of aluminum chloride can be used to synthesize dichlorophenylphosphine . The reaction proceeds analogously to a Friedel-Crafts acylation . The Lewis acid aluminum chloride first activates phosphorus trichloride and thus enables the subsequent electrophilic attack on the benzene.
- Reaction of phosphorus trichloride with benzene to form dichlorophenylphosphine. Ph = phenyl. The hydrogen chloride formed as a by-product escapes from the reaction mixture as a gas.
properties
Dichlorophenylphosphine is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor with a melting point of −51 ° C and a boiling point of 225 ° C. It decomposes with water to form hydrogen chloride .
use
Dichloride can be used for synthesis of chlorodiphenylphosphane be used. At temperatures above 280 ° C, dichlorophenylphosphine disproportionates to chlorodiphenylphosphine and phosphorus trichloride.
- Disproportionation of dichlorophenylphosphine into chlorodipenylphosphine and phosphorus trichloride.
Reduction of the compound using lithium aluminum hydride in diethyl ether gives the phenylphosphine .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on dichloro (phenyl) phosphine in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 23, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ A. Michaelis: About the compounds of the elements of the nitrogen group with the radicals of the aromatic series . In: Justus Liebig's Annals of Chemistry . tape 181 , no. 3 , 1876, p. 265-363 , doi : 10.1002 / jlac.18761810302 .
- ^ Georg Wittig, Helmut Braun, Henri-Jean Cristau: Presentation and resolution of chiral triarylphosphines . In: Justus Liebig's Annals of Chemistry . tape 751 , no. 1 , October 12, 1971, p. 17-26 , doi : 10.1002 / jlac.19717510103 .
- ↑ Data sheet dichlorophenylphosphine (PDF) from Merck , accessed on March 24, 2011.
- ^ F Simeon, P.-A Jaffres, D Villemin: A direct and new convenient oxidation: synthesis of substituted arylphosphonates from aromatics . In: Tetrahedron . tape 54 , no. 34 , 1998, pp. 10111-10118 .
- ↑ A. Broglie: About the behavior of phosphenyl chloride at higher temperatures . In: Reports of the German Chemical Society . tape 10 , no. 1 , 1877, p. 628 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.187701001174 .
- ↑ Leon D. Freedman, GO Doak: The Reduction of Benzenephosphonyl Dichloride . In: Journal of the American Chemical Society . tape 74 , no. July 13 , 1952, p. 3414–3415 , doi : 10.1021 / ja01133a504 .


![{\ displaystyle \ mathrm {PCl_ {3} \ + \ C_ {6} H_ {6} \ {\ xrightarrow {[AlCl_ {3}]}} \ \ PhPCl_ {2} + HCl \ uparrow}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6ba67dfe19bc55b1737caf0f4e785c68d2acff33)

