Piperonyl butoxide
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
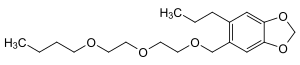
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Piperonyl butoxide | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 19 H 30 O 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless to yellowish odorless oily liquid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class |
Antiparasitic agent (external) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 338.4 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.06 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
2 Pa at 60 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water (14.3 mg l −1 at 25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
As a synergist, piperonyl butoxide ( PBO ) enhances the insecticidal effect of pyrethrins , pyrethroids , Rotenone and some carbamates . Piperonyl butoxide itself has no insecticidal effect.
Extraction and presentation
Piperonyl butoxide is produced semi-synthetically from safrole or sassafras oil.
use
Piperonyl butoxide can be added to insecticides , which are commercially available as a spray, oil, emulsion or powder. When mixed with pyrethrins, these preparations usually contain 3 to 10 times more PBO than pyrethrins (parts by weight).
Medicine and veterinary medicine
Piperonyl butoxide is an additive in lice products containing pyrethrin or pyrethroid
Plant protection
According to EU Directive 91/414 / EEC, piperonyl butoxide is not regarded as an active ingredient , but as a co-additive in insecticides. The use as a synergist to natural pyrethrins is also permitted in organic farming .
In Austria, preparations containing PBO are mainly available for protecting stored products. In Austria and Germany, piperonyl butoxide is listed as an active ingredient. No preparations containing PBO are permitted in Switzerland.
Pest Control
PBO is added to many household insecticides that contain pyrethrins or pyrethroids.
Mode of action
Piperonyl butoxide inhibits insects in the body's detoxification of insecticides captured by one of the cytochrome P450 - enzymes . As a result, for example, the insecticidal effect of pyrethrum is increased by around 30 times, and in some cases resistance is also eliminated.
Half-life
The half-life of PBO indoors is around three to four and a half years, depending on the surface and exposure to light. It is not persistent in soil with a half-life of 13 days.
Degradation in the organism
The breakdown of PBO in the body of insects and warm-blooded animals takes place on the one hand through oxidative breakdown of the side chain, on the other hand through oxidative cleavage of the C-atom of the methylenedioxy group. The residue, which cannot be further degraded, is excreted as a glycoside or amino acid derivative.
toxicology
The acute toxicity of piperonyl butoxide to mammals is low. The LD 50 in test animals was in the range from 2.5 to 11.5 g / kg body weight. The irritant effect of PBO on the skin is low and it is hardly absorbed through the skin.
In long-term feeding studies, however, severe liver damage occurred, and in some cases damage to the kidneys or changes in the blood count . Based on these long-term studies, the WHO considers a permitted daily dose of 0.2 mg / kg body weight / day to be still acceptable.
PBO has no mutagenic effect; it only has a reproductive toxicity in concentrations that already severely damage the parent animals. Whether it is carcinogenic has not yet been clearly established. The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) classified the carcinogenicity of piperone butoxide in 2006 on the basis of studies on animals in Group C (Possibly Carcinogenic to Humans).
PBO increases the toxic effect of insecticides in mammals or in humans when taken at the same time.
Environmental impact
Piperonyl butoxide is not toxic to bees. However, the toxicity to water fleas and fish is high.
Risk assessment
In 2012, piperonyl butoxide was included in the EU's ongoing action plan ( CoRAP ) in accordance with Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH) as part of substance evaluation . The effects of the substance on human health and the environment are re-evaluated and, if necessary, follow-up measures are initiated. The reasons for the uptake of piperonyl butoxide were concerns regarding consumer use and widespread use as well as the dangers arising from a possible assignment to the group of PBT / vPvB substances and as a potential endocrine disruptor . The re-evaluation was supposed to be carried out by Sweden but has been withdrawn.
literature
- Werner Perkow: Active substances in pesticides and pesticides . 2nd edition, Erg. Current issue April 1996, Paul Parey publishing house.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on piperonyl butoxide in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on June 19, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on piperonyl butoxide in the EU pesticide database ; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on December 6, 2019.
- ↑ Insect sprays and electric vaporizers against mosquitoes and vermin are by no means harmless for humans! June 30, 2018, accessed June 19, 2019 (German).
- ↑ Entry on piperonyl butoxide in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB) of the University of Hertfordshire , accessed on June 19, 2019.
- ↑ EPA: Reregistration Eligibility Decision for Piperonyl Butoxide (PBO). June 14, 2006, accessed 2006 .
- ^ Pyrethrum and synthetic pyrethroids . In: Matthias Brockstedt, Reinhard Bunjes, Ursula Oberdisse, Karl Ernst von Mühlendahl (Ed.): Poisoning in childhood . 4th edition. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart 2003, ISBN 3-13-129814-6 , p. 344 .
- ↑ Registration dossier on 2- (2-butoxyethoxy) ethyl 6-propylpiperonyl ether (section Ecotoxicological Summary ) at the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on April 27, 2019.
- ↑ ECHA: Justification for removing a substance from CoRAP prior to evaluation , March 19, 2019.
- ↑ Community rolling action plan ( CoRAP ) of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA): 2- (2-butoxyethoxy) ethyl 6-propylpiperonyl ether , accessed on March 26, 2019.
