Presidential election in the United States in 1920
| ‹ 1916 • |
|||||||||||
| 34th presidential election | |||||||||||
| November 2, 1920 | |||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
| Republican Party | |||||||||||
| Warren G. Harding / Calvin Coolidge | |||||||||||
| electors | 404 | ||||||||||
| be right | 16,144,093 | ||||||||||
|
|
60.3% | ||||||||||
| Democratic Party | |||||||||||
| James M. Cox / Franklin D. Roosevelt | |||||||||||
| electors | 127 | ||||||||||
| be right | 9,139,661 | ||||||||||
|
|
34.1% | ||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
| Election results by state | |||||||||||
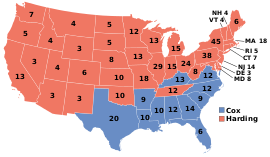
|
|||||||||||
|
37 states
Harding / Coolidge |
11 states
Cox / Roosevelt |
||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
| President of the United States | |||||||||||
In the 1920 presidential election in the United States , Democrats James Middleton Cox and Franklin D. Roosevelt (later US President) were on one side , and Republicans Warren G. Harding and Calvin Coolidge were on the other .
The Democrats stood for the continuation of the policy of Woodrow Wilson , who demanded and initiated a stronger engagement of the USA internationally. The United States should also join the League of Nations . The state should intervene and regulate in economic policy.
The Republicans demanded a return to normalcy ( back to normalcy ), ie isolationism , a no to the League of Nations , tax cuts, the state renouncing interventions in the economy, protective tariffs and consent to prohibition . At the same time they stood up for women's rights. Warren Harding wanted back to the laissez-faire principle, as it was under the William McKinley era . Coolidge later put it in his tenure as president that "the main business of the American people is business." Even Herbert Hoover , who was under Harding and Coolidge economy minister, pursued a policy based on the laissez-faire theory in his term as US President.
Socialist candidate Eugene V. Debs was sentenced to 10 years in prison for speaking against war recruits and was running from prison. For the first time, celebrities were also involved in the election campaign. Conservative celebrities like Al Jolson , Lillian Russell , Douglas Fairbanks , Mary Pickford , Louis B. Mayer , David Wark Griffith, and Lillian Gish supported Harding. Business people like Thomas Alva Edison and Henry Ford traveled to Washington, DC to help Harding. The media also gave Harding massive support. The 1920 election was the first presidential election to be broadcast.
Result
| candidate | Political party | be right | electors | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| number | percent | |||
| Warren G. Harding | republican | 16,144,093 | 60.3% | 404 |
| James M. Cox | democrat | 9,139,661 | 34.1% | 127 |
| Eugene V. Debs | socialist | 913,693 | 3.4% | 0 |
| Parley P. Christensen | Farmer Labor Party | 265.411 | 1.0% | 0 |
| Aaron S. Watkins | Prohibitionist | 188,787 | 0.7% | 0 |
| James E. Ferguson | American party | 47,968 | 0.2% | 0 |
| William W. Cox | Socialist Labor Party | 31,716 | 0.1% | 0 |
| Other | 34,496 | 0.1% | 0 | |
| total | 26.765.180 | 100% | 531 | |
266 votes were necessary for the election to the president.
literature
- Donald Richard Deskins, Hanes Walton, Sherman C. Puckett: Presidential Elections, 1789-2008: County, State, and National Mapping of Election Data. University of Michigan, Ann Arbor 2010, ISBN 978-0-472-11697-3 , pp. 316-326 (= Chapter 36: Warren G. Harding's Election. ).

