Saloum (river)
| Saloum | ||
| Data | ||
| location |
|
|
| River system | Saloum | |
| Headwaters | Northern border of the Tambacounda region, approx. 36 km west of the N7 14 ° 24 ′ 39 ″ N , 13 ° 52 ′ 17 ″ W |
|
| Source height | approx. 40 m | |
| muzzle |
Atlantic Ocean Coordinates: 13 ° 50 ′ N , 16 ° 45 ′ W 13 ° 50 ′ N , 16 ° 45 ′ W |
|
| Mouth height | 0 m | |
| Height difference | approx. 40 m | |
| Bottom slope | approx. 0.11 ‰ | |
| length | approx. 378 km | |
| Right tributaries | Sine , Marigot de Faoye | |
| Medium-sized cities | Kaolack | |
| Navigable | 112 km | |
|
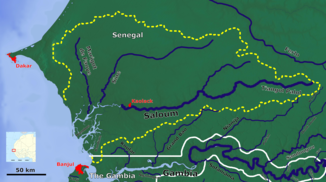
The Saloum river system |
||
The Saloum is a river in the West African state of Senegal .
geography
The Saloum is centrally located in Senegal, north of the state of Gambia . The headwaters of the river can be found 70 kilometers north-north-west of Tambacounda and the valley path of its water begins with a barely visible bed, only understandable on the basis of the orohydrographic gradient , as an intermittent body of water whose bed only fills with water in the rainy season . As such, it runs in a general westward direction with a valley path of approx. 246 kilometers to just before Kaolack through the central Senegalese lowlands. Only for the last 132 kilometers does the Saloum have water all year round.
The catchment area of the Saloum river system includes parts of the Tambacounda , Kaffrine and Kaolack regions . Then in the Fatick region it flows together with the Sine in an estuary into the Atlantic Ocean . There is the Delta du Saloum National Park . This estuary is also designated as a biosphere reserve by UNESCO .
traffic
The river is navigable over a length of 112 kilometers (to Kaolack ) for seagoing vessels under 2000 GRT. In order to be able to navigate the Saloum with a seagoing ship, a sandbar (bar) had to be crossed in the mouth, which, depending on the draft of the ship and the respective water level, was only passable at certain times of the day - status 1956/57.
Both the national road N 1 , which leads from Dakar in the west to Tambacounda and on to the Malian border to Kayes , as well as the parallel railway line Dakar – Niger cross the dry valley of the Saloum near Birkelane in the Kaffrine region and the N 4 , or the N 5 , at Kaolack.
Salinity
During the dry season, the catchment area supplies practically no water to the river. The water of the lower course subject to the tidal current is salt water from the Atlantic. There is a negative runoff in the Saloum and Casamance , as water evaporates and more water flows in from the ocean. The amount of salt added can be up to more than 100 g / l. This is why the hypersaline water is evaporated in salt pans around the city of Kaolack, and salt is thereby obtained.
The salinity of the Saloum was measured from the mid-1920s. The following diagram shows the average salinity from 1928 to 1969, and 1970 to 1985. An increase can be observed during the drought in the Sahel in the 1970s and 1980s. Assuming a salinity of the Atlantic of about 35 g / l, there was practically no runoff into the Atlantic during the drought.
Average salinity of the Saloum in g / l

Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ OpenTopoMap
- ↑ Measure distances with google maps
- ^ A b Rainfall and Salinity of a Sahelian Estuary between 1927 and 1987