Rail transport in Indonesia
Rail traffic in Indonesia was on the islands of Java , Sumatra , Borneo , Madura , New Guinea and Sulawesi . At the beginning of the 21st century, there is still a rail network that serves most parts of the densely populated island of Java. There are three disconnected route networks in Sumatra. In addition, there are a number of small factory railways that mainly serve the sugar cane and palm oil industries . One of them, a former forest railway , still has steam locomotives and operates tourist trains.
history
The first railway on the East Indies was a line from Semarang to Tanggung on the island of Java, opened in 1867 . It was built in standard gauge (1435 mm), but this turned out to be uneconomical for an extension due to the terrain and the expected volume of traffic, which is why all other railways were built in Cape gauge (1067 mm).
Route network
The entire length of the Indonesian rail network is approx. 8,000 km including all inner-city and industrially operated routes.
According to the Mid-Term Development Plan, around 3,300 km of railway line on the Indonesian islands of Java, Sumatra, Sulawesi and Kalimantan should be expanded between 2015 and 2019. Half of the expenditure, which amounts to around 17 billion US dollars, is said to come from the private sector . According to information from the Indonesian Ministry of Transport, only 2.8 billion US dollars has flowed from the private sector since 2014. Until 2017, only 400 km of the route had been realized.
The planned infrastructure offensive in Indonesia is entitled to 55 strategic construction projects; 23 fall on rail transport. This includes various prestige projects such as:
- the construction of the first subway in Jakarta,
- the first high-speed line between Jakarta and Bandung,
- the airport transfer connection in Jakarta , which is in operation in the first stages ,
- the construction of a continuous railway line on Sulawesi.
Java
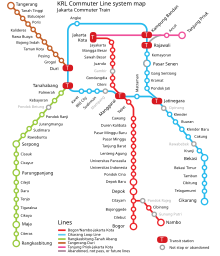
The railways in Java are being modernized and improved. Jakarta has an electrically operated network of suburban railways. In 2016, construction began on a new 142-kilometer high-speed line connecting Jakarta with Bandung . The planned completion should be completed by 2021. The construction and financing are guaranteed by China.
Sumatra
In 2014, a 255 km long standard gauge line was opened in South Sumatra which the lignite mines of Tanjung Enim with a new port in Srengsem in the province of Lampung connects.
Borneo
In 2011 the construction of a standard-gauge heavy - duty railway was planned in the province of Kalimantan Timur in the east of the island of Borneo. The 130 km long route was intended to connect the Muara Wahau coal mine with a new industrial area and the port in Bengalon . The project was funded by Mineral Energy Commodities in the United Arab Emirates and was expected to cost 1.5 billion US dollars. The plan is to transport 34 million tons of coal per year, which will be carried in 120-car trains with three locomotives.
Madura
A steam tram operated on Madura from 1901 to 1987 , connecting the west and east of the island. It was operated by the Madoera Stoomtram Maatschappij and served a Cape gauge route network of 142 km in length.
Papua
Feasibility studies are being carried out for two railway projects: a 390 km line from Sorong to Manokwari and a 205 km line from Sarmi to Jayapura , which is due to be completed a few years after the first line. The routes could be combined into a 595 km continuous route along almost the entire north coast of the Indonesian part of the island. The project is carried out under the name KA Trans Papua .
Sulawesi
In 2015, work began on a 145-kilometer railway in the south of the island between Parepare and Makassar , which is due to be completed in 2019. A separate 400 km long railway is proposed in the north between Manado and Gorontalo . Discussions are currently under way to set up a network of up to 2000 km.
Societies
Most of the railway lines are operated by the state-owned Kereta Api Indonesia (KAI). These are the existing routes on Java and Sumatra, but also future routes on Borneo and Sulawesi. Jakarta's electrically powered suburban railways are operated by Kereta Commuter Indonesia (KCI), which is a subsidiary of KAI.
Individual evidence
- ^ A b c d e Glyn Williams: Railways in Indonesia. 2017 (English).
- ↑ Indonesia wants to expand rail network | Industry report | GTAI. Retrieved February 13, 2020 .
- ↑ iXPOS 2018 - reports. Retrieved February 18, 2020 .
- ↑ Indonesia wants to expand rail network | Industry report | GTAI. Retrieved February 11, 2020 .
- ^ Private pioneers - International Railway Journal . In: International Railway Journal . February 10, 2014 ( railjournal.com ).
- ^ Government To Launch KA Trans Papua Rail Project . In: Indonesia Expat . June 6, 2017 ( indonesiaexpat.biz ).
- ↑ Gubernur Sulsel: 150 km Rel KA Trans Sulawesi Akan Beroperasi 2019. March 9, 2018 (id-ID).