Tortoiseshell
| Tortoiseshell | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Gobiesocidae | ||||||||||||
| Bleeker , 1860 |
The shield fish (Gobiesocidae), also called shield bellies or suckers , are a family from the group of perch relatives (Percomorphaceae). They are closest to the mucus Fishy related (Blenniiformes). The approximately 160 species in almost 50 genera live in temperate, subtropical and tropical seas, a few also in freshwater and brackish water .
features
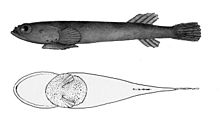
They are goby-like , highly specialized animals. The pelvic fins have grown together to form a suction disk with which the fish can hold on to the ground. The skin has no scales but a thick layer of mucus. A swim bladder is missing. Mention should also be made of the genital papilla of the males and the absence of the basi- and orbitosphenoid in the skull. Half or all of the gills on the fourth arch are missing.
Most of the fish are only about five centimeters long, some only 2-3 centimeters, the largest species ( chorisochism dentex ) can be 30 centimeters long. The species of the genus Alabes (subfamily Cheilobranchinae) are eel ("coastal eels") or actually (because of their small size) worm-shaped, their sucker is small or has disappeared.
Way of life
Tortoiseshell fish mostly inhabit shallow waters with a rocky bottom and algae growth or live in seagrass meadows. Only a few species are found in coral reefs . Some species also live in symbiosis with invertebrates , such as the hair star shield belly ( Discotrema crinophila ) and the sea urchin shield belly ( Diademichthys lineatus ). In the case of the sea urchin shield belly, which lives between the spines of diadem sea urchins ( Diadema sp. ), However, it has been found that it eats the sea urchin's feet . So it is more likely to be parasitism .
Internal system
- Subfamily Aspasminae
- Genus Aspasma
- Aspasma minima (Döderlein, 1887) .
- Genus Aspasmichthys
- Aspasmichthys alorensis Allen & Erdmann, 2012 .
- Aspasmichthys ciconiae (Jordan & Fowler, 1902) .
- Genus Lissonanchus
- Lissonanchus lusheri Smith, 1966 .
- Genus Pherallodichthys
- Pherallodichthys meshimaensis Shiogaki & Dotsu, 1983 .
- Genus Aspasma
- Subfamily Cheilobranchinae
- Genus Alabes
- Alabes bathys Hutchins, 2006 .
- Alabes brevis Springer & Fraser, 1976 .
- Alabes dorsalis ( Richardson , 1845) .
- Alabes elongata Hutchins & Morrison, 2004 .
- Alabes gibbosa Hutchins & Morrison, 2004 .
- Alabes hoesei Springer & Fraser, 1976 .
- Alabes obtusirostris Hutchins & Morrison, 2004 .
- Alabes occidentalis Hutchins & Morrison, 2004 .
- Alabes parvula (McCulloch, 1909) .
- Alabes scotti Hutchins & Morrison, 2004 .
- Alabes springeri Hutchins, 2006 .
- Genus Alabes
- Subfamily Chorisochisminae
- Genus Chorisochism
- Chorisochism dentex ( Pallas , 1769) .
- Genus Chorisochism
- Diademichthyinae Whitley subfamily , 1950 .
- Genus Diademichthys
- Diademichthys lineatus (Sauvage, 1883) .
- Genus Lepadichthys
- Lepadichthys akiko Allen & Erdmann, 2012 .
- Lepadichthys bilineatus Craig et al., 2015 .
- Lepadichthys bolini Briggs, 1962 .
- Lepadichthys caritus Briggs, 1969 .
- Lepadichthys coccinotaenia Regan , 1921 .
- Lepadichthys ctenion Briggs & Link, 1963 .
- Lepadichthys erythraeus Briggs & Link, 1963 .
- Lepadichthys frenatus Waite, 1904 .
- Lepadichthys lineatus Briggs, 1966 .
- Lepadichthys minor Briggs, 1955 .
- Lepadichthys sandaracatus Whitley, 1943 .
- Lepadichthys springeri Briggs, 2001 .
- Genus Diademichthys
- Subfamily Diplocrepinae
- Genus Barryichthys Conway et al., 2019 .
- Barryichthys hutchinsi Conway et al., 2019 .
- Barryichthys algicola Conway et al., 2019 .
- Genus Diplocrepis
- Diplocrepis puniceus ( Richardson , 1846) .
- Genus Flexor Conway, Stewart & Summers, 2018 .
- Flexor incus Conway, Stewart & Summers, 2018 .
- Genus Gastrocyathus
- Gastrocyathus gracilis Briggs, 1955 .
- Genus Gastroscyphus
- Gastroscyphus hectoris ( Günther , 1876) .
- Genus Parvicrepis
- Parvicrepis parvipinnis (Waite, 1906) .
- Genus Pherallodus
- Pherallodus indicus (Weber, 1913) .
- Pherallodus smithi Briggs, 1955 .
- Genus Barryichthys Conway et al., 2019 .
- Subfamily Gobiesocinae
- Genus Acyrtops
- Acyrtops amplicirrus Briggs, 1955 .
- Acyrtops beryllinus (Hildebrand & Ginsburg, 1927) .
- Genus Acyrtus
- Acyrtus artius Briggs, 1955 .
- Acyrtus lanthanum Conway, Baldwin & White, 2014 .
- Acyrtus pauciradiatus Sampaio, de Anchieta, Nunes & Mendes, 2004 .
- Acyrtus rubiginosus ( Poey , 1868) .
- Genus Arcos
- Arcos decoris Briggs, 1969 .
- Arcos erythrops ( Jordan & Gilbert, 1882) .
- Arcos macrophthalmus ( Günther , 1861) .
- Arcos nudus (Linnaeus, 1758) .
- Arcos poecilophthalmos (Jenyns, 1842) .
- Arcos rhodospilus (Günther, 1864) .
- Genus Aspasmodes
- Aspasmodes briggsi Smith, 1957 .
- Genus Aspasmogaster
- Aspasmogaster costata ( Ogilby , 1885) .
- Aspasmogaster liorhyncha Briggs, 1955 .
- Aspasmogaster occidentalis Hutchins, 1984 .
- Aspasmogaster tasmaniensis (Günther, 1861) .
- Genus Briggsia
- Briggsia hastingsi Craig & Randall, 2009 .
- Genus Cochleoceps
- Cochleoceps bassensis Hutchins, 1983 .
- Cochleoceps bicolor Hutchins, 1991 .
- Cochleoceps orientalis Hutchins, 1991 .
- Cochleoceps spatula (Günther, 1861) .
- Cochleoceps viridis Hutchins, 1991 .
- Genus Creocele
- Creocele cardinalis (Ramsay, 1882) .
- Genus Derilissus
- Derilissus altifrons Smith-Vaniz, 1971 .
- Derilissus kremnobates Fraser, 1970 .
- Derilissus nanus Briggs, 1969 .
- Derilissus vittiger Fraser, 1970 .
- Genus Discotrema
- Discotrema crinophilum Briggs, 1976 .
- Discotrema monogrammum Craig & Randall, 2008 .
- Discotrema zonatum Craig & Randall, 2008 .
- Genus Eckloniaichthys
- Eckloniaichthys scylliorhiniceps Smith, 1943 .
- Genus Gastrocymba
- Gastrocymba quadriradiata ( Rendahl , 1926) .
- Genus Gobiesox
- Gobiesox adustus Jordan & Gilbert, 1882 .
- Gobiesox aethus (Briggs, 1951) .
- Gobiesox barbatulus Starks, 1913 .
- Gobiesox canidens (Briggs, 1951) .
- Gobiesox crassicorpus (Briggs, 1951) .
- Gobiesox daedaleus Briggs, 1951 .
- Gobiesox eugrammus Briggs, 1955 .
- Gobiesox fluviatilis Briggs & Miller, 1960 .
- Gobiesox fulvus Meek, 1907 .
- Gobiesox funebris Gilbert, 1890 .
- Gobiesox juniperoserrai Espinosa Pérez & Castro-Aguirre, 1996 .
- Gobiesox juradoensis Fowler, 1944 .
- Gobiesox lucayanus Briggs, 1963 .
- Gobiesox maeandricus ( Girard , 1858) .
- Gobiesox marijeanae Briggs, 1960 .
- Gobiesox marmoratus Jenyns, 1842 .
- Gobiesox mexicanus Briggs & Miller, 1960 .
- Gobiesox milleri Briggs, 1955 .
- Gobiesox multitentaculus (Briggs, 1951) .
- Gobiesox nigripinnis ( Peters , 1859) .
- Gobiesox papillifer Gilbert, 1890 .
- Gobiesox pinniger Gilbert, 1890 .
- Gobiesox potamius Briggs, 1955 .
- Gobiesox punctulatus ( Poey , 1876) .
- Gobiesox rhessodon Smith, 1881 .
- Gobiesox schultzi Briggs, 1951 .
- Gobiesox stenocephalus Briggs, 1955 .
- Gobiesox strumosus Cope , 1870 .
- Gobiesox varius (Briggs, 1955) .
- Gobiesox woodsi (Schultz, 1944) .
- Genus Gouania
- Gouania willdenowi ( Risso , 1810) .
- Genus Gymnoscyphus
- Gymnoscyphus ascitus Böhlke & Robins, 1970 .
- Genus Lecanogaster
- Lecanogaster chrysea Briggs, 1957 .
- Lecanogaster gorgoniphila Fricke & Wirtz, 2017 .
- Genus Liobranchia
- Liobranchia stria Briggs, 1955 .
- Genus Modicus
- Modicus minimus Hardy, 1983 .
- Modicus tangaroa Hardy, 1983 .
- Genus Nettorhamphos Conway et al., 2017 .
- Nettorhamphos radula Conway et al., 2017 .
- Genus Opeatogenys
- Opeatogenys cadenati Briggs, 1957 .
- Opeatogenys gracilis (Canestrini, 1864) .
- Genus Posidonichthys
- Posidonichthys hutchinsi Briggs, 1993 .
- Genus Propherallodus
- Propherallodus briggsi Shiogaki & Dotsu, 1983 .
- Propherallodus longipterus Fujiwara & Motomura, 2018 .
- Genus Rimicola
- Rimicola cabrilloi Briggs, 2002 .
- Rimicola dimorpha Briggs, 1955 .
- Rimicola Eigenmanni (Gilbert, 1890) .
- Rimicola muscarum (Meek & Pierson, 1895) .
- Rimicola sila Briggs, 1955 .
- Genus Sicyases
- Sicyases brevirostris (Guichenot, 1848) .
- Sicyases hildebrandi Schultz, 1944 .
- Sicyases sanguineus Müller & Troschel, 1843 .
- Genus Tomicodon
- Tomicodon absitus Briggs, 1955 .
- Tomicodon abuelorum Szelistowski, 1990 .
- Tomicodon australis Briggs, 1955 .
- Tomicodon bidens Briggs, 1969 .
- Tomicodon boehlkei Briggs, 1955 .
- Tomicodon briggsi Williams & Tyler, 2003 .
- Tomicodon chilensis Brisout de Barneville, 1846 .
- Tomicodon Clarkei Williams & Tyler, 2003 .
- Tomicodon cryptus Williams & Tyler, 2003 .
- Tomicodon eos ( Jordan & Gilbert, 1882) .
- Tomicodon fasciatus (Peters, 1859) .
- Tomicodon humeralis (Gilbert, 1890) .
- Tomicodon lavettsmithi Williams & Tyler, 2003 .
- Tomicodon leurodiscus Williams & Tyler, 2003 .
- Tomicodon myersi Briggs, 1955 .
- Tomicodon petersii ( Garman , 1875) .
- Tomicodon prodomus Briggs, 1969 .
- Tomicodon reitzae Briggs, 2001 .
- Tomicodon rhabdotus Smith-Vaniz, 1969 .
- Tomicodon rupestris ( Poey , 1860) .
- Tomicodon vermiculatus Briggs, 1955 .
- Tomicodon zebra (Jordan & Gilbert, 1882) .
- Genus Unguitrema Fricke, 2014 .
- Unguitrema nigrum Fricke, 2014 .
- Genus Acyrtops
- Subfamily Haplocyclicinae
- Genus Haplocylix
- Haplocylix littoreus ( Forster , 1801) .
- Genus Haplocylix
- Subfamily Lepadogasterinae
- Genus Apletodon
- Apletodon bacescui (Murgoci, 1940) .
- Apletodon barbatus Fricke, Wirtz & Brito, 2010 .
- Apletodon dentatus (Facciolà, 1887) .
- Apletodon gabonensis ricke & Wirtz, 2018 .
- Apletodon incognitus Hofrichter & Patzner, 1997 .
- Apletodon pellegrini (Chabanaud, 1925) .
- Apletodon wirtzi Fricke, 2007 .
- Genus Diplecogaster
- Diplecogaster bimaculata ( Bonnaterre , 1788) .
- Diplecogaster ctenocrypt Briggs, 1955 .
- Diplecogaster megalops Briggs, 1955 .
- Diplecogaster tonstricula Fricke et al., 2015 .
- Diplecogaster umutturali Bilecenoğlu et al., 2017 .
- Genus Lepadogaster
- Connemara shield belly ( Lepadogaster candolii ) Risso, 1810 .
- Blue-spotted aspirator ( Lepadogaster lepadogaster ) ( Bonnaterre , 1788) .
- Lepadogaster purpurea (Bonnaterre, 1788) .
- Genus Apletodon
- Subfamily Protogobiesocinae Fricke et al., 2016
- Genus Lepadicyathus
- Lepadicyathus mendeleevi Prokofiev, 2005 .
- Genus Protogobiesox Fricke et al., 2016
- Protogobiesox asymmetricus Fricke et al., 2016
- Genus Lepadicyathus
- Subfamily Trachelochisminae
- Genus Conidens
- Conidens laticephalus (Tanaka, 1909) .
- Conidens samoensis ( Steindachner , 1906) .
- Genus Dellichthys
- Dellichthys morelandi Briggs, 1955 .
- Dellichthys trnskii Conway et al., 2018 .
- Genus Kopua
- Kopua japonica Moore, Hutchins & Okamoto, 2012 .
- Kopua kuiteri Hutchins, 1991 .
- Kopua nuimata Hardy, 1984 .
- Kopua vermiculata Shinohara & Katayama, 2015 .
- Kopua yoko Fujiwara et al., 2018 .
- Genus Trachelochism
- Trachelochism aestuarium Conway et al., 2017 .
- Trachelochism melobesia Phillipps, 1927 .
- Trachelochism pinnulatus ( Forster , 1801) .
- Genus Conidens
literature
- Joseph S. Nelson : Fishes of the World , John Wiley & Sons, 2006, ISBN 0-471-25031-7
Individual evidence
- ↑ Ricardo Betancur-R, Edward O. Wiley, Gloria Arratia, Arturo Acero, Nicolas Bailly, Masaki Miya, Guillaume Lecointre and Guillermo Ortí: Phylogenetic classification of bony fishes . BMC Evolutionary Biology, BMC series - July 2017, DOI: 10.1186 / s12862-017-0958-3
- ↑ Conway, KW, Moore, GI & Summers, AP (2019): A new genus and two new species of miniature clingfishes from temperate southern Australia (Teleostei, Gobiesocidae). ZooKeys , 864: 35-65.
- ↑ Kevin W. Conway, Andrew L. Stewart and Adam P. Summers. 2018. A New Genus and Species of Clingfish from the Rangitāhua Kermadec Islands of New Zealand (Teleostei, Gobiesocidae). ZooKeys . 786: 75-104. DOI: 10.3897 / zookeys.786.28539
- ↑ Fricke, R., Chen, J.-N. & Chen, W.-J. (2016): New case of lateral asymmetry in fishes: A new subfamily, genus and species of deep water clingfishes from Papua New Guinea, western Pacific Ocean. Comptes Rendus Biologies, December 2016. doi: 10.1016 / j.crvi.2016.11.002
Web links
- Tortoiseshell on Fishbase.org (English)