Spinosad
Spinosad is an insecticide obtained from the actinomycete Saccharopolyspora spinosa and consists of Spinosyn A and D. The spinosyns consist of a ring of four on an amino sugar ( D - forosamine ) and a neutral sugar (tri- Ο -methyl- L - rhamnose ). There are around 200 synthetic and 20 different natural Spinosyns (e.g. Spinetoram ).
composition
Spinosad is a mixture of spinosyns A and D in a ratio of approximately 5: 1.
| Spinosad | ||
| Surname | Spinosyn A | Spinosyn D. |
| Structural formula | 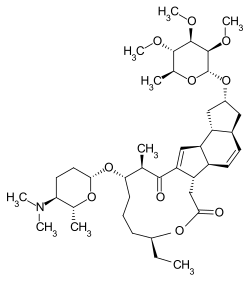 |

|
| CAS number | 131929-60-7 | 131929-63-0 |
| PubChem | 443059 | 183094 |
| Molecular formula | C 41 H 65 NO 10 | C 42 H 67 NO 10 |
| Molar mass | 732 g mol −1 | 746 g mol −1 |
| Physical state | firmly | |
| Melting point | 84-99.5 ° C | 161.5-170 ° C |
| solubility |
|
|
The commercial product is a solid with a slightly earthy odor, has a density of 0.512 g · cm −3 (at 20 ° C) and decomposes at 173 ° C.
use
| safety instructions | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surname |
Spinosad (mixture of Spinosyn A and Spinosyn D in a ratio of 95: 5 to 50:50) |
||||||
| CAS number |
131929-60-7 (Spinosyn A), |
||||||
|
|||||||
Plant protection
Spinosad acts as a contact poison as well as a food poison and is used in plant protection against thrips , fruit peel moth , leaf miners and other caterpillar species . It is also suitable for combating the cherry vinegar fly ( Drosophila suzukii ).
The active ingredient spinosad was approved for use as an insecticide in crop protection products in the European Union with effect from February 1, 2007. Use in organic farming according to the EU organic seal and Bavarian organic seal is permitted, but not according to the guidelines of Biokreis , Bioland and demeter . The agent is often used to control the Colorado potato beetle . Spinosad preparations are, however, classified as dangerous to bees ( bee risk level B1).
In many EU countries, including Germany and Austria, as well as Switzerland, plant protection products with the active ingredient Spinosad are approved ( Conserve , Success , SpinTor ).
House
Use as an active ingredient of insecticide-containing bait gels, e.g. B. against ants in the house.
Medicine and veterinary medicine
In veterinary medicine, Spinosad is used against ectoparasites such as fleas and lice .
The American FDA approved Spinosad in 2011 for the treatment of head lice in children aged four and over.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on Spinosad in Pharmawiki , accessed on January 28, 2017.
- ↑ External identifiers or database links for Spinosyn A : CAS number: 131929-60-7, EC number: 620-162-1, ECHA InfoCard: 100.113.980 , PubChem : 443059 , ChemSpider : 391358 , Wikidata : Q27108323 .
- ↑ External identifiers or database links to Spinosyn D : CAS number: 131929-63-0, EC number: 620-407-2, ECHA InfoCard: 100.149.200 , PubChem : 183094 , ChemSpider : 159214 , Wikidata : Q27108325 .
- ↑ a b c d Spinosad Technical Bulletin , p. 3 (PDF; 1.4 MB).
- ↑ International Chemical Safety Card (ICSC) for Spinosad at the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), accessed December 9, 2014.
- ↑ Entry on Spinosad (mixture of Spinosyn A and Spinosyn B in a ratio of 95: 5 to 50:50) (Spinosyn D is referred to here as Spinosyn B) in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on May 3, 2013(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Spinosad data sheet at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on June 1, 2018 ( PDF ).
- ^ Spinosad. Julius Kühn Institute , accessed June 20, 2018 .
- ↑ Directive 2007/6 / EC of the Commission of February 14, 2007 amending Council Directive 91/414 / EEC to include the active substances Metrafenone, Bacillus subtilis, Spinosad and Thiamethoxam .
- ↑ Regulation (EC) No. 889/2008 of the Commission of September 5, 2008 with implementing provisions for Regulation (EC) No. 834/2007 of the Council on organic production and the labeling of organic products with regard to organic Production, labeling and control .
- ↑ Biokreis guidelines for processing. In: biokreis.de. Retrieved May 24, 2017 .
- ↑ Comparison of Bioland guidelines / EU organic regulation (PDF; 346 kB) In: bioland.de . August 3, 2017. Archived from the original on March 26, 2017. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
- ↑ Difference between organic and Demeter . In: demeter.de . October 2017. Retrieved July 1, 2018.
- ↑ FiBL : Colorado beetle: Neem and Spinosad approved with immediate effect. bioaktuell.ch, June 13, 2018, accessed on June 20, 2018 .
- ↑ Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Spinosad in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on February 23, 2016.
- ↑ entry to spinosad in Vetpharm, accessed June 23, 2013.
- ↑ COMFORTIS- spinosad tablet, chewable . DailyMed .
- ↑ Deutsches Ärzteblatt: Spinosad: Ökogarten-Poison against hair lice , January 19, 2011.
- ↑ NATROBA- spinosad suspension . DailyMed .
