Thallium (III) oxide
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
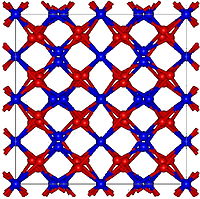
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Thallium (III) oxide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Dithallium trioxide |
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | Tl 2 O 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
brown to black solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 456.76 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
10.11 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
717 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
875 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Thallium (III) oxide is a chemical compound from the group of oxides of thallium .
Occurrence
Thallium (III) oxide occurs naturally in the form of the very rare mineral avicennite .
Extraction and presentation
Thallium (III) oxide can be obtained by reacting thallium (I) nitrate with potassium hydroxide and chlorine , whereby the red-brown thallium (III) oxide hydrate with the approximate composition Tl 2 O 3 · 1.47 H 2 O is formed, which can be converted into the anhydrous form by vacuum desiccation .
properties
Thallium (III) oxide is a brown to black (depending on the presentation conditions) solid that is insoluble in water. It has a defect structure of calcium fluoride type ( a = 10.543 Å). Above 500 ° C and 65 kBar it takes on a crystal structure of the corundum type. In contrast to the "isoelectronic" lead (IV) oxide , thallium (III) oxide is only a moderate oxidizing agent and only decomposes to thallium (I) oxide and oxygen at high temperatures .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Georg Brauer (Ed.), With the collaboration of Marianne Baudler a . a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume II, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1978, ISBN 3-432-87813-3 , p. 884.
- ↑ a b EPA: Toxicological Review of Thallium and Compounds (PDF; 1.1 MB)
- ↑ a b c data sheet Thallium (III) oxide, 99.99% trace metals basis from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on December 1, 2019 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Not explicitly listed in Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008 (CLP) , but with the specified labeling it falls under the group entry thallium compounds, with the exception of those specified elsewhere in this Annex in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA ), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ^ Mineral Atlas: Avicennit
- ^ A b Anthony John Downs: Chemistry of aluminum, gallium, indium, and thallium , p. 286; ISBN 978-0751401035
- ↑ Peter Paetzold; Chemie, p. 205; ISBN 978-3110202687



