Thiocyanic acid methyl ester
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
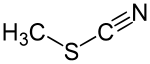
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Thiocyanic acid methyl ester | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 3 NS | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with an onion-like odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 73.12 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.07 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−5 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
131 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
16.1 hPa (25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.469 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Thiocyanic acid methyl ester is a chemical compound from the group of thiocyanates . It is isomeric to methyl isothiocyanate .
Occurrence
Thiocyanic acid methyl ester occurs naturally in Chinese cabbage .
Extraction and presentation
Thiocyanic acid methyl ester is formed when methionyl residues in proteins are broken down with cyanogen bromide .
It can also be obtained by reacting methylamine with carbon disulfide and ethyl chlorocarbonate, or dimethyl sulfate with barium thiocyanate .
properties
Thiocyanic acid methyl ester is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with an onion-like odor that is practically insoluble in water.
use
Thiocyanic acid methyl ester is used as an insecticide and fumigant, and as an intermediate in the synthesis of isothiocyanates and other chemical compounds.
safety instructions
The vapors of thiocyanic acid methyl ester can form an explosive mixture with air ( flash point 38 ° C).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l Entry on methyl thiocyanate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 9, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Entry on methyl thiocyanate in the Hazardous Substances Data Bank , accessed on August 4, 2016.
- ↑ Data sheet Methyl thiocyanate, 97% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on August 2, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Hubert Siegl: Volatile aromatic substances of Chinese cabbage (Brassica pekinensis [Lour.] Rupr.): Dependence on varieties . Herbert Utz Verlag, 1999, ISBN 978-3-89675-579-7 ( books.google.com ).
- ↑ D. Gröger, J. Harkin, F. Bohlmann, H. Muirhead, G. Bodo: Naturstoffe . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-662-25280-2 ( books.google.com ).
- ^ Maurice L. Moore, Frank S. Crossley: METHYL ISOTHIOCYANATE In: Organic Syntheses . 21, 1940, p. 81, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.021.0081 ; Coll. Vol. 3, 1955, p. 599 ( PDF ).
- ^ Stanley A. Greene: Sittig's Handbook of Pesticides and Agricultural Chemicals . William Andrew, 2013, ISBN 978-0-8155-1903-4 ( books.google.com ).
- ↑ Houben-Weyl Methods of Organic Chemistry Vol. E 9c, 4th Edition Supplement: Hetarenes III . Georg Thieme Verlag, 2014, ISBN 978-3-13-181514-9 , p. 513 ( limited preview in Google Book search).

