Translohr
Translohr is a public transport system originating from France , which is a Tramway sur pneumatiques , French for tram on pneumatic tires or rubber- tire tram . Low -floor bidirectional vehicles run on their own routes and are permanently tracked by a centrally arranged guide rail . The system was developed by the French company Lohr Industrie , sold to Alstom (51 percent) and the French state investment bank Bpifrance (49 percent) in 2012 and is now held by NewTL SAS, which operates under the name NTL.
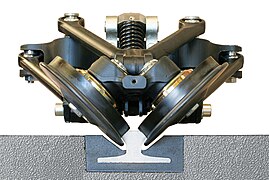
principle
The railcars are articulated vehicles that run exclusively on a central track - also in the depot and in the workshop - and the cars are not freely steerable. The track is guided by two inclined wheels, each with a flange , which are at an angle of 90 degrees to each other and laterally engage in the guide rail. The maximum speed is 70 kilometers per hour.
The vehicles run with 750 volts direct current under a single-pole overhead contact line and each have a single-arm pantograph , the return current flows over the guide rail. If necessary, they could also be used in multiple traction, although this has not yet been practiced. Similar to the ultra-low-floor tram, the wheels are housed in the articulated portals, which both optimizes the clearance profile of the car and allows the interior to be designed more flexibly without platforms . In addition, the Translohr has a traction battery . With this he can cover shorter distances without power supply from the overhead line in the event of operational disruptions.
The vehicles produced so far are only 2.20 meters wide. Your seat distribution is therefore 2 + 1, with wider seats being used for the joints. The manufacturer also offers the Translohr with a 2.40 or 2.65 meter wide car body . The floor height is 25 centimeters above the road surface. The following configurations are possible (capacity four people per square meter):
- STE3: three-part, four-axle, 25 meters long, 127 people
- STE4: four-part, five-axis, 32 meters long, 170 people
- STE5: five-part, six-axle, 39 meters long, 213 people
- STE6: six-part, seven-axle, 46 meters long, 255 people
So far, only bidirectional vehicles have been manufactured, but the Translohr is also offered as a one-way vehicle .
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of the Translohr system over conventional trams are smaller minimum radii and thus less space required, as well as steeper possible gradients - for example in the area of tunnel ramps - and lower construction costs. Compared to the trolleybus , the exact track guidance results in a smaller space requirement. Nevertheless, if vehicles are used for a correspondingly long period, the capacity can be greater. The bi-directional design of the vehicles enables end stations with little space requirement, i.e. without turning loops .
On the other hand, it is often criticized that the system combines the disadvantages of the tram (high costs for the route, separate route required) with those of the bus (concrete route required instead of grass track, higher energy consumption and larger space requirements for the wheels in the car).
A sensible use arises accordingly in difficult route conditions, but where the high capacity of the tram is still required.
Establishments
So far, eight Translohr systems with a total length of around 85 kilometers have been put into operation with a total of 134 vehicles. With the exception of Venice, every system built so far consists of only one line :
| image | country | place | opening | length | Stops | number of vehicles | Vehicle type | Article / remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|
Clermont-Ferrand | October 14, 2006 | 15.4 km | 34 | 26th | STE4 | Translohr Clermont-Ferrand |

|
|
Tianjin | December 6, 2006 | 7.86 km | 14th | 8th | STE3 | Translohr Tianjin |

|
|
Padua | March 24, 2007 | 10.3 km | 25th | 16 | STE3 | About 600 meters of catenary-free route that is driven through in battery mode |

|
|
Shanghai | July 1, 2009 | 9.8 km | 15th | 9 | STE3 | |

|
|
Venice | December 19, 2010 | T1: 14 km T2: 6 km |
T1: 23 T2: 17 |
20th | STE4 | in the area of the railway station Mestre an underground station, see tram Venice |

|
|
Saint-Denis - Garges-lès-Gonesse | July 29, 2013 | 6.6 km | 16 | 15th | STE3 | Line 5 of the Paris tram |

|
|
Châtillon - Viroflay | December 13, 2014 | 14.0 km | 23 | 28 | STE6 | Line 6 of the Paris tram , in Viroflay there are two underground stations |

|
|
Medellin | 15th October 2015 | 4.3 km | 9 | 12 | STE5 | Ayacucho tram |
|
|
L'Aquila | canceled | 7.5 km | 16 | 7th | STE3 | Not pursued due to the 2009 earthquake |
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ https://www.alstom.com/press-releases-news/2012/6/alstom-and-the-fonds-strategique-dinvestissement-fsi-have-reached-an-agreement-with-lohr-industrie-for -the-acquisition-of-translohr ; accessed December 13, 2019
- ^ Universität Karlsruhe: Transport in Europe - Intermodality between Germany, France and Switzerland ( Memento from October 29, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF; 2 MB)
- ↑ railway-technology.com of October 26, 2015: Medellin starts commercial operations on Ayacucho tramway line, accessed on January 12, 2016
- ↑ Pictures of the dismantling of already laid guardrails and overhead lines