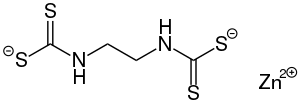
Zineb
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Zineb | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | (C 4 H 6 N 2 S 4 Zn) x | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
flammable, yellow, crystalline powder |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 275.76 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.74 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
157 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
1.07 · 10 −5 Pa (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water (10 mg l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Zineb is a chemical compound from the group of dithiocarbamates . It is in the form of a crystalline powder.
Extraction and presentation
Zineb can be obtained by reacting Nabam with zinc sulfate .
properties
Zineb is a polymeric complex of zinc and bis (dithiocarbamate). The polymer consists of Zn (dithiocarbamate) 2 subunits that are bound to an ethene backbone. A reference compound is [Zn (S 2 CN (C 2 H 5 ) 2 ) 2 ] 2 , which has a pair of tetrahedral zinc centers that are bridged by a sulfur atom.
use
Zineb has been used as a broadly effective plant protection product (foliar fungicide ) on a number of fruits and vegetables. It has also been used with other combinations of similar active substances (e.g. as Metiram ). The approval as a plant protection product was revoked in 2001 in the EU and Switzerland. Zineb is used as a biocide in antifouling products. It has been included in the EU test program for use in product type 21.
safety instructions
Zineb is only slightly toxic, but hormonally effective.
proof
Zineb can be detected by HPLC , whereby similar thiocarbamates can be distinguished by subsequent atomic spectroscopy and the mixing ratio can be determined.
Web links
- Joint Meeting on Pesticide Residues (JMPR), Monograph for Zineb
- Entry for Zineb in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB) of the University of Hertfordshire
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on Zineb in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ^ Howard, PH, Editor (1991) Handbook of Fate Exposure Data for Organic Chemicals. Vol. III. Pesticides. Lewis Publishers, Inc., Chelsea, Michigan.
- ↑ Entry on Zineb in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ a b Extoxnet: Zineb Toxicologic Informations .
- ↑ Ullmann's Agrochemicals, Wiley-VCH Staff, Wiley-Vch (COR), 2007, ISBN 3-527-31604-3 .
- ↑ M. Genchev, K. Davarski: Structure of some metal complexes of ethylenediaminebis (dithiocarbamate) used as active fungicides . Burgas 1978, 13, Pt. 1, 39-44.
- ↑ M. Bonamico, G. Mazzone, A. Vaciago, L. Zambonelli: Structural studies of metal dithiocarbamate. III. The crystal and molecular structure of zinc diethyldithiocarbamate. In: Acta Crystallographica. 19, 1965, pp. 898-909, doi : 10.1107 / S0365110X65004620 .
- ↑ Decision of the Commission of March 22, 2001 on the non-inclusion of the active ingredient Zineb in Annex I of Council Directive 91/414 / EEC and the cancellation of the authorizations for plant protection products containing this active ingredient . In: Official Journal of the European Communities .
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Zineb in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on March 11, 2016.
- ↑ Regulation (EC) No. 2032/2003 of the Commission of November 4, 2003 on the second phase of the ten-year work program in accordance with Article 16 (2) of Directive 98/8 / EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on the placing of biocides on the market -Products and amending Regulation (EC) No. 1896/2000 . In: Official Journal of the European Union .
- ↑ Chi-Chu Lo, Ming-Hsun Ho, Ming-Der Hung: Use of High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic and Atomic Absorption Methods To Distinguish Propineb, Zineb, Maneb, and Mancozeb Fungicides. In: Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 44, 1996, p. 2720, doi : 10.1021 / jf960008l .

