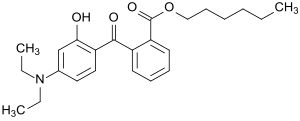
2- (4- (Diethylamino) -2-hydroxybenzoyl) benzoic acid hexyl ester
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Hexyl 2- [4- (diethylamino) -2-hydroxybenzoyl] benzoate | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 24 H 31 NO 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
almost white fine powder |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 397.52 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.156 g cm −3 (20 ° C ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
54 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
Slightly soluble in water (0.01 g · l −1 ), soluble in oils, such as B. Olive oil (25%) and in Finsolv® EB (ethylhexyl benzoate, 56%) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
2- [4- (Diethylamino) -2-hydroxybenzoyl] benzoic acid hexyl ester or diethylamino hydroxybenzoyl hexyl benzoate ( INCI ) or DHHB is an asymmetrically substituted benzophenone which, like the more simply structured oxybenzone, is used as a UV filter in sunscreens . While the benzophenone structural unit is responsible for UV absorption , the hydrophobic substituents ensure oil solubility and water resistance in dermatological and cosmetic preparations. DHHB has a relatively broad UV absorption spectrum with an absorption maximum λ max in the UV-A range at 354 nm.
presentation
In the two-step synthesis of 2- [4-diethylamino-2-hydroxybenzoyl] benzoic acid hexyl ester is first 3-diethylaminophenol with phthalic anhydride in 90% yield to 2- (diethylamino-2-hydroxybenzoyl) benzoic acid and then reacted with n-hexanol in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid esterified in practically quantitative yield.
DHHB is produced as a yellow, sticky oil which, after cleaning with activated charcoal and carefully removing solvent residues, crystallizes as an almost white, fine powder.
properties
2- [4- (Diethylamino) -2-hydroxybenzoyl] benzoic acid hexyl ester DHHB dissolves in alcohols and oils such as those used for cosmetic preparations. The benzophenone derivative DHHB is extremely photostable and, unlike other UV filters, does not form any toxic or allergenic photodegradation products. However, the biodegradability in surface waters appears to be critical after traces of DHHB have been detected in seawater on beaches in Gran Canaria .
use
2- [4- (Diethylamino) -2-hydroxybenzoyl] benzoic acid hexyl ester DHHB is with a specific extinction coefficient of 940 at a UV-A absorption maximum of 354 nm (under standard conditions in ethanol ) a strong UV-AI absorber (in the range 340-400 nm), which also shows high absorption capacity in the UV-AII range (315–340 nm) up to approx. 330 nm. In dermal preparations, DHHB does not penetrate through intact skin, but remains in the outer layer ( stratum corneum ).
Since it is compatible with other sunscreens and can be formulated into stable preparations for topical applications with common auxiliaries , DHHB (in a maximum concentration of 10 percent by weight in the oil phase) is found as a UVA filter in sunscreens and increasingly also in cosmetic anti-aging products . It is mostly used in combination with other UV filters, some of which are stabilized by DHHB.
In the USA, sunscreens, as OTC drugs, are subject to the specifications of the US drug agency FDA , which has not approved any new active ingredients for sunscreens for more than ten years. Despite the so-called Time and Extend Applications (TEA) introduced in 2002 to accelerate the approval process and the so-called Sunscreen Innovation Act (SIA) enacted at the end of 2014, a total of eight modern sunscreens approved in Europe and other regions are not in the USA for the time being available. In 2018, the state of Hawaii issued a legal ban on the UV filters oxybenzone and octinoxate commonly used in the USA from 2021 on account of their damaging effects on corals. An application for approval for Diethylamino hydroxybenzoyl hexylbenzoate DHHB is being considered by the manufacturer.
Diethylamino hydroxybenzoyl hexylbenzoate is sold by BASF SE under the brand name Uvinul® A Plus and by the Chinese company MFCI Co., Ltd. manufactured and sold under the name MFSORB 512.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on DIETHYLAMINO HYDROXYBENZOYL HEXYL BENZOATE in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on February 13, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet Diethylamino hydroxybenzoyl hexyl benzoate from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on January 10, 2020 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d e f Opinion on Diethylamino hydroxybenzoyl hexyl benzoate, Colipa No. S83. (PDF) Scientific Committee on Consumer Products (SCCP), April 15, 2008, accessed January 10, 2020 .
- ↑ Ethylhexyl Benzoate, FinsolvR EB. (PDF) innospec, January 2009, accessed on January 10, 2020 .
- ↑ Entry on hexyl 2- (1- (diethylaminohydroxyphenyl) methanoyl) benzoate in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on January 12, 2020. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Patent EP1506159B1 : Process for the preparation of 2- [4-N, N-dialkylamino-2-hydroxybenzoyl] benzoic acid esters. Registered on May 12, 2003 , published on September 19, 2007 , applicant: BASF AG, inventor: T. Heidenfelder, K. Beck.
- ↑ a b C.M. Kawakami, LN Máximo, BB Fontanezi, RS da Silva, LR Gaspar: Diethylamino hydroxybenzoyl hexyl benzoate (DHHB) as additive to the UV filter avobenzone in cosmetic sunscreen formulations - Evaluation of the photochemical behavior and photostabilizing effect . In: Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. tape 99 , 2017, p. 299–309 , doi : 10.1016 / j.ejps.2016.12.031 .
- ↑ Impacts of sunscreens on coral reefs. (PDF) incri, February 2018, accessed on January 10, 2020 .
- ↑ T. Haque, JM Crowther, ME Lane, DJ Moore: Chemical ultraviolet absorbers topically applied in a skin barrier mimetic formulation remain in the outer stratum corneum of porcine skin . In: Int. J. Pharm. Volume 510 , no. 1 , 2016, p. 250-254 , doi : 10.1016 / j.ijpharm.2016.06.041 .
- ↑ a b Sun Protection inspired by life. (PDF) BASF, 2013, accessed on February 22, 2020 .
- ↑ a b M. S. Reisch: After More Than A Decade, FDA Still Won't Allow New Sunscreens . In: Chemical & Engineering News . tape 93 , no. 20 , 2015, p. 10-15 ( acs.org ).
- ^ U. Osterwalder: US with a gap in UVA protection . In: COSSMA . tape 1–2 , 2016, pp. 16-18 ( cossma.com [PDF]).
- ↑ Rulemaking History for OTC Sunscreen Drug Products. In: fda.gov. Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, 2019, accessed February 22, 2020 .
- ^ Sunscreen Innovation Act (SIA). In: fda.gov. Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, 2018, accessed February 22, 2020 .
- ↑ Rebecca Trager: Hawaii set for first ever ban on two sunscreen ingredients. In: chemistryworld.com. May 9, 2018, accessed January 10, 2020 .
![Synthesis of 2- [4- (diethylamino) -2-hydroxybenzoyl] benzoic acid hexyl ester](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/13/DHHB-Synthese.svg/450px-DHHB-Synthese.svg.png)