3-diethylaminophenol
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 3-diethylaminophenol | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 15 NO | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
gray to red-brown solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 165.24 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.0203 g cm −3 at 20 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
65-78 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point | |||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water, ethanol , diethyl ether , carbon disulfide , petroleum ether |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4620 (25 ° C, 589 nm) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
3-diethylaminophenol is a phenol having a diethylamino group at the meta-position to the hydroxy group . The compound serves as a starting material for dyes (especially fluorescent dyes ) and pigments , for printing inks , tattoo inks and hair dyes , as well as for UV filters .
Occurrence and representation
The synthesis of 3-diethylaminophenol, referred to here as "diethyl meta-amidophenol", was first described in 1888.
It was 3-aminophenol under pressure at 170 ° C and ethanol as the ethylating agent reacted and the pure product by extraction , distillation and repeated recrystallization obtained as a white crystalline material (mp. 74 ° C).
Because of the importance of the N, N -dialkylaminophenols, different synthesis routes have been worked out - starting from the simple aromatics nitrobenzene or aniline or phenol - which, however, due to the formation of large amounts of salt (e.g. in the alkali melt of 3-dialklyaminobenzenesulfonic acids), are corrosive Reactants and poor yields could not prevail.
A more modern process suggests inexpensive resorcinol as the starting compound , with 3-diethylaminophenol also being obtained analogously to the 3-dibutylaminophenol described.
The primary amine in the presence of phosphonic acid H 3 PO 3 as reducing agent is used to first substitute one of the two hydroxyl groups on the 1,3-dihydroxybenzene and then to alkylate this with the corresponding alkyl halide to form the secondary amine. The specified conditions (200 ° C temperature, 12 bar pressure, 6h reaction time in the first and 6-20h in the second stage), large amounts of salt and yields below 70% make this reaction path seem unsuitable for an industrial process.
Starting from 3-aminophenol (e.g. from resorcinol and ammonia at 230 ° C. and 35 bar), which is subjected to reductive alkylation with acetaldehyde under 10 bar hydrogen pressure in the presence of palladium on activated carbon , 3-diethylaminophenol can also be used in a continuous Process can be obtained in yields of up to 95%.
properties
3-Diethylaminophenol is a white-gray to red-brown crystalline solid with a pungent odor that dissolves in water, ethanol and diethyl ether.
Applications
The reaction of 3-diethylaminophenol with acetoacetic ester in the presence of zinc chloride / tin (II) chloride gives the coumarin derivative 7-diethylamino-4-methylcoumarin,
which is used as an optical brightener for textiles and as a laser dye .
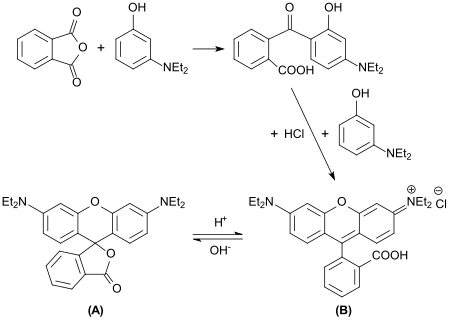
When 3-diethylaminophenol is reacted with phthalic anhydride , 2- (4- (diethylamino) -2-hydroxybenzoyl) benzoic acid is formed, the n-hexyl ester DHHB of which is added as a UV-A filter to sunscreens under the name Uvinul A Plus .
If double-stoichiometric amounts of 3-diethylaminophenol are used in this reaction, then rhodamine B , a fluorescent dye from the series of xanthene dyes, is obtained . - still called "tetraethyl-rhodamine" here.
While the lactone form ( A ) is colorless and does not fluoresce, aqueous solutions of the cationic ring-open acid form ( B ) show an intense carmine-red color and orange-red fluorescence.
From 3-diethylaminophenol and diphenyl malonate, 7-diethylamino-4-hydroxycoumarin is produced, from which, through reaction with the DHHB precursor, deep red fluorescent dyes can be obtained that can be used as biomarkers and biosensors .
Basic substituted 1,4-oxazines or phenoxazines , such as. B. the cationic dye Basic Blue 3 , were already at the end of the 19th century - starting from 3-diethylaminophenol - as blue textile dyes, especially for polyacrylonitrile fibers, synthesized.
The ethyl ether of 3-diethylaminophenol reacts in dioxane solution with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid to form 6-nitroso-3-diethylaminophenol , which is then reacted with further 3-diethylaminophenol in approx. 80% yield to form the phenoxazine derivative, which is green in substance. The ethoxy group is split off as ethanol in the condensation reaction to form the phenoxazine ring system.
The reaction of the nitroso derivative of 3-diethylaminophenol with 1-naphthylamine produces the fluorescent dye Nile blue , which changes to Nile red when heated with sulfuric acid .
Nile red can also be formed directly from 3-diethylaminophenol and 2-naphthol .
Because of the importance of the dyes Nile blue and Nile red in biology - starting from 3-diethylaminophenol - a large number of benzophenoxazines were synthesized, e.g. Sometimes also with active ester functions for covalent linkage with biomolecules.
Dichroic dyes by reacting 3-diethylaminophenol with tetrachloro-p-benzoquinone have been proposed as mixture components in so-called guest-host displays of liquid crystal displays because of their high absorption coefficient for contrast improvement.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Data sheet 3-Diethylaminophenol from Acros, accessed on January 13, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d Entry on 3-diethylaminophenol in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 13, 2020 (JavaScript required)
- ^ A b c William M. Haynes: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 97th Edition . CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA 2017, ISBN 978-1-4987-5429-3 , pp. 3-174 .
- ↑ a b c Patent US377350 : Production of new red coloring matter. Registered on November 17, 1887 , published on January 31, 1888 , applicant: Badische Anilin und Soda Fabrik, inventor: M. Ceresole.
- ↑ Patent DE4116830A1 : Process for the preparation of N, N-disubstituted m-aminophenols. Applied on May 23, 1991 , published on November 26, 1992 , applicant: BASF AG, inventor: M. Hauptreif, H. Reichelt.
- ↑ Patent EU0197633A1 : Method for the production of m-aminophenol. Applied on February 12, 1986 , published October 15, 1986 , Applicant: Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd., Inventor: H. Harada, H. Maki, S. Sasaki.
- ↑ Patent US5276193 : Process for preparing N-alkyl-substituted aminophenols. Applied on August 1, 1990 , published on April 1, 1994 , Applicants: Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd., Inventors: H. Maki, M. Kawasaki, H. Shimizu, Y. Ito.
- ↑ K. Venkataraman (ed.): The Chemistry of Synthetic dyes, Volume V . Elsevier, Inc., Amsterdam 1971, ISBN 978-0-12-717005-3 , pp. 599-600 .
- ^ R. Möhlau, K. Uhlmann: On the knowledge of the quinazin and oxazine dyes . In: Liebigs Ann. Chem. Band 289 , no. 1 , 1896, p. 90-130 , doi : 10.1002 / jlac.18962890112 .
- ↑ Patent US4196286 : Process for the manufacture of basic oxacine dyes. Applied December 21, 1977 , published April 1, 1980 , applicant: Ciba-Geigy Corp., inventor: E. Brunn.
- ↑ Patent US3655601 : Process for the manufacture of basic oxazine dyestuffs. Applied on February 13, 1969 , published on April 11, 1972 , applicant: Farbwerke Hoechst AG, inventor: N. Ottawa, G. Schäfer.
- ^ J. Jose, K. Burgess: Benzophenoxazine-based fluorescent dyes for labeling biomolecules . In: Tetrahedron . tape 62 , no. 48 , 2006, p. 11021–11037 , doi : 10.1016 / j.tet.2006.08.056 .
- ↑ Patent US6703084B2 : Quinone compound, liquid crystal composition, and guest-host-type liquid crystal cell employing the same. Applied on April 19, 2002 , published on March 9, 2004 , applicant: Fuji Photo Film Co., Ltd., inventor: T. Katoh.