9,10-dihydro-9-oxa-10-phosphaphenanthrene-10-oxide
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 9,10-dihydro-9-oxa-10-phosphaphenanthrene-10-oxide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 9 O 3 P | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white crystal powder |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 216.18 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.37 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point | ||||||||||||||||
| boiling point | ||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
very soluble in methanol , ethanol , chloroform , dioxane , dimethylformamide , soluble in benzene and toluene , practically insoluble in water and n -hexane |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.645 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
9,10-Dihydro-9-oxa-10-phosphaphenanthrene-10-oxide is a phosphinic acid ester in which a phosphorus and an oxygen atom are integrated into the basic structure of a phenanthrene . The compound has flame-retardant properties and is the parent compound for a large number of highly effective halogen-free flame retardants for thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics.
Manufacturing
The synthesis of 9,10-dihydro-9-oxa-10-phosphaphenantren-10-oxide was first mentioned in 1972 in the patent literature, but not described in the examples.
In the reaction of 2-phenylphenol with phosphorus trichloride in the presence of the Lewis acid , zinc chloride is produced at high temperatures (about 180 ° C) under elimination of hydrogen chloride is also known as DOP-Cl designated 6-chloro- (6 H ) dibenz [ c , e ] [1,2] -oxaphosphorine in 96% yield. The conversion of the DOP-Cl to DOPO takes place by heating with water first to 110 ° C., then to 180 ° C., DOPO being obtained quantitatively in high purity.
The hydrolysis of DOP-Cl with dilute hydrochloric acid and subsequent distillation in vacuo gives DOPO in a very high yield (98%) and excellent purity (99.25%).
properties
9,10-Dihydro-9-oxa-10-phosphaphenantren-10-oxide is a solid that is obtained as a white crystalline powder during synthesis. The compound is practically insoluble in water, but dissolves in many organic solvents. The 6 H -dibenzo [ c , e ] [1,2] oxaphosphorin-6-one (tautomer I) is in tautomeric equilibrium with 6-hydroxy- (6 H ) -dibenzo [ c , e ] [1,2] oxaphosphorin (Tautomer II) before and hydrolyzed with ring cleavage to 2'-hydroxydiphenyl-2-phosphinic acid.
Applications
9,10-Dihydro-9-oxa-10-phosphaphenantren-10-oxide is used as a halogen-free flame retardant u. a. in polyolefins and epoxy resins - often in mixtures with others, e.g. B. intumescent fire retardant agents - used. The flame-retardant effect is attributed to the formation of reactive radicals of the PO • and HPO • type in the gas phase formed during the pyrolysis of the material ( gas phase mechanism ). Disadvantageous properties of DOPO as a flame retardant are its tendency to hydrolyze and its relatively low decomposition temperature (<200 ° C), which makes it unsuitable for protecting many thermoplastic polymers that can only be processed at temperatures above 200 ° C. The most precise coordination of the decomposition points of additives and polymers is crucial for the flame-retardant effect, since extremely high-melting flame retardants in the range of the decomposition temperature of the polymer may not yet form any (or too few) reactive radicals in the gas phase.
In recent years, a number of DOPO derivatives, especially for use in epoxy resins for electrical and electronic applications, have been synthesized that are hydrolysis-stable and have significantly higher melting points (up to 320 ° C).
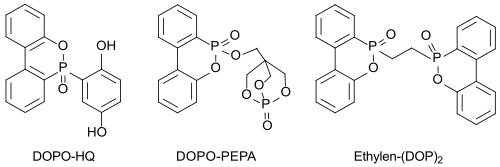
Bifunctional derivatives (such as DOPO-HQ), which can be incorporated into the polymer chain, preventing segregation and diffusion of the flame retardant, are also of interest. However, the incorporation usually leads to an undesirable lowering of the glass transition temperature T g of the polymer, which should not be the case with the compound DOPO-HQ.
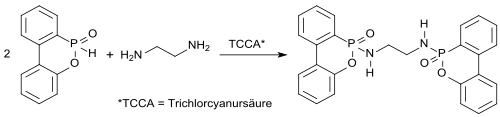
Effective high-melting nitrogen-containing DOPO derivatives such as EDA-DOPO , whose flame-retardant effect could play a role in the flame-retardant effect of these , synergies between phosphorus and nitrogen appear to be particularly suitable even with small amounts added (<5%) .
DOPO is also used in a variety of polymers, such as B. ABS ( acrylonitrile butadiene styrene ), polypropylene , phenolic resins or alkyd resins are added to protect against discoloration. DOPO has an anti-corrosive effect and inhibits the oxidation of copper . Because of its simple functionalization and its planar molecular shape, DOPO is suitable as a starting material for organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs).
literature
- Edward D. Weil, Sergei V. Levchik: Flame retardants for Plastics and Textiles - Practical Applications, 2nd edit. Carl Hanser, Munich 2015, ISBN 978-1-56990-578-4 .
- Rudolf Pfaendner, Manfred Döring: Eco-Friendly Fire Prevention . In: Kunststoffe International . Carl Hanser, Munich 2014 ( fraunhofer.de [PDF]).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Entry on 9,10-Dihydro-9-oxa-10-phosphaphenanthrene-10-oxide at TCI Europe, accessed on May 25, 2018.
- ↑ a b c d e HCA. Sanko Co., Ltd., accessed May 25, 2018 .
- ↑ a b c Patent US20110034717A1 : Method for synthesizing 9,10-dihydro-9-oxa-10-phosphaphenanthrene-10-oxide. Filed August 5, 2009 , published February 10, 2011 , applicant: UFC Corp., inventor: L. Lu, K.-C. Huang, K.-C. Tseng, C.-N. Fan, Y.-C. Lee, T.-W. Lo, Y.-C. Lee.
- ↑ a b Patent EP2557085A1 : Novel phosphonamidates - synthesis and flame retardant applications. Registered on August 8, 2011 , published on February 13, 2013 , applicant: EMPA Eidgenössische Materialprüfungs- und Forschungsanstalt, F. Nauer AG, inventors: H. Mispreuve, R. Näscher, S. Gaan, M. Neisius, P. Mercoli, S. Liang.
- ↑ Patent US3702878 : Cyclic organophosphorus compounds and process for making same. Applied on December 31, 1969 , published on November 14, 1972 , applicant: Sanko Chemicals Co., Ltd., inventor: T. Saito.
- ↑ Patent US5391798 : Process for preparing 6-chloro- (6H) -dibenz- [c, e] [1,2] -oxaphosphorine. Registered on August 9, 1993 , published on February 22, 1995 , applicant: Hoechst AG, inventor: H.-J. Smaller.
- ↑ Patent US5481017 : Method for preparing 6H-dibenzo [c, e] [1,2] oxaphosphorin-6-one. Registered on June 30, 1994 , published on January 2, 1996 , applicant: Hoechst AG, inventor: H.-J. Smaller.
- ↑ Patent US5821376 : Process for the preparation of a DOP-containing mixture. Applied on January 9, 1997 , published October 13, 1998 , applicant: Schill & Seilacher GmbH & Co., inventors: P. Rathfelder, H. Rieckert, J. Dietrich.
- ↑ M. Rakotomalala, S. Wagner, M. Döring: Recent developments in halogen free flame retardants for electrical and electronic applications . In: Materials . tape 3 , 2010, p. 4300-4327 , doi : 10.3390 / ma3084300 .
- ↑ Patent US9522927B2 : DOPO derivative flame retardant. Filed August 20, 2014 , published December 20, 2016 , applicant: Albemarle Corp., inventor: YL Angell, KM White, SE Angell, AG Mack.
- ^ Y. Zhang, B. Yu, B. Wang, KM Liew, L. Song, C. Wang, Y. Hu: Highly effective PP synergy of a novel DOPO-based flame retardant for epoxy resins . In: Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. Volume 56 , no. 5 , 2017, p. 1245-1255 , doi : 10.1021 / acs.iecr.6b04292 .
- ^ NM Neisius, M. Lutz, D. Rentsch, P. Hemberger, S. Gaan: Synthesis of DOPO-based phosphonamidates and their thermal properties . In: Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. Volume 53 , no. 8 , 2014, p. 2889-2896 , doi : 10.1021 / ie.403677k .
- ↑ Patent US8394512B2 : Phosphaphenanthrene compounds and organic light emitting diode using the same. Applied on April 5, 2008 , published on March 12, 2013 , applicant: Inktec Co., Ltd., inventor: KC Chung, H.-N. Cho, I.-K. Park, J.-H. Yoo, A.-R. Hyung, Y.-H. Young.