Agan
|
Agan Аган |
||
|
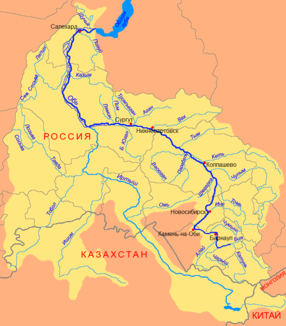
Course of the Agan (Аган) in the catchment area of the Ob |
||
| Data | ||
| Water code | RU : 13011100112115200043362 | |
| location | Khanty and Mansi Autonomous Okrug / Ugra ( Russia ) | |
| River system | If | |
| Drain over | Tromjogan → Ob → Arctic Ocean | |
| origin | Discharge from Mensawemtor lake 62 ° 8 ′ 43 ″ N , 78 ° 44 ′ 9 ″ E |
|
| Source height | 78 m | |
| muzzle | in the Tromjogan east of Surgut Coordinates: 61 ° 23 ′ 34 " N , 74 ° 35 ′ 20" E 61 ° 23 ′ 34 " N , 74 ° 35 ′ 20" E |
|
| Mouth height | 32 m | |
| Height difference | 46 m | |
| Bottom slope | 0.08 ‰ | |
| length | 544 km | |
| Catchment area | 32,200 km² | |
| Discharge at the Var-Yugan A Eo gauge : 15,500 km² Location: 276 km above the mouth |
MQ 1954/1991 Mq 1954/1991 |
121 m³ / s 7.8 l / (s km²) |
| Discharge at the Agan A Eo gauge : 29,700 km² Location: 87 km above the mouth |
MQ 1960/1987 Mq 1960/1987 |
275 m³ / s 9.3 l / (s km²) |
| Left tributaries | Wanjogan | |
| Right tributaries | Nankjogan, amputa | |
| Medium-sized cities | Raduschny | |
| Small towns | Novoagansk , Pokachi | |
| Communities | Agan | |
| Navigable | 360 km | |
The Agan ( Russian Аган ) is a 544 km long left tributary of the Tromjogan in the West Siberian lowlands in Russia .
course
The Agan flows from Lake Mensawemtor at a height of 78 m in the central part of the West Siberian lowlands, not far from the watershed between the right tributaries of the Ob and the catchment area of the Pur . It flows along its entire length in a westerly to south-westerly direction, always on the territory of the autonomous district of the Khanty and Mansi / Ugra , the swampy and lake-rich taiga landscape of the lowlands to its confluence at 32 m height in the Tromjogan, a good 60 km east-northeast of Surgut . Some sources regard the Agan as the right tributary of the Ob, and the Tromjogan as the right tributary of the Agan.
The most important tributaries of the Agan are Nankjogan and Amputa from the right and Wanjogan from the left.
Hydrography
The catchment area of the Agan covers 32,200 km². Near the mouth, the river is up to 200 m wide and 2.5 m deep; the flow velocity here is 0.5 m / s.
The agan freezes from late October to the second half of May. The water flow 87 km above the estuary is an annual average of 275 m³ / s with a minimum of 80.0 m³ / s in March and a maximum of 730 m³ / s in June.
Infrastructure and economy
The river is navigable for 360 km.
The development of almost the entire area through which the Agan flows began with the discovery of the West Siberian oil and natural gas deposits in the 1960s. The towns of Raduzhny and Pokatschi and the Novoagansk urban-type settlement , which are connected by roads to each other and to the Russian road network, were built on the river. Not far from the estuary and the eponymous village of Agan , the river is crossed by the railway line and the road that connect the cities of Surgut and Nizhnevartovsk on the Ob .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Article Agan in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia (BSE) , 3rd edition 1969–1978 (Russian)
- ↑ a b Agan in the State Water Register of the Russian Federation (Russian)
- ↑ Agan at the Var-Yugan gauge - hydrographic data at R-ArcticNET
- ↑ a b Agan at the Agan gauge - hydrographic data at R-ArcticNET
- ^ List of Inland Waterways of the Russian Federation (confirmed by Order No. 1800 of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 19, 2002); on-line