Astragaline
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
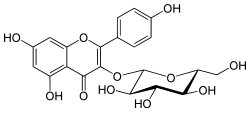
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Astragaline | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 21 H 20 O 11 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 448.38 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
312.58 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Astragalin is the 3- O - glycoside of kaempferol , which belongs to the flavonoids .
Occurrence
Astragalin is a secondary plant material , which occurs in many plants, for example, tragacanth (synonym Astragalus sp. ), Rosa agrestis , Aristolochia indica , Cuscuta chinensis , the American pokeweed , hops extract , goldenrod , elderflower , lime blossom , arnica flowers , wine and grapes , Tea and blueberries .
properties
Astragaline is not found in animals. As an experimental active ingredient in cell cultures of mammalian cells, it has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It inhibits the activity of interleukin-1β , which in turn reduces that of NFκB and inhibits the MAPK signaling pathway. It also inhibits the gene expression of Cox-2 and iNOS . It inhibits apoptosis in lung epithelial cells by inhibiting the gene expression of eotaxin-1 and the MAPK signaling pathway. Astragalin heptaacetate, on the other hand, leads to increased apoptosis in cell cultures of the lung epithelium, which is reversed by administration of the antioxidant acetylcysteine . Astragaline is a 3-O- glucoside from kaempferol .
literature
- Frank Bisby: Phytochemical Dictionary of the Leguminosae. CRC Press, 1994, ISBN 978-0-412-39770-7 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet Kaempferol 3-glucoside from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 20, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Frank Bisby: Phytochemical Dictionary of the Leguminosae. Volumes 1-2 of Phytochemical Dictionary of the Leguminosae: ILDIS, International Legume Database & Information Service: CHCD, Chapman & Hall Chemical Database, IW Southon, CRC Press, 1994. ISBN 9780412397707 . Pp. 841, 842.
- ^ John Buckingham: Dictionary of Natural Products, Volume 3 CRC Press, 1993. ISBN 9780412466205 .
- ↑ R. Hegnauer: Chemotaxonomy of plants. Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-034-87986-6 .
- ↑ a b c Z. Ma, T. Piao, Y. Wang, J. Liu: Astragalin inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammatory mediators production in human osteoarthritis chondrocyte by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK activation. In: International Immunopharmacology . Volume 25, number 1, 2015, pp. 83-87, doi : 10.1016 / j.intimp.2015.01.018 , PMID 25637445 .
- Jump up ↑ LW Soromou, N. Chen, L. Jiang, M. Huo, M. Wei, X. Chu, FM Millimouno, H. Feng, Y. Sidime, X. Deng: Astragalin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses by down-regulating NF-κB signaling pathway. In: Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications . Volume 419, Number 2, March 2012, pp. 256-261, doi : 10.1016 / j.bbrc.2012.02.005 , PMID 22342978 .
- ↑ DC Desai, J. Jacob, A. Almeida, R. Kshirsagar, SL Manju: Isolation, structural elucidation and anti-inflammatory activity of astragalin, (-) hinokinin, aristolactam I and aristolochic acids (I & II) from Aristolochia indica. In: Natural Product Research . Volume 28, number 17, 2014, pp. 1413-1417, doi : 10.1080 / 14786419.2014.905563 , PMID 24854204 .
- ↑ S. Donnapee, J. Li, X. Yang, AH Ge, PO Donkor, XM Gao Chang YX: Cuscuta chinensis Lam .: A systematic review on Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology of an important traditional herbal medicine. In: Journal of Ethnopharmacology . Volume 157, November 2014, pp. 292-308, doi : 10.1016 / j.jep.2014.09.032 , PMID 25281912 .
- ↑ a b c d e Ernst Steinegger: Pharmakognosie. Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-662-09267-5 , p. 288.
- ↑ a b Shmuel Yannai: Dictionary of Food Compounds with CD-ROM, Second Edition. CRC Press, 2012, ISBN 978-1-420-08352-1 , p. 119.
- ↑ a b I. H. Cho, JH Gong, MK Kang, EJ Lee, JH Park, SJ Park, YH Kang: Astragalin inhibits airway eotaxin-1 induction and epithelial apoptosis through modulating oxidative stress-responsive MAPK signaling. In: BMC pulmonary medicine. Volume 14, 2014, p. 122, doi : 10.1186 / 1471-2466-14-122 , PMID 25069610 , PMC 4118077 (free full text).
- ↑ O. Burmistrova, J. Quintana, JG Díaz, F. Estévez: Astragalin heptaacetate-induced cell death in human leukemia cells is dependent on caspases and activates the MAPK pathway. In: Cancer Letters . Volume 309, Number 1, October 2011, pp. 71-77, doi : 10.1016 / j.canlet.2011.05.018 , PMID 21658841 .