Barringtonia
| Barringtonia | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
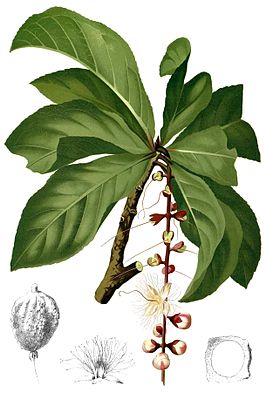
Illustration of Barringtonia racemosa from the Flora de Filipinas (around 1880) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Barringtonia | ||||||||||||
| JR Forest. & G.Forst. |
Barringtonia is a genus of trees and shrubs from the potted fruit tree family(Lecythidaceae). The range of the species is in Africa and Asia.
description
The representatives of the genus form shrubs or small to large trees . The leaves grow in clusters at the ends of the branches. The leaf margins are entire or serrated-notched. The stipules are small and fall off early. The inflorescences are mostly hanging ears or grapes and grow in the leaf axils, less often at the ends of branches or directly on the trunk. The flowers are radial symmetry . The calyx is clearly four-lobed or completely grown together. Seldom three or five, usually four, petals are formed per flower that are over 10 millimeters long. The discus is a clearly formed ring. The numerous stamens are arranged in a ring of three to eight whorls. They have grown together over a length of 1 to 10 millimeters, the innermost ring and often also the next are not fully developed and sterile. The ovary is usually fourfold, less often two or threefold. Two to eight hanging ovules are formed per ovary compartment . The stylus extends beyond the stamens. The fruits are solitary, often four-winged or square drupes .
The number of chromosomes is 2 n = 26.
Distribution and ecology
The natural range of the species is in East Africa, Madagascar and in tropical Asia.
Systematics and research history
Barringtonia is a genus from the family of lecythidaceae (Lecythidaceae) in which they are expected to subfamily Planchonioideae. The genus was established in 1776 by Johann Reinhold Forster and Georg Forster in Characteres Generum Plantarum . Synonyms of the genus are Abdulmajidia Whitmore , Butonica Lam. and Stravadium Juss.
40 to 60 species are assigned to the genus Barringtonia , The Plant List indicates the following species:






- Barringtonia acutangula (L.) Gaertn. : It occurs in two subspecies from Asia to northern Australia.
- Barringtonia apiculata Lauterb. : It occurs in Sulawesi and New Guinea.
- Barringtonia ashtonii Payens : It occurs in northern and central Borneo.
- Barringtonia asiatica (L.) In short : It occurs from Tanzania and the islands in the Indian Ocean to those in the Pacific.
- Barringtonia augusta In short : It occurs from southern Indochina to Malaysia.
- Barringtonia belagaensis Chantar. : It occurs in Sarawak .
- Barringtonia calyptrata (Miers) R.Br. ex Benth. : It occurs from New Guinea to Queensland.
- Barringtonia calyptrocalyx K.Schum. : It occurs in three varieties from New Guinea to the Bismarck Archipelago .
- Barringtonia chaniana (Whitmore) Prance : It occurs on the peninsula of Malaysia.
- Barringtonia conoidea handle. : It occurs from southern Indochina to western Malesia.
- Barringtonia corneri Kiev & KMWong : It occurs on the southeastern peninsula of Malaysia.
- Barringtonia curranii Merr. : It occurs from Borneo to Palawan .
- Barringtonia edulis Seem. : It occurs on islands in the southwestern Pacific.
- Barringtonia filirachis Payens : It occurs from Malaysia to Sumatra.
- Barringtonia fusiformis King : It occurs on the peninsula of Malaysia.
- Barringtonia gigantostachya Koord. & Valeton : It occurs in two varieties; one of them in Java, the other in north-eastern Borneo.
- Barringtonia glomerata Prance : It occurs on the northwestern peninsula of Malaysia.
- Barringtonia hallieri R.Knuth : It occurs in Borneo.
- Barringtonia havilandii Ridl. : It occurs in Borneo.
- Barringtonia integrifolia (Montrouz.) Schltr. : It occurs in New Caledonia and the Loyalty Islands .
- Barringtonia jebbiana Takeuchi : It occurs in New Guinea.
- Barringtonia josephstaalensis W.N.Takeuchi : It occurs in eastern New Guinea.
- Barringtonia khaoluangensis Chantar. : It occurs in Thailand.
- Barringtonia lanceolata (Ridl.) Payens : It occurs in Borneo.
- Barringtonia latiffiana (El-Sherif) Prance : It occurs on the peninsula of Malaysia.
- Barringtonia lauterbachii R.Knuth : It occurs in New Guinea.
- Barringtonia longifolia Schltr. : It occurs in New Caledonia.
- Barringtonia longisepala Payens : It occurs in Brunei and Sabah .
- Barringtonia lumina Jebb & Prance : It occurs from New Guinea to the Solomon Islands .
- Barringtonia macrocarpa Hassk. : It occurs from Indochina to western Malesia.
- Barringtonia macrostachya (Jack) In short : It occurs from Indochina to New Guinea and in China.
- Barringtonia magnifolia Prance : It occurs in Indonesia in the Maluku province.
- Barringtonia maxwelliana (Whitmore) Prance : It occurs on the peninsula of Malaysia.
- Barringtonia monticola Jebb & Prance It occurs in Papua New Guinea.
- Barringtonia neocaledonica Vieill. : It occurs in New Caledonia.
- Barringtonia niedenzuana (K.Schum.) R.Knuth : It occurs from northern Sulawesi to the Solomon Islands.
- Barringtonia norshamiae Prance : It occurs on the peninsula of Malaysia.
- Barringtonia novae-hiberniae Lauterb. : It occurs from Papua New Guinea to Vanuatu .
- Barringtonia palawanensis Chantar. : It occurs in Palawan .
- Barringtonia papeh Lauterb. : It occurs from southeastern New Guinea to the Solomon Islands.
- Barringtonia papuana Lauterb. : It occurs in New Guinea.
- Barringtonia pauciflora King (Syn .: Barringtonia maunwongyathiae Chuakul ): It occurs from Thailand to the Indonesian state of Perak .
- Barringtonia payensiana Whitmore : It occurs on the peninsula of Malaysia.
- Barringtonia pendula (Griff.) In short : It occurs from southern Yunnan and from southern Myanmar to western Malesia.
- Barringtonia pinnifolia Jebb & Prance : It occurs in Papua New Guinea.
- Barringtonia procera (Miers) R.Knuth : It occurs from eastern New Guinea to Vanuatu .
- Barringtonia pseudoglomerata Chantar. : It occurs in Sarawak and Sabah .
- Barringtonia pterita Merr. : It occurs in the Philippines.
- Barringtonia racemosa (L.) Spreng. : It occurs from Kenya to KwaZulu-Natal and the islands in the western Pacific.
- Barringtonia reticulata (flower) Miq. : It occurs from the Andaman and Nicobar Islands to western and central Malesia.
- Barringtonia revoluta Merr. : It occurs in western Malesia.
- Barringtonia ridsdalei Chantar. : It occurs in Palawan .
- Barringtonia rimata Chantar. : It occurs from the peninsula of Thailand to the peninsula of Malaysia.
- Barringtonia samoensis A.Gray : It occurs from southeast Sulawesi to the islands in the western Pacific.
- Barringtonia sarawakensis Chantar. : It occurs in Sarawak .
- Barringtonia sarcostachys (flower) Miq. : It occurs in two subspecies in southern Sumatra and in western and northern Borneo.
- Barringtonia schmidtii Warb. ex Craib (Syn .: Barringtonia badia Prance ): It occurs from western and southern Thailand to the eastern peninsula of Malaysia.
- Barringtonia scortechinii King : It occurs from the peninsula of Thailand to western Malesia.
- Barringtonia seaturae H.B.Guppy : It occurs in the Fiji islands Vitu Levu and Vanua Levu .
- Barringtonia serenae Jebb & Prance : It occurs in Papua New Guinea.
- Barringtonia tagala Jebb & Prance : It occurs in Papua New Guinea.
- Barringtonia terengganuensis Chantar. : It occurs on the peninsula of Malaysia.
- Barringtonia waasii Chantar. : It occurs in western Sri Lanka.
- Barringtonia zainudiniana (El-Sherif & Latiff) Prance : It occurs on the peninsula of Malaysia.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c GT Prance, SA Mori: Lecythidaceae In: Klaus Kubitzki: The Families and Genera of Vascular Plants , Volume VI, p. 230.
- ^ A b Haining Qin, Ghillean T. Prance: Barringtonia In: Flora of China. Volume 13, p. 293.
- ^ A b Barringtonia in the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), USDA , ARS , National Genetic Resources Program. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland.
- ^ Barringtonia. In: The International Plant Name Index. Retrieved March 8, 2015 .
- ^ Barringtonia. In: The Plant List. Retrieved March 8, 2015 .
- ^ Illustration by Frederick Polydore Nodder , around 1798, online
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl Rafaël Govaerts (Ed.): Barringtonia. In: World Checklist of Selected Plant Families (WCSP) - The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew . Retrieved September 28, 2017.
literature
- Klaus Kubitzki (Ed.): The Families and Genera of Vascular Plants . Volume 6: Flowering Plants, Dicotyledons: Celastrales, Oxalidales, Rosales, Cornales, Ericales . Springer, Berlin / Heidelberg / New York 2004, ISBN 3-540-06512-1 , pp. 230 (English).
- Wu Zheng-yi, Peter H. Raven, Deyuan Hong (Eds.): Flora of China . tape 13 : Clusiaceae through Araliaceae . Science Press / Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing / St. Louis 2007, ISBN 978-1-930723-59-7 , pp. 293 (English).
Web links
- Barringtonia at Tropicos.org. Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, accessed March 8, 2015.