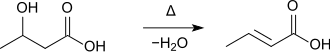3-hydroxybutyric acid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Structural formula without information on stereochemistry | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 3-hydroxybutyric acid | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 4 H 8 O 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 104.10 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.16 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point | |||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
3-Hydroxybutyric acid , systematically 3-hydroxybutanoic acid , is a chemical compound from the group of hydroxycarboxylic acids . Their salts are called 3-hydroxybutyrates.
Isomers
3-Hydroxybutyric acid occurs in two enantiomeric forms [( R ) -3-hydroxybutyric acid and ( S ) -3-hydroxybutyric acid].
| Isomers of 3-hydroxybutyric acid | ||
| Surname | ( R ) -3-hydroxybutyric acid | ( S ) -3-hydroxybutyric acid |
| other names | (-) - 3-Hydroxybutyric acid D -3-hydroxybutyric acid |
(+) - 3-Hydroxybutyric acid L -3-Hydroxybutyric acid |
| Structural formula |

|
|
| CAS number | 625-72-9 | 6168-83-8 |
| 300-85-6 (unspec.) | ||
| EC number | 210-909-6 | 228-209-4 |
| 206-099-9 (unspec.) | ||
| ECHA info card | 100.009.918 | 100.025.646 |
| 100.005.546 (unspec.) | ||
| PubChem | 92135 | - |
| 441 (unspec.) | ||
| Wikidata | Q27075135 | Q27075158 |
| Q223092 (unspec.) | ||
Occurrence
D -3-hydroxybutyric acid occurs naturally in the metabolism of animals. It is one of three so-called keto bodies . It is produced in the liver from acetoacetic acid with the help of the enzyme D- β-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase and is excreted in the urine , the proportion being increased there in ketosis (acetonuria).
presentation
From acetoacetic ester formed by reaction with sodium amalgam in the cold ( RS -3-hydroxybutyric acid).
From 1-chloro-2-propanol is reacted with potassium cyanide in ethanol , the corresponding nitrile is formed, which by hydrolysis can be converted to 3-hydroxybutyric acid.
Reactions
When 3-hydroxybutyric acid is heated, crotonic acid is formed with elimination of water :
use
3-Hydroxybutyric acid can be used industrially for the production of biodegradable plastics ( polyhydroxybutyric acid ).
The butyl ester 3-hydroxybutyric acid butyl ester is a solvent.
See also
- 4-hydroxybutyric acid
- D- β-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase
- Threonine (2-amino-3-hydroxybutyric acid)
- Ketoacidosis
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on 3-hydroxybutyric acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 16, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Material Safety Data Sheet 3-Hydroxybutyric Acid at coleparmer.com.
- ^ A b F. Beilstein: Handbook of organic chemistry , 3rd edition, 1st volume. Verlag Leopold Voss, 1893. P. 561. Full text
- ^ F. Beilstein: Handbook of organic chemistry , 3rd edition, 1st volume. Verlag Leopold Voss, 1893. S. 506. Full text
- ↑ Patent EP0355307 : Extraction agent for poly-D (-) - 3-hydroxybutyric acid. Registered on June 21, 1989 , published on December 28, 1994 , Applicant: PCD Polymers Society, Inventors: Heinz Traussnig, Engelbert Kloimstein, Hans Kroath, Robert Estermann.